Psych IB exam 2014 review0
advertisement

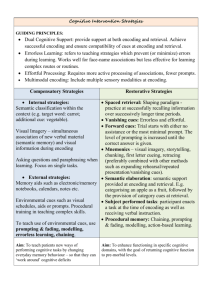
Psychology Review – M/C Drills Which of the following is one of the goals of psychology? a) To describe behaviour by gathering information b) To explain why people behave as they do c) To predict will think feel or do based on acquired knowledge d) To influence behaviour in a helpful manner e) All of the above The factor of an experiment that will be affected by another variable changed on purpose by the experimenter. a) Independent variable b) Dependant variable c) Confounding variable d) Extraneous variable When participants in an experiment try to behave in such a way as to create damaging data or to otherwise sabotage the research, it is known as the … a) Demand characteristics b) Screw-you Effect c) Hawthorne Effect d) Social Distortion Please consider the following study carefully to respond to the questions that follow… Middlemist et al (1976) performed a study on personal space invasion in a public men’s room in which normally men would have a free choice of three urinals. In order to test the effects of having another person close to a man while he urinates, the researchers randomly assigned visitors to the toilet into one of three conditions. One condition forced the participant to use the urinal closest to the toilet stall because the furthest stall had a sign saying “do not use” on it while an accomplice to the study occupied the middle urinal. In the second condition, the accomplice occupied the furthest stall from the participant and the middle stall bore the “do not use” sign. The third condition involved no accomplice. The time it took to begin urination and the length of time for urination to complete for the unknowing participant was measured using a stopwatch and a periscopic mirror by a hidden observer in the toilet stall. The researchers found that having a man standing at the nearest urinal increased the time it took for urination to begin and decreased the length of time it took to finish for the participant. Participants were never informed that the research had taken place. For the above study, what would you define as the independant variable? a) The location of the accomplice b) The researcher in the toilet stall c) The delay in beginning and the persistence of the urination d) The sign “do not use” For the above study, what form of sampling would you say the researchers relied on? a) Opportunity sampling b) Stratified sampling c) Cluster sampling d) Snowball sampling The use of a combination of theoretical approaches to the explanation of a hypothesis to corroborate results is referred to as _______________________. a) Reflexivity b) Theoretical corroboration c) Data corroboration d) Theoretical triangulation Which of the following indicates a strong negative correlation? a) +.87 b) -.87 c) +.08 d) -.08 When the observer becomes part of the group itself, this is known as a ____________ observation. a) Non-participant b) Participant c) Experimental d) Naturalistic A single statement that an experiment seeks to prove or disprove is called a… a) Variable b) Critical variable c) Hypothesis d) Thesis Variables that affect the accuracy of the measurement of the dependant variable are called… a) Extraneous variables b) Placebo variables c) independent variables d) Confounding variables In his landmark study of the nature of love and attachment, Harlow (1958) removed infant Rhesus monkeys from their mothers and studies how they formed bonds with two fake replacement mothers. One of which was a wire mother that would provide milk and another was a cloth mother. Which of the following COULD BE a dependant variable for this study? a) The version of the mothers the infant was exposed to b) The time it took for the infant to be removed from the mother c) The behaviour of the infants when they were introduced to the two fake mothers d) The varieties of milk provided by the wire mother. If shoe size and height in a given set of 30 people is found to have a +.87 correlation coefficient, then which of the following are true? a) that, more often than not, the larger the shoe size, the shorter the individual b) that, rarely, the larger the shoe size, the taller the person c) that, most of the time, the larger the shoe size, the taller the person d) that, every single time, the shorter the person, the larger the shoe size A number that shows you the index of the variability of a set of data – basically, how much the scores differ from each other. a) mean b) median c) mode d) standard deviation Which of the following best defines “operational definition”? a) it’s the thing that researchers must decide indicates the behaviour they are looking to observe is actually taking place b) it’s the behaviour that we have all come to accept means something else c) it’s the common internal emotional reason for a set of behaviours d) it’s the terms we use for a