Bachelor of Science (Forensics Blood Stain Analysis)
advertisement
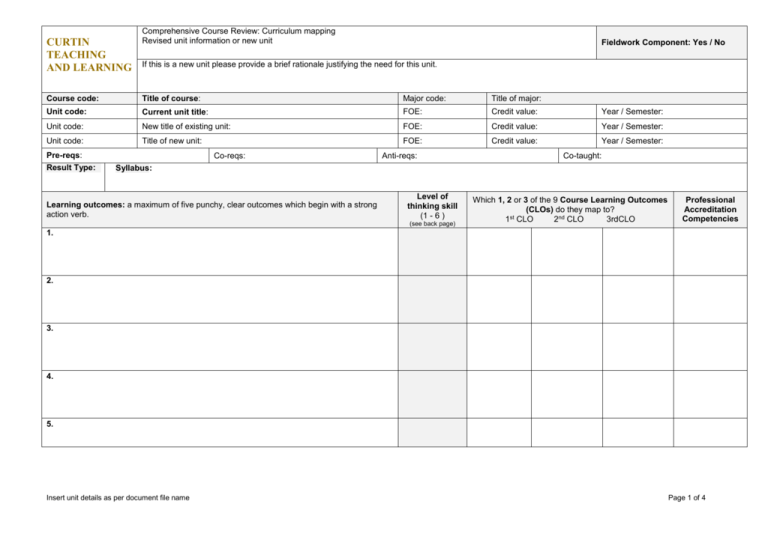
CURTIN TEACHING AND LEARNING Comprehensive Course Review: Curriculum mapping Revised unit information or new unit Fieldwork Component: Yes / No If this is a new unit please provide a brief rationale justifying the need for this unit. Course code: Title of course: Major code: Title of major: Unit code: Current unit title: FOE: Credit value: Year / Semester: Unit code: New title of existing unit: FOE: Credit value: Year / Semester: Unit code: Title of new unit: FOE: Credit value: Year / Semester: Pre-reqs: Result Type: Co-reqs: Anti-reqs: Co-taught: Syllabus: Learning outcomes: a maximum of five punchy, clear outcomes which begin with a strong action verb. Level of thinking skill (1 - 6 ) (see back page) Which 1, 2 or 3 of the 9 Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) do they map to? 1st CLO 2nd CLO 3rdCLO Professional Accreditation Competencies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Insert unit details as per document file name Page 1 of 4 Assessments: including formative and summative tasks (formative tasks have no weighting). Weighting Submission Brief description of task (e.g. Case study on mental health) (include additional rows if required) % Week * 1 2. 3. 4. Moderation Unit Learning Outcomes assessed (description) Assessments: More detail about Assessments shown in the categories below: Type Medium Role Supervision Principal Assessors Authenticity (WIL) Purpose Feedback - Weighted assessment; - Non-weighted assessment. - Grade; - Mark; - Rubric; - Verbal; - Annotated script; - Group report; - Individual email; - Peer feedback; - Specific feedback sessions; - Other electronic means; - Audio feedback; - Audio/video; - Self feedback. 1. 2. 3. 4. Choose from: - Test; - Presentation; - Reflection; - Investigation; - Exercise; - Work placement; - Laboratory; - Exam; - Essay; - Report; - Case study; - Dissertation. - Written; - Oral; - Practical; - Performance; - Visual; - Calculations; - Combination; - Online; - Other. - Individual; - Pair; - Group. - invigilated - non-invigilated - Low e.g. theoretical info based on workplace; - Medium e.g. simulation, role-play or case study; - High e.g. work placement. - Teaching staff only; - Industry only; - Peer only; - Self only; - Teaching staff/ industry; - Teaching staff/ peers; - Teaching staff/self; - External. Learning experiences: What sorts of learning experiences are best for students to achieve these learning outcomes? Choose from the following learning experiences / tuition patterns: Block Teaching, Clinical Placement, Fieldwork, Individual Study, Computing Laboratory, Language Laboratory, Lecture, Online Class, Practical, Project, Science Laboratory, Seminar, Tutorial, Workshop Duration: Frequency: Main student activity 1. 2. Insert unit details as per document file name Page 2 of 4 Key to Duration, Frequency and Main student activity above: Duration: e.g. 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hours, half-day, full day, other. Frequency: e.g.Daily,4 times a week, 3 times a week, twice a week, weekly, fortnightly, monthly, twice a semester, once a semester, other. Main student activity: Listening; viewing; reading; writing; speaking; reflecting; hands-on-practice; problem-solving; role-play; other. Triple-i Curriculum Themes: Indicate how the Curriculum theme has been incorporated into this unit: i Industry ii Indigenous Level: KEY: Explanation of levels: 1. Information about matters relating to the theme Intercultural 2. Up-skilling in the theme International iii 3. Hands on engagement with the theme Interdisciplinary Unit Coordinator: Telephone contact: Course coordinator: Telephone contact: Insert unit details as per document file name Page 3 of 4 Levels of thinking (or cognitive demand) adapted from Bloom’s Revised Teaching Taxonomy1 with star ratings and unit