File - Erica Anacleto`s Nursing Portfolio
advertisement

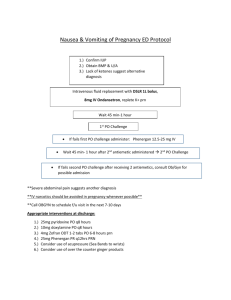
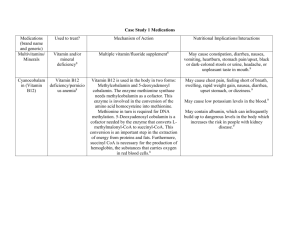
CSU STANISLAUS, B.S.N. CLINICAL PLAN OF CARE Student Erica Anacleto Date of Care 2/27/2014 Room Number 215-2 Patient Data Patient Initials B.D. Gender Male Age Height 1.91 m (75 in) Weight 82.1 kg (192.3 lbs) Spirituality Catholic Ethnicity White Admitting Diagnosis PVD w/ significant ischemic ulceration of the left lower leg and referred for a PTA (percutaneous transluminal angioplasty, patient in persistent pain, rule out sepsis, exhibiting SOB, rule out heart failure. Admitting Date 2/13/2014 Post-Op Day (POD) 55yo (5/6/1958) 11th day (Surgery on 2/16/14) Vital Signs T (max) 0930 - 36.7 C 1100 - 36.5 C P 70 81 R WNL with O2 18 bpm B/P 156/65 131/61 (80) O2 Sat. 98% on 2LPM nasal prongs 90-91% on room air Pain Scale No pain 0 No pain 0 History Related to this Admission Significant ischemic ulceration of the left lower left leg, Possible sepsis, deteriorating condition, Pain management, uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus (hyper/hypoglycemia), dorsal pedal pulse absent in left foot and posterior tibial pulse in left foot ¼. Past Medical History Severe uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, uncontrolled hypertension, uncontrolled hyperlipidemia, COPD (tobacco user), CAD, carotid vascular disease with left carotid artery occlusion, endocarditis, PVD with non-healing ulcers in both legs, iritis inactive, anxiety disorder, depression. Surgical History Prosthetic aortic valve (date unknown). Last bilateral leg intervention done on both legs 8/2010. Multiple stents in coronary arteries (date unknown). CLINICAL PLAN OF CARE Diet ADA diet Activity Advance Directive Unknown Foley N/A Drains/Tubes Bed rest, Ambulate around unit Once every shift & upon return from procedures Wound VAC Code Status Full VS Frequency NG/Feeding Tube N/A Glucose Monitoring Yes DVT Prophylaxis Ambulation PCA/Epidural N/A Telemetry N/A Vascular Access IV Site: PICC line in Left brachial arm IV Solution: N/A (only flushing) Vascular Access IV Site N/A IV Solution N/A Safety Considerations Fall Risk, IV left brachial arm, nasal prongs 2LPM, wound vac on amputated digit Dressing Changes Twice weekly on amputated toe and IVC site to be changed today 2/27/14 Respiratory Treatments Oxygen via nasal prongs at 2LPM, respiratory spirometer Labs for clinical day Blood Glucose and submit pleural fluid to lab for cytology Scheduled Procedures U/S guided Right thoracentesis in radiology with sedation Procedures done this admission pRBC transfusion, FFP transfusion, left and right thoracenetsis, left big toe amputation and debridement, PICC line placement. Allergies NKDA Medications Generic & Trade Name Drug Classification (Therapeutic & Pharmacologic) Acetaminophen (Tylenol)Analgesic, Antipyretic & nonopioid analgesic Acetaminophen/Codeine Phosphate (Tylenol #3) – Analgesic, antipyretic & nonopioid analgesic Acetaminophen/Hydrocodo ne Bitart (Norco 7.5-325) – Analgesic, antipyretic, antiflammatory & opioid analgesic combo Dose/Route Frequency Action of drug and Rationale (Why is patient on medication?) Significant Side Effects (Serious and/or frequent) Nursing implications related to assessment, administration or education 650 mg PO Q4H PRN Reduce pain by means of inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis in CNS. Pt on medication for mild pain. Liver toxicity, rash, nausea, headache, analphlactic reaction, anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal tubular necrosis 1 each PO Q4H PRN Codeine: Opioid agonist; analgesia; blocks pain impulse generation and inhibits ascending pain pathways, thus altering the perception and response to pain. Tylenol: reduce pain by means of inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis in CNS. Pt on medication for mild to moderate pain postoperatively. Hydrocodone binds to carious opioid receptors producing analgesia and sedation, acetaminophen exact mechanism of action unknown Drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, SOB, nausea, vomiting, euphoria, dysphoria, constipation, abd pain, pruritus, rash, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, respiratory depression. Teach pt common side effects of medication and instruct pt to not take other substances containing acetaminophen because of toxicity, monitor patient for adverse effects, assess for pain prior and post administration, do not administer more than 4g/day Teach pt common side effects of medication and instruct pt to not take other substances containing acetaminophen because of toxicity, monitor patient for adverse effects, assess for pain prior and post administration, keep HOB elevated, assess bowel sounds, do not administer more than 4 g/day of Tylenol 2 tab PO Q6H PRN Drowsiness, constipation, nausea, respiratory depression Teach pt side effects of drug, may cause constipation, tell them to report any pain, or abd pain, teach pt safety concerns with drowsiness, effects of drugs, ambulate slowly and call for assistance, monitor pt for pain via pain scale, assess bowel sounds, I & Os, monitor safety precaution’s because sedative quality of drug, do no exceed 4 g in 24 hrs of Tylenol from all sources. Acetaminophen/Hydrocodo ne Bitart (Norco 5-325) – Analgesic, antipyretic, antiflammatory & opioid analgesic combo 1 tab PO Q4H PRN Hydrocodone binds to carious opioid receptors producing analgesia and sedation, acetaminophen exact mechanism of action unknown Drowsiness, constipation, nausea, respiratory depression Albuterol Sulfate (Accuneb 0.083%) – Beta2 agonist, bronchodilator 2.5 mg NEB Q4H PRN It is a Beta-2 receptor agonist with some beta-1 activity. Pt on medication for acute bronchospasm. Alprazolam (Xanax) – Antoanxiety agent, anxiolytics, benzodiazepines 0.25 mgPO Q12H PRN Binds receptors at several sites within the CNS, including the limbic system and reticular formation. Pt on medication