light 7 - Buds Public School
advertisement

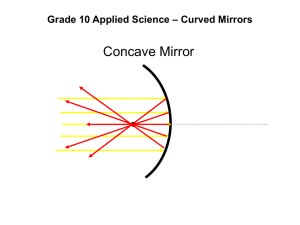
BUDS PUBLIC SCHOOL CLASS - VII Worksheet 1 Science (Light ) 1) Light travels along a ____. A) straight line B) circular path C) zigzag path D) straight line for some distance and then travels in a zigzag path 2) Light from a candle is not visible when it is seen through a narrow bent tube, because ____. A) light is absorbed by the tube B) light travels in a straight line C) candle does not give light D) a tube is narrow and light can't pass through it 3) Which of the following changes the direction of light? A) A board painted black B) A black body C) Carbon suit D) A mirror 4) The path of the light can be changed by ____. A) a polished surface B) a black body C) a black surface D) passing it through vacuum 5) A mirror changes the direction of light that falls on it. This property is called ____ of light. A) changing B) bending C) spreading D) reflection 6) Which of the following cannot change the direction of light? A) A mirror B) A shiny spoon C) A block of wood D) A stainless steel plate 7) The surface of water can also act like a mirror and change the path of light. A) True B) False 8) The surface of ____ acts like a mirror and can change the path of light. A) a road B) water C) a black board D) a wooden board 9) Any polished or shiny surface can act as a ____. A) mirror B) shield C) concave lens D) convex lens 10) When a lighted candle is placed in front of a plane mirror, you can see a similar candle placed behind the mirror. The candle that appears behind the mirror is the image of the candle formed by the mirror. A) True B) False 11) A band of seven colours obtained on screen, after reflection from a prism, is known as a spectrum. A) True B) False 12) The image of an object formed using the convex side of a steel spoon is ____ in size. A) erect and smaller B) inverted and larger C) inverted and smaller D) erect and larger 13) The image formed by a concave mirror can be smaller or larger in size than the object. A) True B) False 14) The image of an object placed in front of a plane mirror ____. A) can be obtained on a screen when it is placed close to the mirror B) can be obtained on a screen when it is placed at any distance from the mirror C) cannot be obtained on a screen D) can be obtained on a screen when it is placed at infinity 15) Ram is observing his image in a plane mirror. If the distance between his image and the mirror is 4 m, then the distance between him and his image is ____ m. A) 0 B) 2 BUDS PUBLIC SCHOOL CLASS - VII Worksheet 2 Science (Light ) I. Fill in the blanks : 1. The change in the direction of light by a mirror is called ______________. 2. The image formed by a ____________ lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size. 3. White light is composed of ______________ colours. 4. The image of an object formed by a _____________ cannot be obtained on a screen. 5. _____________ are used by dentists to see an enlarged image of the teeth. II Name the following : 1. An image that can be obtained on the screen 2. The lens which feel thinner in the middle than at the edges 3. The lens known as magnifying glass 4. The lens known as diverging lens 5. The mirror which can form both real as well as virtual images. 6. The large arc of seven colours VIBGYOR in the sky. III State whether True or False : 1. The image formed by a plane mirror is inverted 2. A convex lens is thicker in the middle than at the edges 3. A concave mirror always forms real image 4. Any polished or shining surface can act as mirror – IV Distinguish: a) Real image & Virtual image b) Convex and Concave Lens c) Concave and Convex mirror d) Reflection and Refraction of light V Give reason for the following a) Headlights of cars and searchlights have reflectors. b) Concave mirrors are used by dentists. c) Light cannot be seen through a bent pipe. VI Answer the following a) Which lens can be used to read very small prints? Explain the following. b) Why does a coloured disc appear white when rotated? c) State three uses of plane mirrors. d) List out the characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror. e) What do you meant by dispersion? f) You are provided with a plane mirror, concave mirror, convex mirror. How will you distinguish them without touching? g) What are primary colours? Why are they so called? h) List out two uses of convex mirrors. i) What are spherical mirrors? j) What do you meant by rectilinear propagation of light? Class VII Science Chapter