learning outcome and assessment verbs Unit learning outcomes are what students are expected to be able to do upon success in the unit. They begin with a strong action verb and describe specific tasks, preferably requiring students to develop higher order thinking skills (levels 4 to 6 in this table). Use the “cues” in this table as the first word in your revised learning outcome. For more information on creating quality unit learning outcomes, and specific information on the table below relating to Bloom’s Taxonomy, see http://otl.curtin.edu.au/publications/tlbookchap4.pdf Level of thinking 1. Remembering 2. Comprehending 3. Applying 4. Analysing 5. Evaluating Skills Demonstrated and Assessment Verbs Observation and recall of information; knowledge of dates, events, places, materials, objects; knowledge of major processes or procedures; mastery of subject matter Unit learning outcome and assessment verbs: arrange, cite, collect, define, describe, duplicate, enumerate, examine, find, identify, indicate, label, list, locate, match, memorise, name, order, outline, quote, recall, recite, recognise, record, relate repeat, reproduce, retrieve, select, show, state, tabulate Understand information, grasp meaning; translate knowledge into new contexts; interpret facts; compare and contrast; order, group, infer causes, predict consequences Unit learning outcome and assessment verbs: arrange, articulate, associate, classify, compare, contrast, describe, differentiate, discuss, distinguish, exemplify, expand, explain, express, extend, identify, illustrate, indicate, interpret, locate, match, outline, paraphrase, recognise, relate, report, restate, review, select, summarise. Use information; use methods, concepts, theories in new situations; solve problems using required skills or knowledge; use equipment, tools Unit learning outcome and assessment verbs: administer, apply, calculate, chart, classify, collect, compute, control, convert, demonstrate, determine, develop, dramatise, draw, employ, estimate, execute, exhibit, illustrate, implement, manipulate, model, modify, operate, practice, prepare, relate, report, select, show, sketch, transfer, use, utilise Discern patterns; organise parts; recognise hidden meanings; identify components, simplify complex information; metacognition Unit learning outcome and assessment verbs: analyse, calculate, categorise, classify, compare, contrast, correlate, deconstruct, detect, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, examine, explain, interpret, organise, quantify, research, scrutinise, separate, sequence, subdivide, survey, test, translate Compare and discriminate between ideas; think critically, make judgments about worth (based on stated premises); assess the value of theories, make choices based on reasoned argument; verify or question the value of evidence Unit learning outcome and assessment verbs: appraise, argue, assess, categorise, choose, compare, conclude, contrast, critique, debate, decide, deduce, defend, discriminate, dispute, establish, estimate, evaluate, gauge, generalise, hypothesise, infer, interpret, judge, justify, measure, monitor, negotiate, predict, prioritise, propose, prove, rank, rate, recommend, relate, select, solve, support, validate, verify 6. Creating 1 Combining ideas to develop an original idea or product, engage in creative thinking. Unit learning outcome and assessment verbs: adapt, anticipate, assemble, change, communicate, compare, compile, compose, construct, create, derive, design, develop, devise, formulate, generate, hypothesise, improve, incorporate, infer, initiate, integrate, interpret, invent, make, modify, originate, plan, produce, reconstruct, revise, synthesise, transform, visualise Krathwohl, David R. (2002). A Revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy: An Overview. Theory Into Practice, 41(4), 212-218. Insert unit details as per document file name Page 4 of 4






