APES Sem Exam Rev Sheet F`12
advertisement

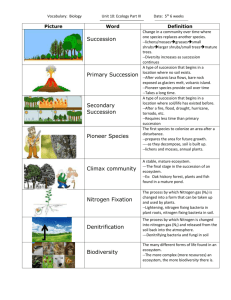
APES Review Sheet Chapter 1 Neuse River, Pfiesteria Environment Environmental science vs environmental studies System, ecosystem Biotic, abiotic factors Examples of human impact on natural systems (good and bad) Ecosystem services Environmental indicators Sustainability Genetic, species, ecosystem biodiversity Species Extinction rate: background vs human caused Conversion factors in calculations Food production: overall vs per capita long term vs recent trends greenhouse gases: recent trend natural vs anthropogenic human population trends stabilization development, sustainable development biophilia ecological footprint world wide, if lifestyle of americans for all scientific method steps hypothesis null hypothesis replication, sample size accuracy vs precision uncertainty inductive vs deductive reasoning theory control group vs experimental group chloropyrifos study natural experiment ethics environmental justice San Francisco sustainability plan of 1997 Chapter 2 Mono Lake Terminal lake, Diversions Principle of unexpected effects Matter, mass, weight Atomic theory Radioactivity Half-life Carbon-14 dating Chemical bonds Hydrogen bonds Polar molecule Water Surface tension Capillary action H-bonding and mp,fp Density and temperature Acids and bases pH scale Law of conservation of matter Organic, inorganic compounds Cell structure Energy Electromagnetic radiation Photons 4.18 Joules = 1 calorie Calorie vs calorie Btu, kWh Do the Math, p38 Potential vs kinetic 1st law, 2nd law of Thermodynamics (entropy) energy efficiency high vs low energy quality food chain Open , closed system Steady state Feedback loop positive, negative (examples) Managing the Everglades Halting the Growth of the Ozone Hole Chapter 3 Haiti, before and after earthquake of 2010 Ecosystem Ecosystem boundaries in Yellowstone Park Photosynthesis Producers (autotrophs) Cellular respiration Consumers (heterotrophs) Food chain Primary, secondary, tertiary consumers Trophic levels Food web Scavengers Detritivores (detritus feeders) Decomposers Ecosystem productivity Gross primary productivity Net primary productivity Biomass Standing crop Ecological efficiency Trophic pyramid (10 percent rule) Biosphere Biogeochemical cycles Hydrologic cycle Runoff Transpiration Evapotranspiration Carbon cycle Carbon sink Fossil fuels Nitrogen cycle Macronutrients Limiting nutrient Nitrogen fixiation Leaching Phosphorus cycle Eutrophication Algae blooms Sulfur Calcium, magnesium, potassium Disturbance Watershed Hubbard Brook study Resistance Resilience Restoration ecology Intermediate disturbance hypothesis Vs rare and frequent disturbances Instrumental value Intrinsic value Chapter 4 Climate vs weather Processes that affect distribution of heat and precipitation Layers of the atmosphere and temperature gradient Troposphere Stratosphere Ozone, UV-B, UV-C Mesosphere Thermosphere Ionosphere (aurora borealis) Exosphere Tilt of axis (23.5o) Angle of sun’s rays Albedo Convection currents Saturation point Adiabatic cooling, heating Latent heat release Formation of Hadley cell Intertropical convergence zone Coriolis effect Northeast trade wind Westerlies Seasons Tropic of cancer, Capricorn Longest, shortest day Gyres Upwelling Thermohaline circulation Heat transport El Nino Rainshadow effect Leeward, windward sides of a mountain Climate and biomes, Climate diagrams Leaf adaptations Tundra, permafrost Boreal forest, Temperate rainforest Temperate seasonal forest (temperate deciduous forests) Woodland/shrubland (chaparral) Temperate grassland/cold desert Tallgrass, shortgrass prairies Tropical rainforest Stratified Canopy, understory, floor (light conditions) Epiphytes Mycorrhizae fungus, mutualistic relationship Buttressed roots Subtropical (hot) deserts Adaptations Streams and rivers Lakes Zones Freshwater wetlands Salt