First Grade Science Pacing Guide
advertisement

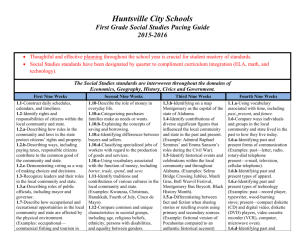
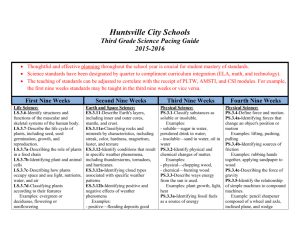
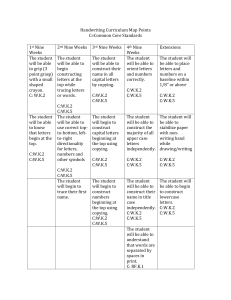
Huntsville City Schools First Grade Science Pacing Guide 2015-2016 Thoughtful and effective planning throughout the school year is crucial for student mastery of standards. Science standards have been designated by quarter to compliment curriculum integration (ELA, math, and technology). The teaching of standards can be adjusted to correlate with the receipt of PLTW, AMSTI, and CSI modules. For example, the first nine weeks standards may be taught in the third nine weeks or vice versa. First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Physical Science: PS.1.1-Select appropriate tools and technological resources needed to gather, analyze, and interpret data. Examples: platform balances, hand lenses, computers, maps, graphs, journals. Physical Science: PS.1.2-Identify basic properties of objects. Examples: size, shape, color, texture PS.1.3-Describe effects of forces on objects, including change of speed, direction, and position. Life Science: LS.1.4-Describe survival traits of living things, including color, shape, size, texture, and covering. LS.1.4a-Classifying plants and animals according to physical traits Examples: animals—six legs on insects, plants—green leaves on evergreen trees LS.1.4b-Identifying developmental stages of plants and animals Examples: plants—seed developing into seedling, seedling developing into tree; animals—piglet developing into pig, kid developing into goat LS.1.4c-Describing a variety of habitats and natural homes of animals Life Science: LS.1.6-Recognize evidence of animals that no longer exist. Third Nine Weeks Fourth Nine Weeks Earth and Space Science: ES.1.7-Identify components of Earth’s surface, including soil, rocks, and water. ES.1.8-Recognize daily changes in weather, including clouds, precipitation, and temperature. ES.1.8a Recognizing instruments used to observe weather Examples: thermometer, rain gauge, wind sock, weather vane ES.1.8b-Recording weather data using weather journals, charts, and maps ES.1.9-Identify ways to conserve Earth’s resources. Example: turning off lights and water when not in use ES.1.10-Describe uses of recycled materials. Examples: manufacture of paper products from old newspapers, production of mulch from trees ES.1.11-Compare the day sky to the night sky as observed with the unaided eye. Life Science: LS.1.5-Identify parts of the human body, including the head, neck, shoulders, arms, spine, and legs. LS.1.5a-Recognizing the importance of a balanced diet for healthy bones LS.1.5b-Discussing the relationship of muscles and bones to locomotion LS.1.5c-Discussing the relationship of bones to protection of vital organs Example: protection of brain by skull LS.1.5d-Identifying technology used by scientists to study the human body Examples: X-ray images, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Science utilizes a variety of standards and may be cross-referenced, integrated, and assessed in both subject areas. Informational Text RI.1.1 Ask and answer questions about key details in a text. RI.1.2 Identify the main topic and retell key details of a text. RI.1.3 Describe the connection between two individuals, events, ideas, or pieces of information in a text. RI.1.4 Ask and answer questions to help determine or clarify the meaning of words and phrases in a text. RI.1.5 Know and use various text features (e.g., headings, tables of contents, glossaries, electronic menus, icons) to locate key facts or information in a text. RI.1.6 Distinguish between information provided by pictures or other illustrations and information provided by the words in a text. RI.1.7 Use the illustrations and details in a text to describe its key ideas. RI.1.8 Identify the reasons an author gives to support points in a text. RI.1.9 Identify basic similarities in and differences between two texts on the same topic (e.g., in illustrations, descriptions, or procedures). RI.1.10 With prompting and support, read informational texts appropriately complex for Grade 1. Writing W.I.2 Write informative or explanatory texts in which they name a topic, supply some facts about the topic, and provide some sense of closure. W.1.7 Participate in shared research and projects (e.g., explore a number of “how to” books on a given topic and use them to write a sequence of instructions). W.1.8 With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. Speaking and Listening SL.1.1 Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about Grade 1 topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. SL.1.2 Ask and answer questions about key details in a text read aloud or information presented orally or through other media. SL.1.3 Ask and answer questions about what a speaker says in order to gather additional information or clarify something that is not understood. SL.1.4 Describe people, places, things, and events with relevant details, expressing ideas and feelings clearly. SL.1.5 Add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions when appropriate to clarify ideas, thoughts, and feelings. SL.1.6 Produce complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation. Math – Measurement and Data MD.1 Order three objects by length; compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object. MD.4 Organize, represent, and interpret data with up to three categories; ask and answer questions about the total number of data points, how many in each category, and how many more or less are in one category than in another.