hypothesis determined through the process of laboratory studies The distribution that results from outlying results that pull the mean away from the median and the mode are called ______________. a) warped b) skewed c) biased d) corrupted The strengths of a laboratory experiment are … a) Allows for very high levels of reliability b) Allows for valid cause-effect conclusions to be drawn c) Allows for precise replicability d) All the above Allowing themes to emerge from the data obtained in an interview is called… a) Template analysis b) Inductive content analysis c) Discourse analysis d) None of the above Neurons carry information about the strength of a stimuli by varying: a) The size of their action potentials b) The speed of their action potentials c) The number of neurons that are firing at once d) All of the above The minimum intensity required to trigger a chain reaction in a neuron is called: a) Resting potential b) Action potential c) Threshold d) Minimum potential These positive ions are responsible for the electro-potential difference that makes neuron transmission possible. a) Potassium b) Sodium c) Iodine d) Both a and b The reticular formation regulates this vital bodily function and is stimulated by the drug caffeine. a) Breathing b) Eating c) Reproduction d) Sleep Which of the following is NOT one of the lobes of the cerebral cortex? a) Frontal b) Occipital c) Parietal d) Spinal This part of the brain is linked with primitive, basic functions like motivation and emotion and is referred to as the “old cortex”. a) The limbic system b) The hippocampus c) The thalamus d) The basal ganglia This part of the brain is the location of the highest functions of the brain like planning, speech, memory, and organizational perception. a) The cerebellum b) The medulla c) The cerebral cortex d) The corpus callosum Excessive neurotransmitters remaining in the synapse are removed by: a) enzymes located in the synapse that break down chemicals into their component substances b) the receiving axon terminal becomes saturated and cannot take any more stimulation c) the sending axon terminal will reabsorb excess neurotransmitter d) both a and c What is one weakness of Computed Tomography images (CT scans) a) it does not show enough detail to see tumors or lesions b) it is dangerous to inject things like radioactive dyes c) it cannot show structural changes in the brain d) it does not show brain activity This researcher found that when cats with severed corpus callosums were placed in a maze with one eye covered, they would eventually learn their way out of it, however, when the blindfold was moved to the other eye, they could no longer remember their way out of the same maze. a) Ogden b) Sperry c) Damasio d) Wernicke By injecting subjects with adrenaline and then deceiving them as to the anticipated consequences, these researchers discovered the origins of emotion when they found that people would label their emotions based on their physiological state and their environmental context. a) Damasio et al. b) Myers and Sperry c) Schachter and Singer d) Yerglin and Todd This hormone has been shown to be related to trust and love because when injected into rats, the mothers will switch from grooming themselves to grooming their pups, and blood tests show that brides at their weddings show huge increased in this hormone in their blood. a) melatonin b) adrenaline c) oxytocin d) dopamine Analyze the following data chart carefully Monozygotic male Monozygotic female Dizygotic male Dizygotic female Rate of concordance of schizophrenia 0.35 0.36 0.05 0.06 According to the above chart… a) there is a strong indication that schizophrenia is a result of environmental factors b) there is a strong indication that schizophrenia is a result of genetic factors c) there is a strong indication that schizophrenia is acquired (you catch it) rather than innate (you’re born with it) d) nothing conclusive was found with the data According to Lu, Chang et al. 2012, if a man approaches a woman and asks her to dance while staring at her hips… a) he’s interested in a long term relationship in which he will invest heavily in any potential offspring b) he’s interested in dancing c) he’s only after one thing (wink wink) and when he gets it he’s OUT like bellbottoms! d) he’s interested in your friend, not you According to Yeglin-Todd (1999), teenagers cannot accurately weight the future costs of behaviour choices the same way adults do because they lack this… a) an occipital cortex, vital for calculations b) a lateral gyrus, vital for assessing danger in the environment c) a prefrontal cortex, vital for inhibition d) nothing, their brains are the same as adults According to Fussell and Stollery (2012), when a man gets cheated on, he will only dump his partner if they actually had sex with someone else, on the other hand – a woman who gets cheated on will… a) dump the guy whether sex