Study Island
Copyright © 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
Generation Date: 09/04/2014
Generated By: Kurt Ritter
1. Which of the following is true of prokaryotic cells?
A.
B.
C.
D.
They may be found in unicellular or multicellular organisms.
They tend to be large and complex in comparison to eukaryotic cells.
They function as individual organisms.
They contain nuclei and other membrane-bound organelles.
2. Multicellular organisms are composed of a variety of living structures that are formed when
cells differentiate. How could the living structure pictured below be classified?
A. cell
B. tissue
C. organ
D. organism
3. The diagrams below display different types of cells as viewed by a microscope under low
magnification.
These diagrams demonstrate how cells can be differentiated by their
A. cell structures.
B. means of replication.
C. sizes and densities.
D. modes of locomotion.
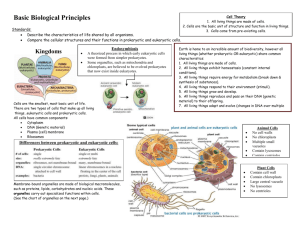
4. Cell theory states that
A. new cells are produced by existing cells.
B. All of these answers are correct.
C. all living things are composed of cells.
D. cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things.
5. Which of the following describes the fundamental difference between prokaryotic and
eukaryotic cells?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Prokaryotic cells are all viruses and rely on the infection of a host cell to replicate.
Eukaryotic cells are the only type of cells that can possess a cell wall.
Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic cells are only found in protists, bacteria, and viruses.
6. Both eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells possess DNA and engage in genetic processes.
Which of the following is true of their cellular genetics?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Eukaryotic cells generally require fewer genes to operate than prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA use different genetic codes (i.e. nucleotides).
Eukaryotic DNA is linear, whereas most prokaryotic DNA is circular.
Prokaryotic DNA cannot be translated into proteins because of the lack of a nucleus.
7. What is the single most abundant compound in living organisms?
A. fat
B. water
C. carbon
D. sugar
8. Technology Enhanced Questions are not available in Word format.
9. All multicellular organisms benefit from the organization of __________ into tissues, organs,
and organ systems.
A. organelles
B. cellulose
C. specialized cells
D. daughter cells
10. The life forms exhibiting the simplest cellular structure are _______.
A. eukaryotes
B. proteins
C. prokaryotes
D. organelles
11. Cellular organelles have different structures. Mitochondria, for example, possess highly
folded inner membranes in addition to their outer membranes. Vacuoles, on the other hand, are
only surrounded by a single-layer membrane; they do not have an inner membrane.
Why do cellular organelles have different structures?
A.
B.
C.
The structure of a cellular organelle mimics the appearance of the organism.
Organelles that are less important to the cell have less sophisticated structures.
The structures of cellular organelles are related to their functions.
All of the organelles in a particular organism are identical, but organelles in different
D. organisms are unique.
12. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the ability to continue to grow and divide in
their nonspecialized state for long periods of time (e.g., months or years).
Although the genes found within stem cells are the same, stem cells differentiate into unique cell
types (e.g., muscle cells, nerve cells, etc.) due to
A. different patterns in their gene expression.
B. meiotic division and fertilization.
C. mutations in their genetic code.
D. random segregation and proliferation.
13. How does the size of a eukaryotic organism normally compare to the size of a prokaryotic
organism?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Eukaryotes are usually much larger than prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes are usually much smaller than prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes are both usually very large organisms.
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes are both usually very small organisms.
14. An organ system is made up of
A. organisms that have similar behaviors and appearances.
B. identical cells that perform the same function.
C. organs that work together to perform a certain function.
D. all of the tissues found in an individual organism.
15. _______ are RNA and protein complexes that are found in all cells. These complexes help
cells during protein translation by joining amino acids together to form polypeptides.
