Physics IA Lab Report
advertisement

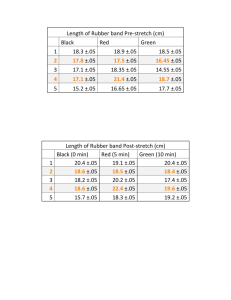
Design Research Question/Problem How does the number of rubber bands in a rubber band chain affect how far each rubber band stretches? Variables Independent - number of rubber bands Dependent - distance the rubber band stretches (cm) Control - type of rubber bands, screwdriver, height from where the screwdriver was dropped Materials - 2 Measuring tape (1.5 m) - Duct tape - Video Camera - 15 Rubber bands that are 6.7 ± 0.1cm in length when flat - 89 ± 1 g Screwdriver - 523 ± 1 g Weight to straighten measuring tape - 10 ± 0.1 cm Platform Procedure 1. 2. Duct tape both measuring tapes together, overlapping 1 cm at each end Duct tape measuring tape to screwdriver at the 5 cm mark 3. Duct tape platform to a surface approximately 10 feet off the ground so that it sticks off approximately 7 cm 4. Clip weight to the end of the measuring tapes 5. Get partner to stand at the bottom, get ready to video record with video recorder level to the measuring tape at the level the screwdriver will drop 6. Tie a rubber band to the middle of the screwdriver and add 10 rubber bands in a chain to the end of the rubber band around the screwdriver 7. Put the end of the rubber chain in the ridge at the end of platform so that it doesn’t fall out 8. Place the screwdriver directly in front of the platform horizontally so that the end of the screwdriver touches the end of the platform 9. Start recording on videorecorder 10. Drop the screwdriver 11. Stop recording after first drop 12. Repeat steps 7-11 three additional times 13. Repeat steps 6-12 with one additional rubber band after step 12 until 14 bands used 14. Look at the video recordings frame by frame and see where the screwdriver reaches its minimum point. 15. Record where the bottom of the rubber band tied to the screwdriver lined up with the measuring tape in cm for every trial Data Collection and Processing Raw Data Processed Data Conclusion and Evaluation Conclusion Our data from this experiment shows that generally, an increase in the number of rubber bands in the chain of rubber bands causes the stretch of each individual rubber band to increase. This is due to the chain becoming longer with each additional rubber band, causing the screwdriver to fall a longer distance and time, thus the screwdriver is able to have more time to accelerate to a higher maximum speed. However, this data is not absolutely conclusive due to our set of trials with 12 bands showing a decrease in individual rubber band stretch from 11 bands. This can be due to the uncertainty of our measurements causing discrepancies in our data. We had systematic error in our uncertainty of measurements and random error when occasionally the rubber bands got tangled together, causing the rubber bands to stretch less. When this happened, we did another trial, not discarding the previous trial with the error. Evaluating Procedure We could have improved our procedure in making our measurements more accurate by using a contraption that would ensure that the screwdriver would be dropped from the exact same height every trial. In addition, it would have helped if we had used a heavier object to hang from the rubber bands because doing so would have given us a larger stretch, and possibly larger differences in the different numbers of rubber bands. In addition, our results were probably not as accurate as they should have been due to the uncertainty that the partner would hold the videorecorder in the same place level to the drop of the screwdriver like a stand would have. Improving the Investigation We could have improved our investigation in making it more reproducible by choosing metric weight blocks instead of a random tool with a random weight. We also could have made a contraption that would ensure that we dropped the screwdriver from the exact same height in every trial. If we had put the video recorder on a stand, we could have also ensured more accurate and precise measurements. In addition, we should have added more sets of trials in which we used different numbers of rubber bands, possibly with a higher difference in number of bands between each set i.e. using 5 rubber bands in set 1, 10 rubber bands in set 2, and so on. This would have made our results more valid and allow us to make a better conclusion because our current results show that the increase in each rubber band stretch is very close. This would have also helped our data because it would have allowed us to make a better graph that shows a better relation of the general relationship between number of bands and the amount of stretch in each band. With our current data, when we extrapolate our graph, it shows very unrealistic/impossible results with lower numbers of rubber bands.