Xi Wang_HW1_BSYSE595
advertisement

Xi Wang
HW1 BSYSE 595
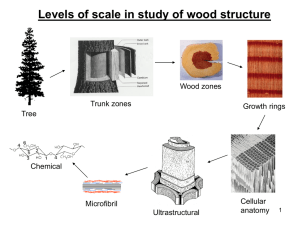
BSysE 595 Biosystems Engineering for Fuels and Chemicals
Spring 2013
Xi Wang
Homework 1 Reproduce model using MATLAB
The plot result is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1 The changing rates of cellulose, cellobiose and glucose with time
Appendix:
MATLAB code:
clear all; close all; clc;
%Content of Langmuir_M.m
%Create this file and place in the default m file directory
% Make rate constants available to function
global E1max E1maxL E2maxL K1ad K1adL K2adL alpha lambda k1r ...
K1IG2 K1IG k2r K2IG2 K2IG k3r K3M K3IG ...
S0 C0 L E1T E2T S ...
SR E1bC E2fL E1f E1fL
%% Model parameters
% Parameters of the Langmuir adsorption and substrate reactivity
E1max = 42.55;
E1maxL = 86.07;
E2maxL = 173.50;
K1ad = 0.6;
Xi Wang
HW1 BSYSE 595
K1adL = 0.51;
K2adL = 0.75;
alpha = 1.007;
lambda = 1;
% Parameters obtained by regression of saccharification data
k1r = 16.5;
K1IG2 = 0.04;
K1IG = 0.1;
k2r = 7.1;
K2IG2 = 132.5;
K2IG = 0.01;
k3r = 267.6;
K3M = 25.5;
K3IG = 2.1;
%% Initialize - Initial conditions
C0 = 40;
G20 = 0;
G0 = 0;
% Cellulose concentration at given time [mg/mL]
% Cellobiose conc. at given time [mg/mL]
% Glucose concentration at given time [mg/mL]
E1T = 54;
% Total EG/CHB concentration [mg/mL]
E2T = 65;
% Total beta-glucosidase concentration [mg/mL]
S0 = 2/125;
% Substrate (cellulose) concentration at t=0 [g/mL]
L = 0.0;
% Lignin content conc. [g/mL]
SR = alpha*C0/C0;
E1bC = 0;
E2fL = E2T;
E1f = E1T;
E1fL = E1T;
y0 = [C0 G20 G0]
% Call a routine to solve ODE
%
[t, y]=ode45('name of equation', [t0:step:tf], y0);
[t, y]=ode45('MonodFunc', [0:0.1:48], y0);
% Plot results
plot(t,y,'LineWidth',2 ); grid on;
xlabel('Time (Hr)');
ylabel('Concentration (g/L)');
legend('Cellulose','Cellobiose','Glucose');
%Content of MonodFunc.m
%Create this file and place in the default m file directory
Xi Wang
HW1 BSYSE 595
function dydt = MonodFunc(t,y)
%% Get rate constants from outside this function
global E1max E1maxL E2maxL K1ad K1adL K2adL alpha lambda k1r ...
K1IG2 K1IG k2r K2IG2 K2IG k3r K3M K3IG ...
S0 C0 L E1T E2T S ...
SR E1bC E2fL E1f E1fL
%% More comprehensible names for the variables
C = y(1);
G2 = y(2);
G = y(3);
%
SR = y(4);
E1bC = y(5);
E2fL = y(6);
%
E1f = y(7);
E1fL = y(8);
S = C;
%
%% Enzyme adsorpiton equations
% The Langmuir isotherm for endogluconase/cellobiohydrolase (EG/CBH)
% adsorption onto the pretreated CWR which contains cellulose and lignin
E1b = ((E1max * K1ad * E1f) / (1 + K1ad * E1f)) * S;
%
%
%
%
Since EG/CBH was proved to be adsorbed not only on cellulose, but also
on lignin, and b-glucosidase is adsorbed only to lignin (Zheng, 2007),
the Langmuir adsorption of EG/CBH and b-glucosidase onto lignin
was expressed
E1bL = ((E1maxL * K1adL * E1fL) / (1 + K1adL * E1fL)) .* L;
E2bL = ((E2maxL * K2adL * E2fL) / (1 + K2adL * E2fL)) .* L;
% Due to the adsorption of EG/CBH on both cellulose and
% lignin, the amount of EG/CBH adsorbed on cellulose, E1bC
E1bC = E1b - E1bL * lambda;
%% Calculate Rate of reaction
% Cellulose-to-cellobiose reaction with competitive glucose and
cellobiose
r(1) = (k1r * E1bC * SR * C) ./ (1 + G2./K1IG2 + G./K1IG);
% Cellulose-to-glucose reaction with competitive glucose and cellobiose
% inhibition
r(2) = (k2r * E1bC * SR * C) ./ (1 + G2./K2IG2 + G./K2IG);
% Cellobiose-to-glucose reaction with compeititve glucose inhibition
r(3) = (k3r * E2fL * G2) ./ (K3M * (1 + G./K3IG) + G2);
E1f = E1T - E1b;
E1fL= E1T - E1b;
Xi Wang
HW1 BSYSE 595
E2fL = E2T - E2bL;
%
S = C/1000;
SR = alpha .* C ./ C0;
% Substrate reactivity
%% Dynamic equations
dydt(1) = -r(1) -r(2);
dydt(2) = 1.056 .* r(1) - r(3);
dydt(3) = 1.1116 .* r(2) + 1.053 .* r(3);
%
%
%
%
%
dydt(4)
dydt(5)
dydt(6)
dydt(7)
dydt(8)
=
=
=
=
=
% dC/dt
% dG2/dt
% dG/dt
alpha .* C./1000./S0;
E1bC;
E2fL;
E1f;
E1fL;
dydt = dydt';
%MATLAB v5 wants a column vector
![[t,y]=ode45(‘ ',[0 tlim], [4 4]); dydt= (t,y)](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/013524672_1-a672587e3d402c460771d7b588302558-300x300.png)