for anxiety. Tremors, nausea, fever, bronchospasm, vomiting, headache, dizziness, cough, UTI, increased appetite, dry mouth, pain, dyspepsia, hyperactivity, nervousness, sweating, epistaxsis, epigastric pain, tachycardia, increased blood glucose levels Drowsiness, depression, headache, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth, tachycardia, confusion, insomnia, nausea/vomiting, hypotension, blurred vision, syncope, nervousness, tremor, nasal congestion 25 mg PO Daily SCH Blocks response to betaadrenergic stimulation; cardioselective for beta 1 receptors at low doses, with little or no effect on beta 2 receptors. Pt on medication for hypertension. Atenolol (Tenormin) – Beta blockers, beta-1 selective, antihypertensive Tiredness, hypotension, bradycardia, cold extremeties, postural hypotension, depression, nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, vertigo, lightheadedness, dyspnea, AV block. Teach pt side effects of drug, may cause constipation, tell them to report any pain, or abd pain, teach pt safety concerns with drowsiness, effects of drugs, ambulate slowly and call for assistance, monitor pt for pain via pain scale, assess bowel sounds, I & Os, monitor safety precaution’s because sedative quality of drug, do no exceed 4 g in 24 hrs of Tylenol from all sources. Teach pt side effects of drug, may cause tremors, headache, dizziness and nervousness, tell them to ambulate slowly and call for assistance, monitor pt for pain and fever, monitor BS post treatment, keep HOB elevated Teach pt side effects of drug, may cause insomnia, tremors, nasal congestion, constipation or diarrhea and nausea/vomiting, tell them to ambulate slowly and call for assistance, tell them to report any abd pain, monitor pt for hypotension, tachycardia and confusion, keep HOB elevated and assess bowel sounds. Teach pt side effects of drug, may cause nausea, diarrhea and tiredness, tell them to sit up slowly from lying position and ambulate slowly, monitor for hypotension, bradycardia, vertigo and dyspnea. Bisacodyl (Dulcolax) – laxative, stimulant 10 mg PR X1 PRN Ciprofloxacin (Ciloxan) – Quinolones, ophthalmic solution 1 drop RIGHT EYE TID PRN Dextrose (D50w) – Glucose elevating agent 12.5 gm IV PUSH per parameter PRN Dextrose (D50w) – Glucose elevating agent 25 gm IV PUSH per parameter PRN Irritates the smooth muscle of the intestine and possibly the colonic intramural plexus, which in turn increases peristalsis. Increases intestinal fluid accumulation and laxation by altering water and electrolye secretion. Pt on medication for constipation. Absorption through the cornea into acqueous humor; enhanced in presence of ocular inflammation &/or epithelial defects; some systemic. Unsure why pt on medication, indications for medication are for bacterial conjunctivitis or corneal ulcers (keratitis). Parenteral dextrose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, and provides 3.4 cal/gram of d-glucose. Pt on medication PRN for hypoglycemia. Parenteral dextrose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, and provides 3.4 cal/gram of d-glucose. Pt on medication PRN for hypoglycemia Abdominal cramping, excessive diarrhea, electrolyte and fluid imbalance, rectal burning, vertigo, nausea, vomiting. Teach pt side effects of drug, may cause abdominal cramping, vomiting, diarrhea, tell pt to ambulate slowly due to vertigo and call for assistance, monitor pt for electrolyte and fluid imbalance, keep HOB elevated. Burning, stinging, lid margin crusting, crystals/sclaes on eyelashes, foreign body sensation, itching, conjunctival hyperemia, ocular discomfort, lid edema, tearing, photophobia, decrease in vision, corneal infiltrates, keratopathy. Teach pt side effects of drug, itching, burning, stinging, ocular discomfort and tell pt to avoid rubbing eye and to call for assistance when ambulating as a decrease in vision can occur. Monitor pt for lid edema, conjunctival hyperemia and decreased vision. Hyperosmolarity, hypervolemia, phlebitis, pulmonary edema, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral ischemia, hyperglycemia, injection site extravasation. Teach pt effects of drug and that it will only be administered in the event that the pt is severely hypoglycemic, monitor pt for s/s of cerebral hemorrhage &/or ischemia, monitor BS post administration, and inspect IV site. Teach pt effects of drug and that it will only be administered in the event that the pt is severely hypoglycemic, monitor pt for s/s of cerebral hemorrhage &/or ischemia, monitor BS post administration, and inspect IV site. Hyperosmolarity, hypervolemia, phlebitis, pulmonary edema, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral ischemia, hyperglycemia, injection site extravasation. Generic & Trade Name Drug Classification (Therapeutic & Pharmacologic) Dextrose (D5w) – crystalloid fluid that has 5% dextrose in water, intravenous volume expander Dextrose (D10w) – crystalloid fluid that has 10% dextrose in water, intravenous fluid expander Dose/Route Frequency Action of drug and Rationale (Why is patient on medication?) Significant Side Effects (Serious and/or frequent) Nursing implications related to assessment, administration or education 1,000 mls @ 75 mls/hr IV Q13H20M PRN Hypertonic solution that raises total fluid volume, helpful in rehydrating and excretory processes, provides a source of calories, it pulls the fluid into the vascular by osmosis resulting in an increase in vascular volume. Unsure why pt receiving D5W, indications for this therapy is for a source of water, electrolytes and calories. Used for hypertonic hydration and to replace extracellular fluid losses. Hypertonic solution that raises total fluid volume, helpful in rehydrating and excretory processes, provides a source of calories, it pulls the fluid into the vascular by osmosis resulting in an increase in vascular volume. Unsure why pt receiving D5W, indications for this therapy is for a source of water, electrolytes and calories. Used for hypertonic hydration and to replace extracellular fluid losses. Hypervolemia (fluid overload), pain (phlebitis at injection site), hyperglycemia and glycosuria. Teach pt that administration of this IV fluid will help with rehydration, teach pt effects of the fliud, monitor pt for fluid overload, auscultate lungs pre, during and post fluid administration, monitor IV site for pain and monitor BS during infusion and post infusion. Hypervolemia (fluid overload), pain (phlebitis at injection site), hyperglycemia and glycosuria. Teach pt that administration of this IV fluid will help with rehydration, teach pt effects of the fliud, monitor pt for fluid overload, auscultate lungs pre, during and post fluid administration, monitor IV site for pain and monitor BS during infusion and post infusion. 