Light Mirror and Lens Solved questions and Notes Short types Questions Q1. What do you mean by reflection of light? Ans. Bouncing back of light when it falls on a shiny surface is called reflection of light. Q2. How does a path of light can be changed? Ans. By reflecting it from a Polished Surface. Q3. What are the laws of reflection? Ans. Angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.Incedent, reflected ray & the normal lie on the same plane. Q4. What is the nature of image formed in a plane mirror? Ans. Virtual, erect, same image, laterally Inverted (left appears right & vice versa), at same distance from the mirror as the object. Q5. Difference between real & virtual image? Ans Real Image Image which can be obtained on a screen Image e.g.- Plane Mirror Virtual Image Image which cannot be obtained on a screen e.g. – Pinhole Camera, Photograph Camera. Q6. What type of mirror – the inner surfact of the Spoon acts as and the outer surface of the spoon acts as ? Ans. Inner surface of the spoon acts as Concave mirror and the outer surface of the spoon acts as concave mirror. Q7. Which concave mirror called a converging mirror and a convex mirror called a diverging mirror? Ans. Concave mirror is called a converging mirror because parallel rays of light fall on the mirror they Converge at a point called focus. Convex mirror is called a diverging mirror because parallel rays of light fall on it they diverge after reflection. Q8. What is the nature of image formed in a convex mirror? Ans. It is always virtual, erect and diminished. Q9. What is the nature of image formed in a concave mirror? Ans. It depends on the portion of the object in front of the mirror. If the object is very close to the mirror the image is virtual, erect & magnified. As the distance increases image becomes real, inverted & its size keeps changing. Q10. What are the uses of concave mirror? Ans. 1) Used by the ENT Specialists, dentists. 2.) Used as Shaving mirror. 3) Used by makeup artists. 4) Used in torches & Car headlights to get a parallel beam of light. Q11. What are the uses of Convex mirror? Ans. 1) Used as a rear view mirror in vehicles because it has a wide field of view as images are smaller. 2) Used at metro Stations and big departmental stores to keep a check. Q12. What are uses of Plane Mirror? Ans. Plane Mirrors are used in optical testing, blind corners instrumental scales, Periscopes, telescope etc. Q13. What is a lens? Ans. A piece of transparent material bound by curved surfaces. Q14. Difference between a convex lens & a Concave lens? CONVEX LENS 1. It is Thick at the Centre and thinner at edges 2. It is called converging lens CONCAVE LENS 1. It is thin at the center and thicker at edges 2. It is called diverging lens. Q15. Why a convex lens is called a converging lens and a concave lens a diverging lens? Ans. If parallel rays of light fall on a convex lens they converge at a point. If parallel rays of light fall on a concave lens they diverge as they pass through the lens. Q16. What is the nature of image formed in a concave lens? Ans. Virtual, erect & diminished. Q17. What is the nature of image formed in a convex lens? Ans. Same as in Concave mirror. Q18. What are the uses of lenses? Ans. 1.Magnifying glass – Convex lens. 2. To correct eye defects –people who can not see far off objects clearly wear Concave lens. People who cant not see nearby object clearly wear Convex lens. 3. lenses are also used in Microscope, Telescope etc. Q19. How is the rainbow formed? Ans. Rainbow is formed after rainfall when Sun Shines. When sunlight passes through suspended raindrops it is split into seven colours “VIBGYOR’. Q20. Where else you can see seven colours of sunlight? Ans. You can see Seven colours of Sunlight when it falls over Soap bubbles, oil films, Shiny surfaces of CD etc. Q 21. State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror. Ans: 1. Image is Virtual 2. It is behind the mirror 3. Image is erect (means not inverted) 4. Image is of same size as the object 5. Image is at same distance from the mirror as the object is from the mirror. Q22. Fill in the blanks a. An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called -------b. Image formed by a convex ------------- is always virtual and smaller in size. c. An image formed by a ------------- mirror is always of the same size as that of the object. d. An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a ----------- image. e. An image formed by a concave ------------ cannot be obtained on a screen