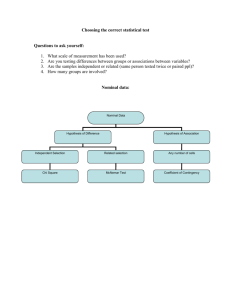
Appendix. Summary of Published SMT Studies Intervention
advertisement
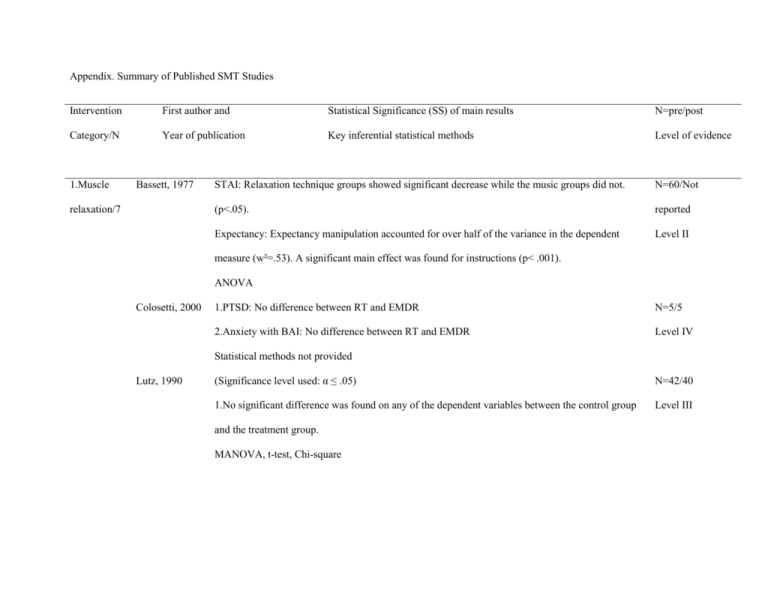
Appendix. Summary of Published SMT Studies Intervention First author and Statistical Significance (SS) of main results N=pre/post Category/N Year of publication Key inferential statistical methods Level of evidence 1.Muscle Bassett, 1977 relaxation/7 STAI: Relaxation technique groups showed significant decrease while the music groups did not. N=60/Not (p<.05). reported Expectancy: Expectancy manipulation accounted for over half of the variance in the dependent Level II measure (w²=.53). A significant main effect was found for instructions (p< .001). ANOVA Colosetti, 2000 1.PTSD: No difference between RT and EMDR N=5/5 2.Anxiety with BAI: No difference between RT and EMDR Level IV Statistical methods not provided Lutz, 1990 (Significance level used: α ≤ .05) N=42/40 1.No significant difference was found on any of the dependent variables between the control group Level III and the treatment group. MANOVA, t-test, Chi-square Murphy, 1995 (Significance level used: α ≤ .05) N=31/27 1.Anger:No significant difference between treatment groups Level II 2.Impulsivity: No significant difference between treatment groups 3.Cortisol levels: Significant difference was found in PRT group only (20 vs 40 min, p=.026, w²=.180) 4.Egocentrism: Significant group differences in favor of MM found on the negative self focused subscale (p=.008, w²=.186). 5.One month follow up: No significant differences between groups. One way ANOVA, ANOVA, ANCOVA Shanmugam, 1: Extroversion/introversion: No significant changes were found pre and post test between the three N=265/134 1992 research groups in this category (p=.05). Level III 2.Neuroticism: TM had increased scores while RT group did not change. In post-test 2 the TM had a significant more score in this category then the control group (t=2.0, p=.05). 3.Self ideal self in congruency: TM showed significant decrease compared to both control group and RT group (p=.01). 4.Verbal Creativity: Both TM (p=.05) and RT groups (p=.01) increased creativity scores compared to control group. Chi-square, ANOVA, Critical ratio Toler, 1978 1.Sleep:No significant difference was found between groups, except progressive relaxation group N=27/24 with stimulus control had significantly reduced night awakenings compared to control group Level II (p<.05). 2.STAI: State anxiety was significantly reduced pre to post-test for both treatment groups compared to control group (p<.05). 3:Locus of control: No significant pre and post-test differences. 4.No significant changes were maintained on eight week follow up. One way ANOVA, Scheffe’s post hoc test Vasilos, 1979 SS missing from article. N=60/60 Level IV 1.Skin temperature: Both high and low baseline groups reached a significantly higher absolute skin temperature during second training session 2.Subjective anxiety scale: Both relaxation training and autogenic suggestion groups displayed significantly greater tension/anxiety reductions in session 1 then direction instruction groups. ANCOVA 2.Transcend ental Meditation/6 Alexander, 1982 See other three articles by same author below. They cover all the major findings from this study. See next three This is the original dissertation they are based on. rows below with same Primary Investigator Alexander 2003 1.Ego development: TM group advanced more then one step, significant compared to the four N=271/264* comparison groups (p<.0025). Level III 2.States of consciousness: Advanced active and new active TM members scored higher on the postconceptual experience factor then Non-TM-members (F=6.47, p<.01, r=.2989). *** 3.STAI: Trend for TM improvement compared to comparison groups (p<.10). 