A. Ribosomes
B. Lysosomes
C. Vacuoles
D. Chloroplasts
16. Which of the following is true about cells?
In general, prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles,
A. whereas eukaryotic cells contain both a nucleus and organelles enclosed by membranes.
Neither prokaryotic cells nor eukaryotic cells ever contain both a true nucleus that is wellB. defined and organelles that are separated from the cytoplasm by membranes.
In general, eukaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles,
C. whereas prokaryotic cells contain both a nucleus and organelles enclosed by membranes.
Both eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells always contain both a true nucleus that is wellD. defined and organelles that are separated from the cytoplasm by membranes.
17. What are the most basic building blocks of all organisms?
A. bones
B. muscles
C. organs
D. cells
18. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another
characteristic of all living organisms?
A. All living organisms consist of many cells with specialized organelles.
B. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
C. All living organisms must consume food in order to acquire nutrition.
D. All living organisms can produce glucose through photosynthesis.
19. The diagram below shows a T4 bacteriophage.
This virus consists of a single strand of DNA enclosed in a protein capsule. Is this virus
considered a living organism?
A. Yes; since the virus contains protein, it is a living organism.
B. Yes; since the virus contains DNA, it is a living organism.
C. No; viruses are not considered to be living organisms.
D.
No; living organisms must have two characteristics of life, and the T4 bacteriophage only
has one.
20. Within eukaryotic cells, there is an intricate network of _______ with unique functions.
A. organelles
B. vacuoles
C. mitochondria
D. lysosomes
21. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have many differences, but they also share some common
features. Which of the following may be found in either type of cell?
A. Golgi bodies
B. mitochondria
C. cell walls
D. nuclei
22. Membrane organelles known as _______ contain enzymes specialized to break down
ingested materials, secretions, and wastes.
A. chloroplasts
B. lysosomes
C. vacuoles
D. ribosomes
23. Which of the following organelles contains most of the cell's DNA?
A. mitochondrion
B. lysosome
C. nucleus
D. ribosome
24. Which of the following organelles stores information and is considered the control center of
the cell?
A. mitochondrion
B. nucleus
C. endoplasmic reticulum
D. Golgi complex
25. Technology Enhanced Questions are not available in Word format.
26. All living things must possess certain characteristics.
They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on
to their offspring. They can respond and adapt to their environment, maintain homeostasis, and
evolve.
Given these characteristics of life, which of the following objects is considered a living
organism?
W.
X.
Y.
Z.
A. Z
B. W
C. Y
D. X
27. Which of the following organelles plays a role in the disposal of cellular waste and is
responsible for processing, sorting, and modifying proteins?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. plasma membrane
C. mitochondrian
D. ribosome
28. All living organisms share many characteristics necessary for life. For example, all
organisms, including both prokaryotic and eukaryotic,
A.
B.
C.
D.
have cells arranged into complex organ structures.
must obtain and use energy for life processes.
can sexually reproduce to produce unique offspring.
can use abiotic factors to make their own food.
29. When a group of cells work together, such as in bones, muscles, or nerves, they are known
as _______.
A. an organism
B. an organelle
C. a tissue
D. an organ
30. There are many criteria that are used to define living things. Living things reproduce, grow,
and develop. They respond to stimuli, use materials and energy, and evolve and adapt over time
to their environment. What is another criteria used to define living things?
A. All living things are intelligent.
B. All living things are complex.
C. All living things are able to move.
D. All living things are made of cells.
Answers
1. C
2. C
3. A
4. B
5. C
6. C
7. B
8. -9. C
10. C
11. C
12. A
13. A
14. C
15. A
16. A
17. D
18. B
19. C
20. A
21. C
22. B
23. C
24. B
25. -26. B
27. A
28. B
29. C
30. D
Explanations
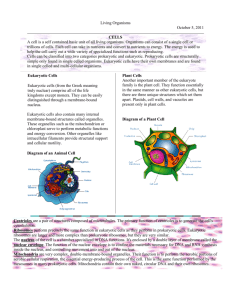
1. Prokaryotic cells are fairly small, simple cells. However, since they are only found in
unicellular organisms, they are versatile enough to provide for all of an organism's functions.
