Chapter 2 Notes
advertisement

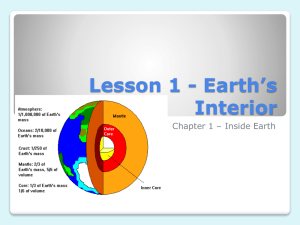
Name: _________________________________ Date: ____________________ Period: _______ Chapter 2.1 Earth: A Unique Planet 1) Earth a) A ______________ planet in our solar system. b) The only planet with ______________ water on its surface. c) The only planet with an __________________ that contains a large amount of _________________. d) The only planet know to support ___________. 2) The Earth’s Shape: A Sphere? a) The Earth appears to be a perfect _____________, however it is not. i) The Earth is an ___________________ _______________________. (1) The circumference around the ______________ is 40,007 km. (2) circumference around the ____________________ is 40,074 km. ii) This shape is caused by the __________________ of the earth on its axis. (1) The ____________ is an imaginary line that runs from the _________ pole to the south pole. 3) Hydrosphere & Atmosphere a) All of the earth’s _____________ makes up the _____________________. i) The earth is ________% covered by water. (1) ________% of that water is in the _______________. (2) ____% of that water is in ________ , rivers, streams, and ____ sheets. b) All of the _________ that surround the earth makes up the _____________. i) The atmosphere is 78% ____________, 21% oxygen, and ___% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and ______________. 4) The Earth’s Interior a) The earth’s interior is made up of ____________ major zones: the _______, _______________, and ____________. b) The Earth’s Crust i) The crust is the __________________ zone of the earth. ii) It is _________ and ___________ and makes up only ___% of the earth’s mass. iii) ____________ crust is found beneath the oceans and is only 5 km to 10 km thick. iv) _________________ crust makes up the continents and is 15 km to 80 km thick. Name: _________________________________ Date: ____________________ Period: _______ c) The Earth’s Mantel i) This zone of rock is _____________ km thick. ii) Makes up 2/3 of the earth’s ____________. iii) It is broken up into two sections: the _____________________ and the _________________________. (1) The lithosphere (a) The _________, ___________, ___________, upper portion of the earth’s crust. (b) It is 15 km to 300 km thick. (2) Asthenosphere (a) An extremely _____ layer of the mantel that is under an enormous amount of ________________. (b) Due to the enormous amount of ___________ and pressure, the solid rock of the asthenosphere has the ability to ___________. This is called ____________________. d) The Earth’s Core i) This section is the _____________ of the earth and is made mostly of _____________. ii) The core makes up 1/3 of the earth’s _____________. iii) The core is also broke into two sections: the ___________ core and the _____________ core. (1) The outer core (a) Scientists believe the outer core is a dense _____________ layer about ____________ km thick. (2) The inner core (a) Scientists believe the inner core is a dense ____________ sphere with a radius of ____________ km. 5) Seismic Waves a) A form of a wave (____________) that scientists use to study the earth’s ______________. b) There are _______ forms of waves that scientists use to study the earth’s interior, they are P waves or ______________ waves and S waves or __________________ waves. c) P waves travel through ______________, ___________, and ___________ while S waves only travel through _______________. Name: _________________________________ Date: ____________________ Period: _______ d) Primary waves travel ______________ than secondary waves. e) Scientists can use these waves to study the earth’s interior because the _____ and _______________ of both types of waves are affected by the _____________________ of the material they travel through. The more ______________ the material the faster the waves travel. 6) Andrija Mohorovicic a) Performed a seismic wave study in 1909 that showed the _______________ of the ______________ in the earth’s interior. b) Mohorovicic discovered that the ___________ of the seismic waves _________________ at the boundary from the crust to the mantel. i) This boundary is called the Mohorovicic discontinuity, or the _________. ii) This also indicates the earth’s mantle is _____________ than the crust. c) Changes in P wave and S wave ____________ occur at the boundary of each __________ of the earth’s interior. The S-waves also appear to disappear at the earth’s outer __________due to its ______________ like properties, and the P-waves slow down for the outer core but speed up for the inner core. d) ___________ zones are areas in the earth where P and S waves do not travel or only P waves travel. i) This absence of waves is caused by a change in _____________ rigidity. Meaning its ability to resist __________________ is different throughout the area of the earth. ii) Shadow zones can be caused by the makeup of the __________________ and ____________________. 7) The Earth’s Magnetic Field a) Along with the __________ and ___________ pole, the earth also has _______________ poles. i) The poles are called the north ___________________ pole and the south geomagnetic pole. b) The ________________________ is a region of space beyond the earth’s __________________ that is affected by the earth’s ______________ field. c) Scientists believe that the _____________ within the earth’s ____________ core creates our magnetic field because it is mostly _______ which is a good conductor. However, scientists also know that the _______ and __________ have magnetic fields but the sun contains _________ iron and the moon doesn’t have a ____________ core. Name: _________________________________ Date: ____________________ Period: _______ d) The exact source of the earth’s magnetic field has yet to be proven. 8) The Earth’s Gravity a) ___________ is the force of attraction that exists between all ____________ in the universe. b) Originally studied and by Sir Isaac Newton who describe the effect of gravity through his __________ ____ _____________________. c) This law states that the _________ of attraction between any ______ objects depends upon their _____________ and the ______________ between them. i) The ____________ the mass and the ______________ the distance between two objects the _____________ the gravitational attraction they have between themselves. d) Weight and mass are not the same. i) __________ is the amount of ______________ in an object and is measured in kilograms (kg). ii) ____________ is the force of ________________ on that matter and is measured in newton’s (N). (1) The weight of an object depends on its ____________ and distance from the earth’s ________________. (2) The ____________ to earth’s center the ________________ the object will become and the ____________ away from the earth’s center the ______________ the object will become. (3) At the earth’s _____________ a 1 kg mass weighs about 10 N, and 19,778 km from the earth’s _________ a 1 kg mass now weighs 1 N. (4) Due to the ____________ spheroid shape of the earth, your ________ at the equator is about .3% less than your weight at the ____________ pole.