occurred or not b) stay with the guy because she is interested in his long term investment in her offspring c) find someone else to cheat on with in revenge to increase the variety of her potential mates d) neglect her own offspring because she doubts its true origins Which of the following are key principles that outline the biological level of analysis? a) Emotions and behaviour are the products of the anatomy and physiology of the nervous and endocrine systems b) Patterns of behaviour are unique to each individual and are comprised of experiences and memory c) Animal research is not sufficient to inform our understanding of the complexity behaviour d) Mental states can be observed through patterns of behaviour Schemas that provide information about the sequence of events that occur in a more or less unchanging order in particular contexts are called… a) scripts b) self-schemas c) social schemas d) stereotypes Which of the following are the principles that define the cognitive level of analysis? a) Mental processes can and should be studied scientifically b) Mental representations guide behaviour c) Studies of animals can inform our knowledge of human cognition d) Both a) and b) We tend to recall items that come first and last in a series but we do poorest for recalling items that come in the middle. This is known as which of the following? a) Primary and secondary effect b) Primacy and recency effect c) Primary and tertiary effect d) First and last effect Memory involves three processes, what are they? a) Intake, possession, output b) Sensation, neuroencoding, retrieval c) Learning, knowing, performing d) Encoding, storage, retrieval When we are paying attention to how the word looks, the font of its letting or the upper or lower casing of the letters, we are using this kind of attention a) b) c) d) Structural Phonemic Semantic None of the above When we are paying attention to the sound of a word, its pitch, its volume or its accent, we are using this kind of attention a) Structural b) Phonemic c) Semantic d) none of the above When we are paying attention to the meaning of the word, examples of the word, or are making links in our minds to other concepts around that word, we are using this kind of attention a) structural b) phonemic c) semantic d) none of the above One way to create more lasting memories is to enrich the encoding process by linking stimuli to other information at the time of encoding like finding examples this is called... a) elaboration b) visual imagery c) self-referent encoding d) none of the above One way to create more lasting memories is to enrich the encoding process by creating visual images that represent the word to be remembered, this is called... a) elaboration b) visual imagery c) self-referent encoding d) none of the above One way to create more lasting memories is to enrich the encoding process by making information personally meaningful, this is called a) elaboration b) visual imagery c) self-referent encoding d) none of the above What are the three phases of memory storage? a) Sensation, attention, encoding b) Stimulation, learning, retrieval c) Sense memory, attenuation, long term encoding d) Sense memory, short term memory, long term memory Events that have just occurred and are still in the consciousness are referred to as short term memory, they can last for up to this long.... a) 5 mins. b) 2 mins. c) 1 min. d) 20 secs. Short term memory can be extended by repeatedly verbalizing or thinking about information, this process is called... a) Retrieval b) Rehearsal c) Reconstituting d) Recounting STS can be extended by grouping information into related units, like a social insurance number or a phone number. What is this technique called? a) Grouping b) Relating c) Clumping d) Chunking When asked to name all the teams on the NFL, a fan will recall them be division and conference, this is an example of long term memory being organized as .... a) Clustering b) Chunking c) Conceptual hierarchies d) None of the above When asked to recall items they saw in a dentist’s office, they usually forget unusual items, why does this happen? a) Unusual items do not fit into their schema of what should be in a dentist’s office b) They are not given enough time to recall all the items completely c) They did not pay attention to all the items in the office even when told to do so. d) None of the above Use the following diagram to answer the next questions... Which word belongs in the center? a) Blue b) Fruit c) Taxi d) Yellow The above network is an example of thinking as it depends on patterns of activation in interconnected networks, like a computer. Specific memories correspond to a pattern of activation in these networks, these networks are called... a) Mnemonic networks b) Brain webs c) Modular networks d) Parallel Distributed Processing Models A stimulus that triggers other codes to move from LTM to STM is called