1,000 mls @ 100 mls/hr IV Q10H PRN Docusate Sodium (Colace)-laxative, stool softner 100 mg PO DAILY SCH Surfactant laxative, which reduces tension of oil-water interface of the stool; enhances incorporation of water and fat into stool, causing stool to soften. Pt on this medication for constipation. Abdominal cramping, diarrhea, excessive bowel activity, intestinal obstruction, throat irritation. Famotidine (Pepcid) – Histamine H2 antagonist, acid controller 20 mg DAILY SCH Blocks H2 receptors of gastric parietal cells, leading to inhibition of gastric secretions. Unsure why pt is receiving this medication, indications for use are for duodenal ulcer, benign gastric ulcer, GERD, hypersecretory conditions, heartburn. Loop diuretic; inhibits reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions at proximal and distal renal tubules and loop of Henle; by interfering with chloride-binding cotransport system, causes increases in water, calcium, magnesium, sodium, and chloride. Headache, constipation, diarrhea, dizziness, anxiety, arrhythmia, confusion, insomnia, nausea, pruritus, vomiting, musculoskeletal pain. Furosemide (Lasix) – Loop diuretic 40 mg IV PUSH DAILY SCH Loop diuretic; inhibits reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions at proximal and distal renal tubules and loop of Henle; by interfering with chloride-binding cotransport system, causes increases in water, calcium, magnesium, sodium, and chloride. Teach pt side effects of drug, abdominal cramping, intestinal obstruction and throat irritation, tell pt to report any abdominal pain, assess bowel sounds, monitor I & O’s, monitor s/s of intestinal obstruction (similar to appendicitis). Teach pt side effects of drug, tell pt to ambulate slowly and call for assistance if dizzy, elevate HOB, monitor pt for pain, assess bowel sounds, assess heart sounds. Teach pt effects of medication and to report any SOB or hearing impairment, as well as any other side effects immediately, tell pt to ambulate slowly, keep urinal next to bed, monitor I & O’s, monitor electrolytes, BUN and Hgb/Hct as ordered per MD, monitor for s/s of hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia and anemia, monitor BS and VS especially BP Gabapentin (Neurontin) – Anticonvulsants, GABA analogue, nonopioid analgesic 300 mg PO TID SCH GABA analogue; structurally related to neurotransmitter GABA, but has no effect on GABA binding, uptake, or degradation; mechanism for analgesic and anticonvulsant activity unknown. Unsure why pt on this medication, but most likely for diabetic neuropathy. Glucagon (Glucagon) – Hypoglycemia antidote, used in GI diagnostics, glucose elevating agent 1 mg IM PER Parameter PRN Glucose (Glucose 15) – Hypoglycemia antidote 1 tube PO PER parameter PRN Insulin antagonist, stimulates cAMP synthesis to accelerate hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, also relaxes smooth muscles in GI tract. Pt receiving medication as PRN for hypoglycemia. A monosaccharide that work quickly to raise the glucose level in the blood. Pt receiving PRN in the event the pt experiences severe hypoglycemia. Ataxia, dizziness, fatigue, diplopia, somnolence, insomnia, nervousness, nystagmus, tremor, amblyopia, back pain, vomiting, nausea, constipation, depression, dry mouth, dysarthria, dyspepsia, increased appetite, leukopenia, myalgia, nervousness, peripheral edema, angioedema, vasodilation, pruritus, pharyngitis, blood glucose fluctuation, elevated liver function tests, HTN, vertigo. Occasional nausea and vomiting, rash, hypotension, tachycardia. Severe allergic reactions include; rash, hives, itching, difficulty breathing, tightness in chest, swelling of mouth, face, lips, or tongue. Teach pt side effects of this drug, instruct pt to take with food, tell pt to report any signs of facial swelling, SOB immediately, maintain HOB elevated and emesis pan available at bedside, tell pt ambulate slowly and call for assistance, monitor for any visual changes, check VS 3060mins post administration and assess pain, monitor BS and monitor liver enzymes. Teach pt of side effects of drug and that drug will only be administered in the event of a severe hypoglycemic event. Maintain HOB elevated w/ emesis pain at bedside. Monitor VS, BP and inspect pt for any signs of a rash. Teach pt effects that can occur as a severe allergic reaction, but otherwise there are no common side effects. Inform pt that this will only be given if the pt experiences a severe hypoglycemic event. Tell pt to report any of the following possible side effects. Monitor BS post administration, monitor for angioedema and SOB. Hydromorphone HCL (Dilaudid) – Opioid analgesic 0.5mg IV PUSH Q4H PRN Mu-opioid receptor agonist; inhibits ascending pain pathways, thus altering response to pain; produces analgesia, respiratory depression, and sedation, suppresses cough by acting centrally in medulla. Pt receiving medication PRN for pain. Imipenem/Cilastatin Sodium 500 mg in Sodium Chloride – Carbapenem type antibiotic 100 mls @ 100 mls/hr IVPB Q6H SCH Inhibits bacterial cell-wall synthesis by binding to penicillin-binding proteins; cilastatin prevents