Still, since they lack nuclei and membrane-bound organelles, they are less efficient than
eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells are found in both unicellular and multicellular organisms. These cells tend to be
larger, more complex, and require more genes to operate than prokaryotic cells.
2. The picture shows a human heart which can be classified as an organ.
3. Organisms differ from each other in many ways. This diversity ranges from simple
prokaryotic cells to complex multicellular organisms.
The diagrams demonstrate how cell structure can be used to differentiate organisms. Organisms
may also be classified using other factors, including their cell number, their mode of nutrition,
their means of movement, and their method for reproduction.
4. According to cell theory, all living things are composed of cells. Some have only one cell,
others have many cells, but the way in which cells function is similar in all living organisms.
Cell theory also states that cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things, and
new cells are produced by existing cells.
5. The most fundamental difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the presence or
absence of a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and
chloroplasts. Eukaryotes have them; prokaryotes do not. In fact, the name prokaryote means
"before a nucleus".
6. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells possess DNA constructed from the same genetic code
(i.e. the same four nucleotides - A, T, C, G). However, eukaryotic DNA is linear, organized into
chromosomes, and packaged in nuclei for greater efficiency, whereas most prokaryotic DNA is
circular and free-floating in the cytoplasm. There are a few cases in which prokaryotes possess
linear DNA, but this is more the exception than the norm.
Both cells also possess ribosomes which enable them to perform protein translation.
7. Water is the single most abundant compound in all living organisms. In fact, about two-thirds
of the weight of cells is accounted for by water. Water is what gives cells so many of their
properties.
8. -9. Specialized cells form tissues, organs, and organ systems in multicellular organisms. Cell
specialization is beneficial because it helps efficiently carry out tasks that are necessary for the
survival of all body cells: transportation of food, gases, wastes, and cell products. Survival of the
body cells is crucial for the survival of the organism as a whole.
10. The life forms exhibiting the simplest cellular structure are prokaryotes. They exist in two
major forms: eubacteria and archaebacteria.
Prokaryotes were first life forms to develop on Earth and are the most abundant inhabitants.
They can survive in a wide range of environments and obtain energy in a variety of ways.
11. The structures of cellular organelles are related to their functions.
For example, many chemical reactions occur in the mitochondria in order to provide the cell with
energy. Having a highly folded inner membrane increases the surface area upon which these
reactions can occur.
Vacuoles, on the other hand, must be able to easily expand and contract as water moves in and
out. Thus, a single-layer membrane is necessary to support the vacuoles' function.
12. The specialization of cells in multicellular organisms is usually due to different patterns of
gene expression rather than to differences of the genes themselves. However, what causes cells
with similar genes to differentiate into unique cell types is not fully understood.
It may be due to the presence of different environmental conditions that signal some genes to be
expressed while other genes remain dormant. It may be due to internal regulators or any of a
number of factors that researchers are currently studying.
Think of it this way: you and three friends are each given 10 cards with the same letters on them
(i.e., you all have the same genes). However, you each choose to use the letters to spell four
different words (i.e., you each expressed your genes in a different way). No one knows why you
each chose to arrange your letters in different ways despite being given the same set of starting
letters, but the end result is four different words (i.e., specialized cells).
13. Most large organisms, such as plants and animals, are eukaryotes, although in a few
instances, some microscopic protists are eukaryotic as well. So, in general, eukaryotes are
much larger than prokaryotes. In addition, there are significant differences between the cells
of eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. This is because
eukaryotic cells contain many membrane-bound organelles.
Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, do not contain any membrane-bound organelles. However,
they do possess ribosomes, which are non-membranous complexes of protein and RNA. The
ribosomes in prokaryotic cells have less RNA and fewer proteins than do eukaryotic ribosomes.