4. Other variables: Aggression decreased in TM members (p<.005) compared to comparison groups. Correlation, One way ANOVA Alexander(b) 1.Recidivism rates (RR) were measured every six months, from six months to 30 months: TM had N=286/286(Retros 2003 32% RR compared to 48% in the combined sample of members of the other four programs pective Study) (Z=1.725, =0.42). Level III Chi square test, Multiple regression analysis Alexander(c) 1.Psychopathology factor: TM group members scored significantly lower, indicating less 281/165* 2003 psychopathology, then the Interested Group (IG) and the Not Interested Group (NIG) ranging from Level III -.75 to -.90 (p<.001). *** 2.Developmental factor: TM group members scored significantly higher then the total non-member group, (d=.65, p<.001). 3.Consciousness factor: TM group scored significantly higher then all nonmember categories, ranging in effect size from .49 to .82 (p=.05to<.01). Factor analysis Ballou, 1977 1.STAI: Significant posttest differences between both control group and experimental group in both N=66/38 for STAI dimensions (p<.001) Level III 2.Increased participation in “prison activities “ significantly: (p>.01) ANCOVA Cunningham,1 1.STAI: At six weeks and 15 weeks after beginning TM the TM group had significantly less Eventual n for 977 anxiety in both scales (p<.001) then the control group of non-meditators. treatment group 2.Likert scale on psychological symptoms: Was not compared to control group was 15. ANOVA Level III Significant differences were found between treatment and control groups on the following N=300/149 dependent variables: Level III Hawkins, 2003 1.Cognitive distortion (p<.036) 2.Intelligence related measures (p<.05) ANOVA, MANOVA, ANCOVA, Chi-square test, Factor analysis Orme— 1.SSSR: Decrease significantly greater for regular meditators (RM) compared to irregular N=17/10 Johnson , 2003 meditators (IM) (t=4.92, p<.001) and non-meditators (NM) (t=1.89, p<.05) Level III 2.MMPI: RM’s decreased significantly more then NM’s on scale 7, Obsessive compulsive behavior and psychasthenia (t=2.53, p<.025) and scale 10, social introversion (t=2.22, p<.05). And more then IM’s on scale 7 (t=2.14, p<.05). ANOVA, Correlation Rainforth, 2003 1.Recidivism rates (RR): Survival analysis based on the Cox regression model indicated that risk of N=306/248 recidivism in TM group compared to control group was reduced by 43.5% (p=.0008). Level III 2. Severity of offenses: A “measure of severity” indicated that it was lower for the TM group compared to the control group (p=.023). Survival analysis- Cox regression Shanmugam, See discussion above, in category 1. 1992 3.Other Bowen, 2006 1.Three months post intervention: Significant less substance use on 4/5 measures compared to TAU N=305/173 post- Eastern (p<.05). Also significantly less psychiatric symptoms, more optimism and drinking related locus of course assessment, meditative control compared to TAU (p<.05). Level III practices/12. 2.Six months post intervention: No significant difference in recidivism rates between the groups. Chi-square- Independent samples t-test Bunk, 1979 1.Internal locus of control: Significant differences using ANOVA between treatment groups and N=100/81 control group (p< .001) Level II 2.Anxiety: Only the Yoga plus meditation group reduced it significantly more then control group (p≤ .05). 3.Institutional adjustment: No significant difference found (p≤ .05). 4.Difference between treatment groups: The Yoga plus meditation group did better then Yoga only and meditation only numerically on all measures, but not significantly (p≤ .05). One way ANOVA, ANOVA, MANOVA Chandiraman, 1998 Significant improvement were found on most psychological parameters, including considerable Level III reductions in anxiety (p<.001) and depression (p<.001). Chi-square, paired t-test, descriptive statistics Jain, 2003 Khurana,1998 No statistical methods were given and no levels of significance, but according to the author the N=28/28 intervention yielded significant improvements on all measures of the study Level III The female inmates in the Vipassana group did have reduced criminal propensity and increased Level III subjective well being post intervention (p<.01). The males did appear to have statistically significant benefits on their subjective well being (p<.01). It also appeared that the longer and more intense the training is, the better the outcome is for the male prisoners on these variables. Descriptive statistics and t-tests Murphy, 1995 See discussion above, in category 1. Perkins, 1995 1.Coping skills: Treatment group (TG) proved significantly higher in coping effectiveness then both control groups (p<.000). Decrease in global levels of distress was also found comparing TG to the N=167/111 attention control group (p<.043) and the wait list control group (p<.000). Level II 2.STAXI: TG demonstrated a significant decrease in situational anger compared to the wait list control group (p<.006) and angry responding (p<.001) but not the attention control group. 