a ... a) Memory activator b) Cognitive trigger c) Retrieval cue d) Process initiaton In order to improve recall, you can place yourself in the same situation in which you learned the original information, this is taking advantage of these... a) Retrieval locators b) Flashbacking c) Short-term associations d) Context cues Rehearsing information by putting it in simple sentences is not as effective as rehearsing it with complex sentences. What process is this an example of? a) Complex rehearsal b) Organized rehearsal c) Semantic rehearsal d) Elaborative rehearsal A good retrieval cue should be appropriate for the original method of encoding, that means that if the information was encoded phonetically, it should cued to retrieval phonetically. This concept is called... a) Matched retrieval b) Context similarity c) Uniform encoding d) Encoding specificity The mental structures and processes involved in the reception, storage, and use of knowledge is the definition of … a) Cognition b) Attention c) Perception d) Memory Cognitive structures that organize our knowledge of events, ourselves, objects, and others. a) Scripts b) Schemas c) Stereotypes d) All of the above are examples When you alter your perception of a thing so it fits into your schema… a) Assimilation b) Accommodation c) Social schemas d) None of the above Long-term storage, the same as short-term storage is also broken down into smaller components, these are: a) Declarative and procedural memory b) Echoic and phonetic memory c) Iconic and echoic memory d) Semantic and structural memory These societies value the group as the main source of identity and have been shown to have less evidence of FBM’s a) Individualist societies b) Communist societies c) Capitalist societies d) Collectivist societies The summary of all the implicit appraisals we make that result in an emotion according to Lazarus’ appraisal theory of emotion a) Future expectancy b) Motivational congruence c) Accountability and coping assessment d) Core-relational theme In addition to proving the unreliability of eyewitness accounts, they also discovered the Weapons Effect – when recalling the identification of individuals, witnesses were significantly less accurate when the individual was holding a weapon rather than another object. This shows us that anxiety can divert our attention and corrupt our encoding of details in memory. a) Basabe and Ross (2005) b) Bartlett and Rubin (1932) c) Loftus and Palmer (1972) d) Brewer and Treyens (1981) Primary appraisal could be replicated through the manipulation of the sound and text in a circumcision film. a) Spiesman et al. (1964) b) Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) c) Baddley and Hitch (1976) d) Loftus and Palmer (1974) Pioneered the serial position test and supported the MSM model of memory by giving participants a distracting task before recalling the items – the distracting test diminished the recency effect. a) Talarico and Rubin (2003) b) Glanzer and Cunitz (1966) c) Baddley and Hitch (1976) d) Loftus and Palmer (1974) Outlined defining characteristics of FBM’s a) Brown and Kulik (1977) b) Basabe and Ross (2005) c) Loftus and Palmer (1972) d) Craik and Lockhart (1981) Showed that memory was an active reconstruction process rather than a passive reproduction process by getting participants to recall an unfamiliar native American folktale over time. a) Spiesman et al (1967) b) Bartlett (1932) c) Piaget (1926) d) Schachter and Singer (1962) According to Lazarus’ Appraisal Theory of Emotion, what is one of the first three questions we instantaneously and implicitly ask ourselves prior to experiencing an emotion? a) Can I change this situation? b) Will the situation eventually resolve itself and go away? c) Can I change the way I feel about this situation? d) Is this situation beneficial to my goals or interests? Part B – Long Answer Please answer ONE of the following questions on the foolscap provided These responses will be marked out of 8 1. Explain how ONE study demonstrates how cognitive and biological factors interact in emotion 2. Explain and describe the principles that define the cognitive level of analysis of behaviour 3. Discuss how social or cultural factors affect one cognitive process. Mark Criteria 0 The answer does not reach a standard described by the descriptors below. 1 to 3 There is an attempt to answer the question, but knowledge and understanding is limited, often inaccurate, or of marginal relevance to the question. 4 to 6 The question is partially answered. Knowledge and understanding is accurate but limited. Either the command term is not effectively addressed or the response is not sufficiently explicit in answering the question. 7 to 8 The question is answered in a focused and effective manner and meets the demands of the command term. The response is supported by appropriate and accurate knowledge and understanding of research.