renal metabolism of imipenem. Pt on drug to stop the bacterial growth from the ulcerative lesion on the left leg. Anticholinergic: dry mouth, palpitation, tachycardia, and urinary retention. Cardiovascular: angina, bradycardia, cardiac arrest, MI, syncope, shock, V-tach. CNS; agitation, coma, dizziness, dysphoria, nervousness, restlessness, sedation, depression. GI: constipation, nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, abdominal distention, GERD, paralytic ileus. Resp: resp depression, hypoxia, resp arrest, bronchospasm, dyspnea. Other: flushing, pruritus, sweating, urticaria, and warmness of face/neck/upper thorax. Swelling, redness, pain, or soreness at the injection site may occur. Upset stomach, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Dark urine, easy bruising/bleeding, hearing changes, confusion, hallucinations, persistent sore throat/fever, swollen tongue, tingling hands/feet, yellowing eyes/skin, muscle spasms, unusual weakness, seizures, anemia, hypotension, neutropenia, increased PT, elevated liver function tests. Teach pt side effects of drug, tell pt to report nausea immediately so that an antiemetic may be given to ease with that symptom, tell pt to ambulate slowly and call for assistance, tell pt to report SOB or flushing feeling of face and thorax. Monitor VS, assess pain 30-60 mins post administration, assess respirations frequently and for s/s of respiratory depression, assess bowel sounds and I & O’s. If pt is known to become nauseous with the drug, administer an antiemetic prior to administering Dilaudid. Teach pt of side effects of drug, dark urine, bruising/bleeding, nausea, swelling, muscle spasms. Tell pt to ambulate slowly and call for assistance. Maintain HOB elevated, monitor VS, BP, inspect eyes, skin, injection/IV site, monitor liver enzymes, CBC, Hgb/Hct, and Coag’s. Generic & Trade Name Drug Classification (Therapeutic & Pharmacologic) Insulin Detemir (Levemir) – Antidiabetic & Insulin, intermediate to long acting insulin Dose/Route Frequency Action of drug and Rationale (Why is patient on medication?) Significant Side Effects (Serious and/or frequent) Nursing implications related to assessment, administration or education 80 unit SUBCUT Bedtime SCH Regulates glucose metabolism, insulin and its analogues lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production; insulin inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis and enhances protein synthesis; targets include skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue. Pt has DM type 2 Stimulates peripheral glucose uptake, inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis regulating glucose metabolism – pt has DM type 2 Hypoglycemia (shakiness, palpitations, nervousness, diaphoresis, anxiety, hunger, pallor), headache, pallor, nausea, urticaria, hypokalemia, rash Monitor pt BS, s/s of hypoglycemia, give appropriate time for meals, and side effects of medication. Teach pt importance of DM management and use of insulin pen, teach side effects of medications, teach pt proper diet that goes along with insulin. Hypoglycemia (shakiness, palpitations, nervousness, diaphoresis, anxiety, hunger, pallor), hypokalemia, rash Restores normal bowel flora that inhibit growth of harmful bacteria; stimulates local immunity; promotes water reabsorption in colon. Pt on antibiotics. Hives, chest tightness, difficulty breathing, angioedema Monitor pt BS, s/s of hypoglycemia, give appropriate time for meals, and side effects of medication. Teach pt importance of DM management and use of insulin pen, teach side effects of medications, teach pt proper diet that goes along with insulin. Teach pt about possible side effects and to call for assistance immediately with any signs of difficulty breathing and angioedema or chest tightness. Instruct pt to take at least 2 hours after antibiotic and to continue for several days after antibiotic treatment is finished. Insulin Human Lispro (Humalog) – Antidiabetic & Insulin, Rapid acting insulin 0-24 unit SUBCUT ACHS SCH P Lactobacillus Acidoph/Bulgaricus (Lactinex) – Gastrointestinal, Herbal, Probiotic, digestion aid, antidiarrheal properties 1 each PO TIDWM SCH Lactulose (Cephulac) – Osmotic Laxative, Ammonium Detoxicant Lisinopril (Zestril) – ACE inhibitor, Antihypertensive 20 gm PO BID SCH 20 mg PO DAILY SCH Constipation: Hyperosmotic agent increases stool water contents, softens stool, promotes peristalsis, and reduces blood ammonia concentration. Portal systemic encephalopathy: Breakdown of lactulose to organic acids by colonic bacteria acidifies colonic contents, thereby subsequently inhibiting diffusion of ammonia back to blood; agent also enhances diffusion of NH3 from blood into gut, where it is converted to NH4+. Pt has had constipation. Prevents the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor) through competitive inhibition of angiotensinconverting enzyme resulting in decreased plasma angiotensin II concentrations; blood pressure may be reduced in part through decreased vasoconstriction, increased renin activity, and decreased aldosterone secretion. Also increased renal blood flow. Pt has hypertension. Abdominal cramping, abd distention, belching, flatulence, dehydration, diarrhea, excessive bowel activity, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, nausea, vomiting, Teach pt of side effects of drug, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abd cramping, tell pt to ambulate slowly and call for assistance, monitor I &O’s, assess bowel sounds, assess abd pain and hydration, look for s/s of hypokalemia and hypernatremia and check electrolytes. Dizziness, cough, headache, hyperkalemia, diarrhea, hypotension, chest pain, fatigue, nausea/vomiting, rash, angioedema Teach pt side effects of drug, cough, hypotension, angioedema, N/V, tell pt to rise slowly and ambulate slowly, monitor VS/BP, Maintain HOB elevated, monitor for hyperkalemia and s/s of swelling. Hold medication if BP low and notify