3.Sick calls: None of the three groups displayed any significant changes in utilization of medical services pre and post-test. ANOVA, Independent t-test, Regression analysis Ranganathan, Younger inmates appeared more open to VM. They further revealed that the inmates felt the VM 2008 was helpful in obtaining peace and holding anger in check as well as in managing stress and Level IV understanding themselves better. Descriptive statistics based on information quantified from interviews. No SS given. Samuelson, 1.Hostility: All subscales showed significant post MBSR course improvement (p= .0001). N= 1350/955-948- 2007 2.Self esteem: Significant increases found in all settings post MBSR course (p=.0001). Women 907 fared better then men, 8.3% vs. 3.8% (p=.006). Level III 3.Mood disturbance: All six subscales showed significant improvement post MBSR course completion. Paired t-test Sumter, 2009 The experimental group experienced fewer sleeping difficulties (p=.01), and a reduced desire to throw things or hit people (p=.007). Nail biting also decreased (p=.002). The experimental group Level II also felt less guilty at post test (p=.002) and less hopeless about the future (p=.006). Independent sample and paired t-tests Simpson, 2007 1.PTSD: PTSD severity of symptoms did not differ significantly between those who volunteered for N=174/88 the VM course and those who did not, F(1,86)<1. 2.Substance abuse and PTSD: Treatment group did show greater reductions in substance abuse then Level III control group regardless of PTSD symptom severity levels (p<.001). t-test, Chi-square test, ANCOVA, Regression analysis Vannoy, 2006 1.The anger subscale of the Aggression Questionnaire: Significant reductions were found in anger N=90/56 with female participants of study (d= -.83, p<.05). 2.Changes on all other dependent variables did not reach statistical significance. Level III Correlation, ANOVA, ANCOVA 4.Cognitive Forde, 2005 methods/2. No significant pre-post intervention differences were found on any of the dependent variables. N=130/31 One way ANOVA- Independent sample t-test- Paired sample t-test Level II Vannoy, 2006 See discussion above, in Category 3. 5.Autogenic Thomson, 1.STAI: Reduced in Biofeedback Group (BG) on both scales (State: p=.005 and trait: p=.001) and training and 1988 Guided Imagery Group (GIG) (State: p=.007 and trait: p=.05). No significant change found in biofeedback/ Autogenic training group (ATG). 2. 2.Locus of control: BG dropped in powerful others (p=.001) and rise in chance scores (p=.006) post- N=86/82 Level II test. Aslo significant for ATG for chance scale increase (.023) after treatment. And GIG dropped in powerful other scores significantly (p=.004) 3.Incident reports: No significant changes pre and post test in the groups. 4. Physical health symptoms: Only significant difference pre and post test1 in BG (p=.004) and post test 2 (p=.005). 5.Psychotropics used: No significant results due to small sample size using psychotropics Correlation, ANOVA, Multiple t-tests, ANCOVA, MANOVA Vasilos, 1979 See discussion above, in category 1. 6. Music Bassett, 1977 See discussion above, in category 1. Therapy/3. Daveson, 2001 Thaut, 1989 Level V 1.Self perceived changes on general beneficial effects of music therapy: Significant positive change N=50/5 pre and post test on all scales in regards to state of relaxation, mood/emotion and thoughts about self, with all groups (p<.05). ANOVA 7. EMDR/1 Colosetti, 2000 See discussion above, in category 1. Level II