14. An organ system is made up of organs that work together to perform a certain function.
For example, the heart and blood vessels form the circulatory system, which functions to pump
blood throughout the body.
15. Ribosomes are RNA and protein complexes that are found in all cells. These complexes help
cells during protein translation by joining amino acids together to form polypeptides.
Ribosomes are composed of two subunits. These subunits attach to and travel along strands of
mRNA during translation. As the anticodons on tRNA molecules attach sequentially to the
codons on an mRNA strand, the amino acids carried by the tRNA molecules take up the proper
position to be joined by peptide bonds and form a polypeptide.
16. Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic
organisms are usually unicellular.
Eukaryotic cells have nuclei and organelles that are separated from the cytoplasm by membranes.
Eukaryotic organisms are usually multicellular.
In general, prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles,
whereas eukaryotic cells contain both a nucleus and organelles enclosed by membranes.
17. All living things are made of one or more cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of all
organisms. Bones, muscles, and organs are all made up of cells organized in different levels of
complexity.
18. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
All of the other listed characteristics are true of some living organisms but not all living
organisms. For example, only plants and some microorganisms perform photosynthesis, and only
eukaryotes contain specialized membrane-bound organelles.
19. All living organisms must
have an organized structure,
obtain and use energy and materials,
maintain homeostasis,
grow, reproduce and pass on genetic information, and
respond to stimuli and evolve/adapt to their environment.
Although viruses contain DNA and pass their DNA on to their offspring, they cannot do this
unassisted, nor do they meet all the other criteria for living organisms. Thus, viruses are not
considered to be living organisms.
20. Cells have characteristic structures and functions that make them distinctive.
Organelles are the membrane-bound structures found in eukaryotic cells that play important
roles, such as maintaining homeostasis and aiding in cell reproduction.
All of the other answer choices listed are types of organelles.
21. Prokaryotic cells do not possess true nuclei or any other membrane-bound organelles. They
do, however, possess plasma membranes, cytoplasm, cell walls, ribosomes, and DNA.
Eukaryotic cells can possess all of these features, too.
22. Membrane organelles known as lysosomes contain enzymes specialized to break down
ingested materials, secretions, and wastes. Lysosomes, along with the Golgi complex, are
responsible for the disposal of cellular waste within a cell.
23. The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in all animal and plant cells. The nucleus
is considered the cell's "control center" because it contains the cell's DNA which directs the cell's
growth and development. The nucleus is also the site of RNA synthesis.
24. The nucleus of the cell stores information in the form of DNA. The DNA inside the nucleus
directs the cell's growth and development. Because DNA controls all of a cell's major functions,
the nucleus containing the DNA is considered the cell's control center.
25. -26. The only object that meets all of the given characteristics of life is the plant.
Batteries, rocks, and seashells are not living organisms.
27. The Golgi apparatus processes, sorts, and modifies proteins in a cell. In fact, the formation
of complex biomolecules is possible because of the modifications that proteins undergo while
they are moved through the Golgi apparatus.
The Golgi apparatus also processes and transports materials, including wastes, out of the cell.
Thus, the Golgi apparatus plays an important role in waste disposal.
28. All living organisms must
have an organized structure,
obtain and use energy and materials,
maintain homeostasis,
grow, reproduce and pass on genetic information, and
respond to stimuli and evolve/adapt to their environment.
Not all living organisms have complex structures such as organs, can make their own food, or
can sexually reproduce. Prokaryotic organisms, for example, are single-celled and can only
reproduce asexually.
29. When a group of cells work together, such as in bones, muscles, or nerves, they are known as
a tissue. Tissues include bone, blood, nerves, muscles, and skin. A group of tissues that work
together, such as the muscles that make up the heart, form an organ.
30. In addition to the other named criteria, all living things are composed of cells.
Although some living things are complex or intelligent and some living things can move, these
are not requirements for all living things.