MD. Lorazepam (Ativan) – Anticonvulsants, Antianxiety agent, Anxiolytics, Benzodiazepines 1 mg IV PUSH Q6H PRN Sedative hypnotic with short onset of effects and relatively long half-life; by increasing the action of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, lorazepam may depress all levels of the CNS, including limbic and reticular formation. Pt receiving medication PRN for anxiety. Magnesium Hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia Susp) Laxative 30 ml PO x1 PRN Laxative: Promotes osmotic retention of fluid, which distends the colon with increased peristaltic activity and stimulates bowel evacuation. Antacid: Reacts with hydrochloric acid in stomach to form the salt magnesium chloride. Miscellaneous Information (Vancomycin Per Pharm) Morphine Sulfate (Morphine) – Opioid Analgesic 1 each MISC PER Parameter SCH 2 mg IV PUSH Q3H PRN N/A Narcotic agonist-analgesic of opiate receptors; inhibits ascending pain pathways, thus altering response to pain; produces analgesia, resp depression, and sedation; suppresses cough by acting centrally in medulla. Pt receiving morphine PRN for pain. Sedation, dizziness, weakness, unsteadiness, fatigue, drowsiness, amnesia, confusion, disorientation, depression, vertigo, ataxia, suicidal ideation, sleep apnea, resp depression, tremor, convulsion/deizures, hypotension, nausea, constipation, paradoxical reactions (anxiety, excitation, agitation, hostility, aggression, rage), increased liver values, jaundice, visual disturbances. Hypotension, Resp depression, diarrhea, abd cramping, electrolyte imbalance, muscle weakness. N/A Pruritus, urinary retention vomiting, constipation, headache, somnolence, abd pain, diarrhea, dyspnea, fever, nausea, insomnia, rash, resp depression, anxiety, orthostatic hypotension, syncope, ileus, vertigo, thinking disturbances. Teach pt that this drug will only be given in the even of an anxiety attack and inform pt of side effects of the drug. Monitor pt for paradoxical reactions, assess bowel sounds, assess VS/BP, tell pt to call for assistance for ambulation, monitor pt respirations closely, may need to administer an antiemetic if nausea persists and to prevent vomiting with risk of aspiration. Teach pt side effects of drug. Assess pt’s need for the drug by evaluating bowel habits. Monitor serum magnesium for signs of hypermangesemia, such as bradycardia. Only give as needed, monitor VS/BP for signs of respiratory depression and hypotension. Inform pt to call for assistance with ambulation due to possible side effects of muscle weakness. N/A Teach pt of side effects of drug, perform a pain assessment 1 hour prior to and 30 mins following administration, assess for s/s of overdose (resp depression), assess bowel function routinely, increase fluid intake to manage constipation, assess VS/BP, tell pt to ambulate slowly or call for assistance and to report any of the side effects immediately. Multivitamins/Minerals (Theragran M)-Vitamins combination Generic & Trade Name Drug Classification (Therapeutic & Pharmacologic) Nicotine (Nicoderm Cq) – Smoking Cessation Aid Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat) – Nitrate, Angina 1 each PO DAILY SCH Vitamins help maintain many different functions in body, but unknown mechanism of action. Pt elderly with vitamin deficiencies. Upset stomach, unpleasant taste, headache, vitamin toxicity Monitor pt nutrition intake and for side effects of medication. Teach pt side effects of medication, and encourage balanced diet with foods from 4 basic food groups. Dose/Route Frequency Action of drug and Rationale (Why is patient on medication?) Significant Side Effects (Serious and/or frequent) Nursing implications related to assessment, administration or education 1 each TRANSDERM DAILY SCH Transdermal nicotine systematically absorbed; binds to nicotine receptors; reduces withdrawal symptoms, including nicotine craving, associated with smoking cessation. Pt uses tobacco. Increased blood pressure, tachycardia, dizziness, insomnia, headache, irritability, anorexia, diarrhea, jaw/neck pain, nausea, vomiting, cough, irritation at application site, bronchitis, indigestion, xerostomia, taste disturbances. 0.4 mg SL Q5M PRN Organic nitrate which causes venodilation, decreasing preload. Cellular mechanism: nitrate enters vascular smooth muscle and converted to NO leading to activation of cGMP an vasodilation. Relaxes smooth muscle via dose-dependent dilation of arterial and venous beds to reduce both preload and afterload, and myocardial O2 demand. Also improves coronary collateral circulation. Lower BP, increased HR, occasional paradoxical bradycardia. Pt receives PRN for angina. Headache, hypotension, tachycardia, dizziness, lightheadedness, blurred vision, flushing, N/V, nervousness, xerostomia, syncope, thrombocytopenia, prolonged bleeding time, rebound hypertension. Teach pt of side effects of patch and importance of continuing with the nicotine patch therapy to help with smoking cessation, and advise pt to not smoke with the patch on. Inspect site of administration for a local reaction (rash), tell pt that exercise may increase absorption, monitor VS/BP. Teach pt of side effects of drug, headache, dizziness, N/V, and hypotension are all common, teach pt that this is only to be used if experiencing symptoms of angina, teach pt that this drug specifically needs to be place under the tongue, do not chew or swallow. Assess location, duration, intensity, and precipitating factors of the angina pain, monitor BP and HR before and after administration. Ondansetron HCL (Zofran) – Antiemetic & Serotonin 3 receptor antagonist 4 mg IV PUSH Q6H PRN Selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist; binds to 5-HT3 receptors in periphery and CNS, primary effects in GI tract. Pt postoperative and on opioids PRN that might cause nausea/vomiting Headache, dizziness, constipation, diarrhea, dehydration, fatigue, dry mouth, IV irritation Pantoprazole Sodium (Protonix) – Proton Pump Inhibitor, 40 mg PO DAILY SCH Headache, abd pain, chest pain, diarrhea, rash, pruritus, flatulence, hyperglycemia, nausea, angioedema, pancreatitis, pancytopenia, rhabdomyolysis, anaphylaxis. Paroxetine HCL (Paxil) – Antidepressant, SSRI 20 mg PO DAILY SCH PPI; binds to H+/K+ exchanging ATPase(proton pump) in gastric parietal cells, resulting in blockage of acid secretion. Unsure why pt is taking this medication but indications for medication are GERD, esophagitis, peptic ulcer. SSRI; little or no affinity for alpha-adrenergic histamine or cholinergic receptor. Pt has depression. Pravastatin Sodium (Pravachol) – LipidLowering Agent, Statin, HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor 40 mg PO BEDTIME SCH HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, inhibits the ratelimiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis by competitively inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Pt has hyperlipidemia. Somnolence, nausea, insomnia, dry mouth, headache, constipation, asthenia, diarrhea, dizziness, sweating, ejaculation disorder, tremor, anxiety, blurred vision, decreased appetite, nervousness, hypotension, tachycardia, tinnitus, vertigo, depression exacerbation. N/V, diarrhea, headache, chest pain, fatigue, rash, cough, heartburn Teach pt side effects of medication, teach pt to report recurring nauseated feelings and vomiting episodes, teach pt to continue to elevate HOB. Monitor pt for nausea & vomiting, monitor I & Os, assess bowel sounds, teach pt side effects of drug, monitor LOC, IV site, elevate HOB and place emesis bin/basin next to pt. Teach pt side effects of drug and to report any abd pain, angioedema, anaphylaxis or chest pain. Monitor pt I & O’s, monitor pt BS and assess bowel sounds. Teach pt side effects of drug, evaluate liver and renal function tests prior to administration, monitor for s/s of depression, assess bowel sounds, advise pt that this should not be stopped abruptly. Teach pt side effects of drug and to report cheat pain, cough, N/V. Assess VS and maintain HOB elevated, check liver function tests prior to starting drug. Senna (Senokot) – Laxative, Stimulant 8.6 mg PO x1 PRN Intestinal irritant/stimulant. Pt has had constipation. Abd pain, diarrhea, excessive bowel activity, melanosis coli, nausea, electrolyte abnormalities, yellow-brown urine discoloration, nephritis Sodium Biphosphate/Sodium Phosphate (Fleet Enema) – Saline Laxative 133 ml PR x1 PRN Draws water into the lumen of the gut where it causes osmotic effect; causes abd distention and promotes peristalsis and evacuation of the bowel. Pt has had constipation. Replace Na and Cl, isotonic solution. Pt only requiring this to flush IVC to maintain patency since pt in not on IV Fluids. Inhibits cell wall biosynthesis; alters membrane permeability and RNA synthesis. Pt had a surgical amputation. Aspiration, dizziness, headache, abd pain, N/V, bloating, electrolyte imbalance, facial edema, cardiac arrhythmia, mucosal bleeding, metabolic acidosis. Sodium Chloride (Nacl 0.9% Flush) – mineral electrolyte Vancomycin HCL 1,000 mg in Sodium Chloride – Glycopeptide, Antobiotic 10 ml IV PUSH Q8H 250 mls @ 166 mls/hr IVPB Q24H SCH Fluid overload, hypernatremia, hyperchloermia. Rash, hypotension, N/V, stomatitis, Chills, drug fever, nephrotoxicity, thrombocytopenia, vasculitis, ototoxicity. Teach pt side effects of drug, abd pain, excessive bowel activity – may need to reduce the dose. Monitor electrolytes for abnormalities and monitor for s/s of dehydration, monitor I & O’s. Teach pt side effects of drug, tell pt to notify and side effects immediately. Monitor electrolytes, I & O’s, provide assistance for ambulation, monitor for facial edema and assess HR. Teach pt that this is only being administered to maintain IVC patency and that the listed side effects are very minimal to none. Teach pt side effects of drug and to report any side effects immediately. Monitor vancomycin serum levels prior to administration, monitor renal function tests, monitor I & O’s, administer drug slowly to decrease risk of adverse effects, assess auditory function, BP, perfusion parameters and liver function tests. Hold drug if vancomycin levels elevated or increased renal values. Generic & Trade Name Drug Classification (Therapeutic & Pharmacologic) Vitamin B Complex (Vitamin B Complex) – B Vitamins, Water soluble Vitamin Dose/Route Frequency Action of drug and Rationale (Why is patient on medication?) Significant Side Effects (Serious and/or frequent) Nursing implications related to assessment, administration or education 1 each PO QDAY SCH Distribution to liver, bone marrow, and other tissues. Participates in physiologic systems and reactions. Unsure why pt is taking this medication, possible Vitamin B deficiency seen on labs. Vitamins and minerals. Headache, dizziness, arthralgia, naspharyngitis, nausea, diarrhea, itching. Teach pt side effects of drugs, stress proper nutritional habits to prevent recurrence of deficiency. Provide assistance with ambulation due to possible dizziness. Lab and Diagnostic Test Data TEST NORMAL VALUES 135-145 PATIENT VALUES (Day of Admission) 137 PATIENT VALUES (Recent Trends) 133 Na K 3.3-5.0 5.1 4.9 C1 95-110 101 97 CO 2 (venous) 24-32 30 28 BUN 8-22 23 21 Creatinine 0.5-1.3 0.89 0.85 Greater than 60 Greater than 60 8.8 8.2 139 299 Blood glucose is not controlled, therefore there are varying results during pt’s stay and attempting to control with insulin 6.4 On the low end possibly due to pleural effusion GFR Ca 8.6-10.5 Ionized CA 1.20-1.32 Blood Glucose 70-110 Cholesterol <200 mg Triglycerides 35-160 Total Proteins 6.3-8.3 Amylase 56-190 Identify why this lab may be normal/abnormal related to patients DX. Identify the purpose behind unusual labs related to patient’s Dx. Identify trends (if any) Value decreased during the stay, possibly due to D5W administration or Lasix administration Values decreasing possibly due to Lasix administration