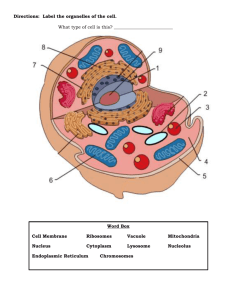
Study guide - Chapter 04

NSB 121 – GENERAL BIOLOGY I CHAPTER 04 – STUDY GUIDE
1.
Briefly describe how a light microscope produces an image. What is the maximum magnification achieved by a light microscope?
2.
Define magnification
3.
Define resolution.
4.
Fill in the blank: a.
______ m = 1 cm = ______ mm b.
______ cm = 1 mm = ______ m c.
______ mm = 1 m = ______ nm
5.
What does the cell theory state?
6.
How does an electron microscope produce an image? What is the m maximum magnification achieved by an electron microscope?
7.
Name and briefly describe the different types of electron microscopy
8.
What is the diameter range of most animal and plant cells?
9.
What is the principle of the differential interference light microscopy?
10.
Which type of microscope would you use to study the following and explain why: a.
the changes in shape of a living human white blood cell b.
the finest details of surface texture of a human hair c.
the detailed structure of an organelle in a liver cell
11.
Why is it important for a cell to be small in size?
12.
What happens to the volume of a cell as it increases in size?
13.
Draw a diagram of a typical plasma membrane with associated proteins. Denote hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions of the phospholipids and proteins
14.
Prokaryotic cells include which organisms? And eukaryotic cells?
15.
List three features that are common to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. List three features that differ.
16.
What feature distinguishes eukaryotes from prokaryotes?
17.
Name and briefly describe the different structures in a prokaryotic cell
18.
What are the four basic functions of organelles and structures in the eukaryotic cell? What organelles/structures belong to each group?
19.
Define cellular metabolism.
20.
In what ways do the internal membranes of a eukaryotic cell contribute to the functioning of the cell?
21.
Almost all of the organelles and other structures of animal cells are present in plant cells. What are the exceptions?
22.
Which of the following cellular structures differ from the others in the list: mitochondrion, chloroplast, ribosome, lysosome, vacuole? How does it differ?
23.
What are the main functions of the cell nucleus?
24.
Briefly describe each of the structures of a eukaryotic cell nucleus.
25.
Briefly describe the differences between mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA.
26.
What are ribosomes? How are ribosomes formed?
27.
Which type of cells would have large quantities of ribosomes?
28.
What are the two forms of ribosomes in the cell? What is the difference in their structure? What is the difference in their products?
29.
What role do ribosomes play in carrying out the genetic instructions of a cell?
30.
What is the endomembrane system? What organelles does it include? What are the common functions of these organelles?
31.
Describe the endoplasmic reticulum.
32.
Name and briefly describe the two kinds of endoplasmic reticulum.
33.
What are the functions of the smooth ER?
34.
What are the functions of the rough ER?
35.
Describe the process of synthesis and packaging of a secretory protein by the rough ER
36.
Explain why it is said that the ER is a biosynthetic factory
37.
Describe the Golgi apparatus. What is its function?
38.
Describe how a transport vesicle and its contents pass through the Golgi apparatus.
39.
Which types of modifications can be made to a molecule while in transit through the Golgi apparatus?
40.
Are the sacs of the ER connected? And the Golgi apparatus sacs?
41.
What is the relationship of the Golgi apparatus to the ER in a protein-secreting cell?
42.
What is a lysosome? What are the two digestive functions of a lysosome? Describe how each takes place
43.
How is a lysosome like a recycling center?
44.
What is a vacuole? Describe the different functions that a vacuole can have in an animal or plant cell
45.
Is a food vacuole part of the endomembrane system?
46.
How do transport vesicles help tie together the endomembrane system?
47.
What are peroxisomes?
48.
List the order of the structures through which a secretory protein, such as insulin, would pass from its production to its exit from the cell
49.
Explain how a protein inside the ER can be exported from the cell without ever crossing a membrane
50.
What are mitochondria? How does a mitochondrion’s structure suit its function?
51.
Describe the different structures and compartments in a mitochondrion
52.
What is cellular respiration?
53.
What are chloroplasts? What is photosynthesis?
54.
Describe the structures and compartments in a chloroplast
55.
Which membrane in a chloroplast appears to be the most extensive? Why might this be so?
56.
What general function do the chloroplast and mitochondrion have in common? How are their functions different?
57.
What does the endosymbiont theory propose?
58.
Describe the different pieces of evidence that support the endosymbiont theory
59.
All eukaryotes have mitochondria, but not all eukaryotes have chloroplasts. Can you propose an evolutionary explanation for this observation?
60.
What is the cytoskeleton of a cell and what is its function?
61.
Name and describe the three different kinds of fibers that make up the cytoskeleton
62.
Which component of the cytoskeleton is most important in: a.
holding the nucleus in place within the cell b.
guiding transport vesicles from the Golgi to the plasma membrane c.
contracting muscle cells
63.
Describe two different ways in which the motion of cilia can function in organisms
64.
How are cilia and flagella different? How are they similar? Compare and contrast
65.
Describe the structure and mechanism of movement of cilia and flagella
66.
What are the two possible causes for decline in sperm quality in developed countries?
67.
In primary ciliary dyskinesia what component is missing in both cilia and flagella? Why does the absence of this component affect the action of both cilia and flagella?
68.
What are the functions of the extracellular matrix and what is it composed of?
69.
What is the function of integrins?
70.
Name and describe the three types of cell junctions found in animal tissues and compare their functions
71.
A muscle tear injury would probably involve the rupture of which type of cell junction?
72.
What is a cell wall? Which types of cells have a cell wall?
73.
What are cell walls made of?
74.
What are pectins and what function do they serve in plant cells?
75.
What are plasmodesmata and where are they found?
76.
Which animal cell junction is analogous to a plasmodesmata?
77.
How do mitochondria, smooth ER, and the cytoskeleton all contribute to the contraction of a muscle cell?