3 Types of Spectra
advertisement

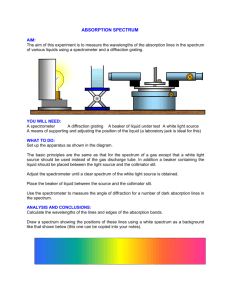
3 TYPES OF SPECTRA (CONTINUOUS, EMISSION, ABSORPTION) Prisms and diffraction gratings split light into the various wavelengths revealing a spectrum. Light source produces various λs Light beam of those λs Prism or diffraction grating separates λs Observer sees a spectrum of those λs Eye sketch by lilmizb3th.deviantart.com Hand out diffraction gratings 1. Continuous spectrum Ex: Spectrum of incandescent bulb Pass around filament bulb Describe: Rainbow like, All Source: Hot, dense object Ex: Filament, surface of sun (photosphere) Light beam of all λs Hot, dense light source produces all λs Prism separates all λs Observer sees a spectrum of all λs, namely a continuous spectrum 2. Emission spectrum Ex: Spectrum of H gas tube Note three lines (maybe four): red, turquoise, violet Describe: Bright line Source: Excited gas Ex: Gas discharge tube, gas clouds in outer space (Radio image of H in galaxy) See http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/features.cfm?feature=573 Ex: Spectrum of He Note: Must be a gas, Not H Each element has a unique spectra. Different gases have different spectra See http://blueox.uoregon.edu/~courses/BrauImages/Chap04/FG04_003.jpg Hot gas produces a few λs Light beam of those few λs Observer sees a bright line spectrum of those few λs, namely an emission spectrum Prism separates λs 3. Absorption spectrum Ex: Use video camera to show spectrum of incandescent bulb through liquid Describe: Missing colors or dark lines or bands, Continuous with certain missing Source: Hot dense object shining through a cooler gas cloud Light beam missing those few λs Hot, dense light source produces all λs Light beam of all λs A few λs are absorbed in gas cloud Prism separates λs Observer sees an absorption spectrum, most λs but missing those few λs absorbed by the gas Summarizes all three Uncertain source