for pleural effusion or pt was mildly dehydrated on admission and is now becoming more hydrated, pt also taking ACE inhibitors which elevate K levels Normal but decreasing possibly due to the administration of D5W and lasix Decreasing possibly due to oxygen therapy and removal of pleural effusion fluid Values decreasing, pt possibly dehydrated and with rehydration BUN is normalizing Normal, but decrease in value suggests better renal perfusion, hydration and Lasix administration This indicates chronic kidney disease but unsure whether stage 1 or 2, CKD probably due to uncontrolled diabetes. Normal, decreasing trend, possible vit D deficiency, and possible Lasix administration TEST NORMAL VALUES PATIENT VALUES (Day of Admission) PATIENT VALUES (Recent Trends) Identify why this lab may be normal/abnormal related to patients DX. Identify the purpose behind unusual labs related to patient’s Dx. Identify trends (if any) Lipase 0-110 Magnesium 1.2-2.0 Phosphorus 3.0-4.5 Troponin <3.1 Myoglobin 0-85 Albumin 3.8-5.1 Alk. Phos. 20-180 GGT 0—65 T. Bili .3-1.3 CPK (total) 0-250 CPK MB <7.5 LDH 90-200 SGOT (AST) 8.42 SGPT (ALT) 10-60 WBC 4.5-11.0 18.6 10.3 13-16 9.1 8.2, 7.4, 9.7 Initial value indicated fairly severe infection, decrease in value suggests that infection is under control and responding to antibiotic therapy Decreasing Hgb – anemia, possible due to recent surgery, loss of blood and infection. Lab values reveal an expected increase in Hgb post pRBC transfusion. Hgb TEST NORMAL VALUES 37-49 PATIENT VALUES (Day of Admission) 27.9 PATIENT VALUES (Recent Trends) 25.4 Hct RBC 4.5-5.3 3.42 3.1 PaO 2 80-100 % SAT 90-100 Ph 7.35-7.45 PaCO 2 35-45 HCO3 22-28 Platelets 130-400 540 500, 19, 59 INR <1.16 PTT 23-33.5 URINALYSIS 2/24/14 urine culture submitted, values unknown Color Pale yellow Clarity Clear Spec. Grav. 1.002-1.030 Identify why this lab may be normal/abnormal related to patients DX. Identify the purpose behind unusual labs related to patient’s Dx. Identify trends (if any) Decrease possibly due to surgery, blood loss, fluid overload, vitamin B deficiency, or CKD Decrease possibly due to surgery, blood loss, fluid overload, vitamin B deficiency, or CKD Initial high values could have been due to CKD, infection, and inflammatory process. Decrease value could have been due to pt going into DIC with the severely ulcerative lesion on the left limb or impaired platelet production, and surgery could have contributed to the decrease. Increased to 59 post FFP transfusions. TEST NORMAL VALUES Occ. Blood 0 Ketones 0 Glucose 0 Albumin 0 PH 4.8-7.8 WBC/HPF 0-2 RBC/HPF 0-2 Bacteria/casts 0 X-RAY CT SCAN PATIENT VALUES (Day of Admission) PATIENT VALUES (Recent Trends) Identify why this lab may be normal/abnormal related to patients DX. Identify the purpose behind unusual labs related to patient’s Dx. Identify trends (if any) 2/27/14 right thoracentesis 950mls submitted fluid to cytology Values unknown LDH 430 (high) TP 6.4 (low) A high protein and high LDH shows that pleural effusion fluid is local exudate rather then transudate or systemically caused. 2/24/14 pleural effusion 2/24/14 pleural effusion EKG US OTHER 2/24/14 blood cultures submitted 2/25/14 Left thoracentesis 900mls Nursing Plan of Care Chief Medical Diagnosis Priority Assessments Left great toe amputation due to PVD, Pleural Effusion, Uncontrolled DM s/s infection, dressings (wound vac), VS, work of breathing, breath sounds, O2 sat, blood glucose monitoring Nursing Diagnosis (Problems) Data to Support Planned Interventions 1) Problem #1 –Risk for infection r/t surgical amputation of left great toe as e/b wound vac dressing and IV insertion a) Wound vac on ulcerative lesion of amputated toe b) IV site left upper arm with NS 0.9% flush and intermittent IV medications c) pt Hx of DM d) Pt limited to bed and minimal ambulation within room a) scheduled dressing changes twice weekly for wound vac b) scheduled IVC care site due today c) continuing with insulin and frequent FSBS checks and attempting to regulate BS d) plan to get pt up and ambulating around the hospital e) pt effectively able to move remaining toes of left foot without pain Evaluation of Interventions a) dressing looks clean and dry on toe amputation site b) IVC site slightly red, hard flush initially but then worked fine c) BS still unregulated d) pt ambulating well with walker 2) Problem #2 – Ineffective breathing pattern r/t pleural effusion as e/b SOB 3) Problem #3 – Ineffective oxygenation r/t COPD as e/b decreased SpO2 on room air 4) Problem #4 – Risk for fall r/t left great toe amputation as e/b a slower, more unstable gait a) Thoracentesis on both right and left sides 3 days apart, each about 900 mls removed from each side b) HOB elevated semi-fowler’s c) Oxygen 2 LPM nasal prong d) Xray revealed large amount of pleural effusion prior to evacuation a) Despite removal of pleural effusion SpO2 remains decreased at 91-92% on room air b) Pt has an intermittent cough c) Oxygen at 2LPM via nasal prongs d) HOB elevated semi-fowler’s a) Requiring the use of a walker for ambulation b) The great toe provides about 40% of the foots support a) thoracentesis right side removed 950 mls a) post thoracentesis pt felt more relieved and breathing is easier a) Nebulize with albuterol b) Maintain O2 at 2 LPM via nasal prongs a) pt breaths better with oxygen and feels more comfortable b) Unable t0 assess pt post nebulization treatment c) Resting comfortably a) pt ambulates well with walker b) Minimal to no pain per pt a) Ambulated well around room b) Able to get in and out of bed c) Not present for ambulation around hospital 5) Problem #5 – Risk for ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion r/t PVD as e/b decreased blood flow to lower extremities 6) Knowledge Deficit - Plan to explain the importance of exercise and diet. Plan to explain the importance of smoking cessation. Plan to explain the importance of controlling DM and controlling hypertension. 