marshes Mangrove forests Adaptations Ecological importance Shrimp farms Intertidal zone Coral reefs Mutualistic relationship: coral and algae bleaching open ocean zones chemosynthesis Chapter 5 Biodiversity Species vs organisms Ecosystem diversity Species diversity Genetic diversity Number of species on earth Species richness, species evenness Phylogenetic tree Evolution Microevolution (adaptation) Macroevolution (speciation) Genes Genotype Mutation Phenotype Artificial selection Natural selection Key ideas of darwin’s theory of evolution Fitness Adaptaions Evolution by random processes Genetic drift (affect on large vs small populations) Bottleneck effect Founder effect Allopatric speciation Geographic isolation Reproductive isolation Sympatric speciation Polyploidy Rate of evolution and: Rate of environmental change Genetic variation Population size Generation time Genetic engineering GMOs Range of tolerance Fundamental niche Realized niche Generalists vs specialists Species distribution and environmental change Evidence in sediment 99% of species that ever live are now extinct fossils 5 mass extinctions 6th mass extinction Nature Conservancy’s methodology Chapter 6 New England forests Population Community Population ecology Population density Population distribution Random. Clumped, uniform Age structure Density dependent population controls Density independent population controls Gause’s paramecium experiment Limiting resource Carrying capacity Growth rate Intrinsic growth rate Exponential growth model (J curve) Logistic growth model (S curve) Overshoot, die off (crash) Reindeer on St Paul Island Predator-prey population relationship Lynx and hares in Canada Wolves and moose on Isle Royale Reproductive strategies K-selected species r-selected species characteristics of each Metapopulations Corridors Community ecology Competition, predation Symbiosis Mutualism, commensalism, parasitism Competition Competitive exclusion principle Resource partitioning (temporal, spatial, morphological) Predation True predators, herbivores, parasites, Prey defense Speed, camouflage, chemical, spines, mimicry Mutualism examples Keystone species Ecological succession Primary succession (steps) Secondary succession Aquatic succession Theory of island biogeography Chapter 7 Controversy concerning human carrying capacity Cultural carrying capacity Malthusean vs cornucopia viewpoint Technology Demography Doubling time TFR, Replacement-level fertility And developing vs developed countries Life expectancy, infant mortality, child mortality Age structure diagram Developed vs developing countries Theory of demographic transition Pre-industrial, transition, industrial, post industrial Family planning IPAT equation Urban area (definition) GDP Chapter 8 Formation of Earth and the solar system Layers of the Earth Asthenosphere Lithosphere Plate tectonics Mantle plumes Hot spots, Hawaii Pangaea Oceanic vs continental plate 3 Plate boundaries Subduction Volcano Himalayas Seafloor spreading Earthquake Epicenter Richter scale Rock cycle Minerals 3 types of rocks Weathering Physical, chemical Erosion, deposition Formation of soil Soil profile Soil horizons (O, A, B, C,), parent material Soil texture Properties of sand, silt, clay Mineral resources Ores, metals, reserves Surface, subsurface mining Pros and cons Strip mining Open pit mining Mountain top removal Placer mining Chapter 9 Aquifers Confined, unconfined Water table Recharge zone Springs Artesian wells Ogallala aquifer Zone of depression Saltwater intrusion Floodplain Droughts and soil The Dust Bowl Flooding Impermeable surfaces Levee Katrina Dikes The Netherlands Dams Reservoir Three Gorges Dam Fish ladders Aqueducts Aral Sea disaster Desalinization Distillation, reverse osmosis 3 main uses of water 4 types of irrigation Hydroponics Water ownership India and Bangladesh Water conservation Gray water California water project