7) Discharge/Transfer - Pt must be able to adequately demonstrate FSBS and insulin administration. Pt must be able to demonstrate adequate foot care. Pt should be able to explain what an adequate diabetic diet is composed of. Pt should be able to demonstrate adequate use of inhalers and have an understanding of each mediation. a) Absent dorsal pedal pulse in left foot and faint in right foot b) poeterior tibial pulse ¼ bilaterally c) Decreased ABI in both limbs d) Previous non-healing ulcers in both legs e) PTA revealed severe blockage of major vessels in both limbs a) encourage frequent ambulation b) encourage frequent ROM while lying in bed c) maintaining left limb elevated on pillows d) Monitoring and inspecting for any signs of new ulcerations . a) pt is moving limbs frequently (ROM) while in bed b) ambulates well in room c) no new ulcerative lesions noted on lower extremities d) limbs warm and equal to the touch SBAR Pass Off Report Situation Background Assessments Recommendation Patient B.D. is a 55 year old male, who presented to the hospital on 2/13/14 as ordered per his family practice physician because of significant ischemic ulceration of the left lower leg. Pt has been non compliant with his diabetes, severe hyperglycemia, as well as the treatment of the left leg wound and now pt condition is deteriorating. Pt complains of persistent pain, not feeling well for the past month. Pt is febrile, very weak and possible risk of sepsis, severe COPD symptoms, Hypertension uncontrolled, dorsal pedal pulses absent in left foot and unsure whether left limb is salvageable. During his stay on 2/24 pt developed a severe episode of SOB, almost requiring a rapid response team, from labs, CT, and Xray a loarge amount of pleural effusion was noted, 2/25 Pt B.D. has been non-compliant with his diabetes and PVD. He has hx of CAD, hx of carotid vascular disease, previous intervention done on both legs about 2 years ago. Pt continues to smoke, left carotid artery occlusion, multiple stents in coronary artery, carotid bilateral bruits, uncontrolled severe COPD, normally functioning prosthetic aortic valve with no aortic insufficiency. Pt also has a previous history of endocarditis and non-healing ulcers on both legs. Last ABI 0.8 Right leg, 0.9 left leg. Pt denies alcohol use and claims to get some exercise. During his stay on 2/14 pt had a PTA looking at the left leg. 2/16 left great toe amputation with debridement. 2/19 wound vac with negative pressure therapy at 80 mmhg. 2/24 pt developed a severe episode of SOB, almost requiring a rapid response team, from labs, CT, and Xray a large amount of pleural effusion was noted. 2/25 left thoracentesis 900mls removed. 2/27 right thoracentesis 950mls yellowish colored fluid removed. Pt on vancomycin and Imipenem, last vancomycin levels elevated therefore one dose skipped. Continues to receive Lasix for heart disease and pleural effusion, BNP on 2/25 was 813 indicating moderate heart failure. 2/26 Hgb 7.4 and platelets decreased to 19K, pt received 2 units pRBC’s, and 5 units FFP, Hgb increased to 9.7 and platelets increased to 59K. WBC at 9.1. Diabetes remains uncontrolled despite being on Humalog, Levemir and a diabetic diet. BP is better controlled, sepsis appears to be resolved with improved WBC, and pain is minimal to none as recorded per patient. Pt remains on 2 LPM O2 via nasal prongs with SpO2 of 97-98%, SpO2 on room air post thoracentesis on 2/27 was 92% with minimal respiratory effort, pt said he did not feel difficult in breathing but did appreciate a little oxygen. Overall pt is feeling better and in better spirits and says he is ready to go home. Recommendations would include getting control of his diabetes with insulin and a proper diabetic diet, maintaining his BP, checking his limbs everyday for any signs of lesions or ulcerations, smoking cessation, implementation of exercise to improve peripheral vascular flow of blood to his extremities, further work up of pleural effusion and severity of heart disease as well as kidney disease. Student Clinical Self-Appraisal Weekly (turn in with Care Plan/Map) Student _Erica Anacleto_________________ Course ADULT HEALTH II CLINICAL Instructor AGNES ALICAR Instructions: Please evaluate your performance during clinical today using the following concepts: Patient Advocate Critical Thinking Self-Initiated Safety Leadership Nursing Process Professional Demeanor Communication/rapport Team Player Organized Well-prepared Knowledgeable Flexible Peer Support Skill Acquisition Educator Dependable Areas of Strength Today (Date) 2/27/14 Areas Needing Growth-Include plan of improvement: Team player – always willing to help teammates with their pt Organized – need to find more time to copy down information and dates, need to learn better organization of patient information, did not have all the information I needed or wanted when writing this care plan, just not sure where to begin when looking at the chart Skill Acquisition - wanted to be more knowledgeable about lung sounds and did not get the chance to auscultate before and after thoracentesis Peer support – able to help my classmates with some charting definitions and able to explain some physiology, procedures and equipment mechanics Communication – I felt that I was able to adequately communicate with the patient and build a rapport. We were able to hold a conversation while I was obtaining vitals and felt comfortable communicating with pt about his hobbies Self-initiated – felt very insecure as to what my role was as a student nurse, felt like I was in the way more than helpful, would like to be able to jump in and feel comfortable with just starting vitals, assessment, and bedside care Nursing process – did not feel that I was following the nursing process, felt very disorganized and unsure of my place in the unit, might have been due to the confusion at the beginning of the shift and the floor nurses not knowing what we were capable of doing Instructor Comments: