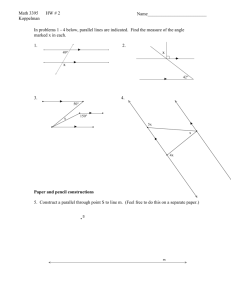
Geometry Model Curriculum - North Arlington School District
advertisement

Mathematics Curriculum: Geometry/Geometry Honors Geometry Mapping Dates Math September 4- October 24, 2014 5 Weeks 2 Weeks Instruction Assessment/ Enrichment/ Unit 1 Asmnt 1/Unit 1 October 27 – December 22 2014 5 Weeks 2 Weeks Instruction Assessment/ Enrichment/ Unit 2 Asmnt 2/Unit2 Mathematics: Geometry Standard G.CO.1 G.CO.4 G.CO.2 G.CO.3 G.CO.5 G.CO.6 G.CO.7 G.CO8 G.CO.9 G.CO.10 G.CO.11 Description Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare January 5 –Feb 27 2015 March 2 – Apr 24, 2015 Apr 27-June 19, 2015 5 Weeks Instruction 5 Weeks Instruction 5 Weeks Instruction Unit 3 2 Weeks Assessment/ Enrichment/ Asmnt 3/Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit #1: Congruence, Proof, and Construction 9/4/14-10/24/14 Student Learning Objectives Use the undefined notion of a point, line, distance along a line and distance around a circular arc to develop definitions for angles, circles, parallel lines, perpendicular lines and line segments. Apply the definitions of angles, circles, parallel lines, perpendicular lines and line segments to describe rotations, reflections, and translations. Develop and perform rigid transformations that include reflections, rotations, translations and dilations using geometric software, graph paper, tracing paper, and geometric tools and compare them to non-rigid transformations. Use rigid transformations to determine, explain and prove 2 Weeks Assessment/ Enrichment/ Asmnt 4/Unit 4 Unit 3 2 Weeks Assessment/ Enrichment/ Asmnt 5/Unit 5 Unit #1 Interdisciplinary Connections/Critical Thinking Translations: Activity: Create your own kaleidoscope http://www.zefrank.com/dtoy_vs_byokal/ Reflections: Activity Lab: Paper Folding and Reflections Activity: Reflect the given pattern in a line: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/online/reflection. swf Rotations: Guided Problem Solving: Understanding Math Problems Activity: Rotate shapes either 90 or 45 degrees: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/online/roration.s wf Activity Lab: Tracing Paper Transformations Use interactive figures to explore geometric transformations (rotations, translations, and reflections and a composition of these): transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). Given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and reflections that carry it onto itself. Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments Given a geometric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transformed figure using, e.g., graph paper, tracing paper, or geometry software. Specify a sequence of transformations that will carry a given figure onto another. Use geometric descriptions of rigid congruence of geometric figures. http://standards.nctm.org/document/eexamples/chap Create proofs of theorems 6/6.4/index.htm involving lines, angles, triangles, and parallelograms. motions to transform figures and to predict the effect of a given rigid motion on a given figure; given two figures, use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to decide if they are congruent. Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent if and only if corresponding pairs of sides and corresponding pairs of angles are congruent. Explain how the criteria for triangle congruence (ASA, SAS, and SSS) follow from the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions. Prove theorems about lines and angles. Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. Technolgy Standard Description Performance Task 8.2.12.D.1 Apply the design process. Design and create a prototype to solve a real world problem using a design process, identify constraints addressed during the creation of the prototype, identify trade-offs made, and present the solution for peer review Explain how material processing impacts the quality of engineered and fabricated products. Develop an innovative solution to a real world problem or issue in collaboration with peers and experts, and present ideas for feedback through social media or in an online community Activity: Create your own kaleidoscope http://www.zefrank.com/dtoy_vs_byokal/ 8.2.12.D.5 Assess the impact of products and systems. 8.1.12.C.1 Contribute to project teams to produce original works or solve problems. Activity: Rotate shapes either 90 or 45 degrees: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/online/roration.swf Use interactive figures to explore geometric transformations (rotations, translations, and reflections and a composition of these): http://standards.nctm.org/document/eexamples/chap6/6.4/index.htm Differentiation-GNT/ELL Standard Description Performance Task 4.1.1. Educators maintain high expectations for all students with gifts and talents as evidenced in meaningful and challenging activities Rotations: Guided Problem Solving: Understanding Math Problems 5.1.1 Educators regularly use multiple alternative approaches to accelerate learning. Reflections: Activity Lab: Paper Folding and Reflections Activity: Reflect the given pattern in a line: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/online/reflection.swf 5.1.5. Educators regularly use current technologies, including online learning options and assistive technologies to enhance access to high-level programming. Activity Lab: Tracing Paper Transformations Use interactive figures to explore geometric transformations (rotations, translations, and reflections and a composition of these): http://standards.nctm.org/document/eexamples/chap6/6.4/index.htm Careers and 21st Century Standard Description Performance Task 9.3.ST‐ET.4 Apply the elements of the design process. Activity: Create your own kaleidoscope http://www.zefrank.com/dtoy_vs_byokal/ 9.3.ST.2 Use technology to acquire, Activity: Reflect the given pattern in a line: 9.3.ST.1 manipulate, analyze and report data. http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/online/reflection.swf Apply engineering skills in a project that requires project management, process control and quality assurance. Activity: Rotate shapes either 90 or 45 degrees: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/online/roration.swf Reading / Writing Standard Description Performance Task CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.2.a Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.6 Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology's capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. Project: Produce Optical Art and Explain & Classify all Rotations, Reflections, and Translations. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.8 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate Project: Create and Design Brochure Promoting Rotations, Reflections, and Translations in Advertising. Project: 1. Identify and Classify Rotations, Reflections, and Translations in Modern Architecture information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. Assessment Geometry Benchmark 1 Exam Mathematics: Geometry Standard G.SRT.1 G.SRT.2 G.SRT.3 G.SRT.4 G.CO.10 Description Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor. a. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. b. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor. Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. Unit #2: Similarity and Proof 10/27/14-12/22/14 Student Learning Objectives Justify the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged (the dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor). Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Prove theorems about triangles. Unit #2 Interdisciplinary Connections/Critical Thinking Interactive webpage allowing students to test all similarity triangle postulates. http://www.keymath.com/x3343.xml Interactive calculator lesson using a TI 83 to experiment with the side splitter theorem http://education.ti.com/calculators/downloads/US/Ac tivities/Detail?id=12318 Multiple TI calculator lessons to explore similar geometric figures http://education.ti.com/calculators/timathnspired/US/ Activities/?t=5053&sa=5024 Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. Technolgy Standard Description Performance Task 8.2.12.D.1 Apply the design process. Design and create a prototype to solve a real world problem using a design process, identify constraints addressed during the creation of the prototype, identify tradeoffs made, and present the solution for peer review Explain how material processing impacts the quality of engineered and fabricated products. Develop an innovative solution to a real world problem or issue in collaboration with peers and experts, and present ideas for feedback through social media or in an online community Activity: Interactive calculator lesson using a TI 83 to experiment with the side splitter theorem http://education.ti.com/calculators/downloads/US/Activities/Detail?id=12318 8.2.12.D.5 Assess the impact of products and systems. 8.1.12.C.1 Contribute to project teams to produce original works or solve problems. Activity: Multiple TI calculator lessons to explore similar geometric figures http://education.ti.com/calculators/timathnspired/US/Activities/?t=5053&sa=5024 Use interactive figures to explore geometric transformations (rotations, translations, and reflections and a composition of these): http://standards.nctm.org/document/eexamples/chap6/6.4/index.htm Differentiation-GNT/ELL Standard Description Performance Task 4.1.1. Educators maintain high expectations for all students with gifts and talents as evidenced in meaningful and challenging activities Similarity: Guided Problem Solving: Understanding Math Problems 5.1.1 Educators regularly use multiple alternative approaches to accelerate learning. 5.1.5. Educators regularly use current technologies, including online learning options and assistive technologies to enhance access to high-level programming. Activity: Students will make a scale drawing of their bedroom. Students need to measure their room and use graph paper to make their drawings. Each drawing must include a scale Interactive webpage allowing students to test all similarity triangle postulates. http://www.keymath.com/x3343.xml Careers and 21st Century Standard Description Performance Task 9.3.ST‐ET.4 Apply the elements of the design process. Activity: Students fold a sheet of paper in half and then measure and reason to decide whether the folded sheet is similar to the original sheet. 9.3.ST.2 Use technology to acquire, manipulate, analyze and report data. Multiple TI calculator lessons to explore similar geometric figures http://education.ti.com/calculators/timathnspired/US/Activities/?t=5053&sa=5024 9.3.ST.1 Apply engineering skills in a project that requires project management, process control and quality assurance. Project: Students draw three parallel lines cut by two transversals. Students use a ruler to measure the segments intercepted on the transversals and observe they are proportional, and not congruent Reading / Writing Standard Description Performance Task CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.2.a Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. Project: Students connect the midpoints of two sides of a large triangle, measure all angles and sides, and then use AA, SAS, and SSS Similarity to explain why the triangles are similar. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.6 Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology's capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. Project: Create and Design Brochure introducing the five ways to prove two quadrilaterals congruent: four theorems and the definition of a parallelogram. Then discuss why both are such a critical term in some theorems. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.8 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate Project: Students think that because the sides of a rhombus are congruent its diagonals must also be congruent. Students draw several counterexamples and explain their conclusions. information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. Assessment Geometry Benchmark Exam 2 Mathematics: Geometry Standard G.GPE.6 G.SRT.4 G.SRT.5 G.SRT.6 G.SRT.7 G.SRT.8 Description Find the point on a directed line segment between two given points that partitions the segment in a given ratio. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. Explain and use the relationship between Unit #3: Trigonometry 1/5/15-2/27/15 Student Learning Objectives Find the point on a directed line segment between two given points that partitions the segment in a given ratio. Prove theorems about triangles. Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Derive the definitions for trigonometric ratios using similarity of right triangles. Explain and use the relationship between the sine and cosine of complementary angles. Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. Unit # 3 Interdisciplinary Connections/Critical Thinking Real-World Applications: Website introduces geometric shapes and their properties using everyday objects. Use classroom objects and household items to discover 3 dimensional shapes and finding volume for those shapes http://www.learner.org/interactives/geometry/index. html Science/Chemistry/Physics Applications: Density based labs that can be constructed in the classroom to model situations http://www.edinformatics.com/math_science/mass_v olume_density.htm the sine and cosine of complementary angles. Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. Technolgy Standard Description Performance Task 8.2.12.D.1 Apply the design process. Design and create a prototype to solve a real world problem using a design process, identify constraints addressed during the creation of the prototype, identify trade-offs made, and present the solution for peer review Real-World Applications: Website introduces geometric shapes and their properties using everyday objects. Use classroom objects and household items to discover 3 dimensional shapes and finding volume for those shapes http://www.learner.org/interactives/geometry/index.html 8.2.12.D.5 Assess the impact of products and systems. Explain how material processing impacts the quality of engineered and fabricated products. 8.1.12.C.1 Contribute to project teams to produce original works or solve problems. Activity: Have students explain how to find tan 30° and tan 60° without using a calculator, and then confirm the values with a calculator. Develop an innovative solution to a real Activity: After students learn and apply Theorem 8-5, world problem or issue in collaboration have them write a formula for the area of an isosceles with peers and experts, and present right triangle whose hypotenuse has length s. ideas for feedback through social media or in an online community Differentiation-GNT/ELL Standard Description Performance Task 4.1.1. Educators maintain high expectations for all students with gifts and talents as evidenced in meaningful and challenging activities Prove Theorems About Theorems: Guided Problem Solving: Understanding Math Problems 5.1.1 Educators regularly use multiple alternative approaches to accelerate learning. Activity: Have students draw and measure right triangles to make a table of sine and cosine values for the angles in the set (10°, 20°, ... , 80°). 5.1.5. Educators regularly use current technologies, including online learning options and assistive technologies to enhance access to high-level programming. Activity: Multiple TI calculator lessons to explore similar geometric figures http://education.ti.com/calculators/timathnspired/US/Activities/?t=5053&sa=5024 Careers and 21st Century Standard Description Performance Task 9.3.ST‐ET.4 Apply the elements of the design process. Activity: Website introduces geometric shapes and their properties using everyday objects. http://www.learner.org/interactives/geometry/index.html 9.3.ST.2 Use technology to acquire, manipulate, analyze and report data. Activity: Interactive webpage allowing students to test all similarity triangle postulates. http://www.keymath.com/x3343.xml 9.3.ST.1 Apply engineering skills in a project that requires project management, process control and quality assurance. Science/Chemistry/Physics Applications: Density based labs that can be constructed in the classroom to model situations http://www.edinformatics.com/math_science/mass_volume_density.htm Reading / Writing Standard Description Performance Task CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.2.a Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. Project: Students will apply your knowledge of trigonometry to shadows in order to calculate the angle of elevation to the sun at different times of day. Graphic organizing report will present the students knowledge of trigonometric ratios. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.6 Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology's capacity to link to other information and to display information Project: Students develop a story involving the missing angle or missing side of a right triangle. They will carefully draw, use a photograph, a picture clipped from a magazine or downloaded from the Internet, illustrating the problem in your story. Gather relevant information from multiple Project: Create a powerpoint presentation and an authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess exercise on the Pythagorean theorem. the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. flexibly and dynamically. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.8 Assessment Geometry Benchmark Exam 3 Mathematics: Geometry Standard G.C.2 G.GPE.1 G.GPE.5 G.CO.11 G.GPE.4 G.GPE.7 Description Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. Derive the equation of a circle of given center and radius using the Pythagorean Theorem; complete the square to find the center and radius of a circle given by an equation. Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a Unit # 4: Circles and Expressing Geometric Properties through Equations 3/2/15-4/24/15 Student Learning Objectives Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. Derive the equation of a circle of given center and radius using the Pythagorean Theorem; complete the square to find the center and radius of a circle given by an equation. Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems (e.g. find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point.) Construct formal proofs using theorems, postulates, and definitions involving parallelograms. * Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. Use coordinates to compute perimeters of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g., Unit # 4 Interdisciplinary Connections/Critical Thinking Data Analysis spiraled with coordinate proofs: Proofs Using Coordinate Geometry: Example: Planning a Coordinate Geometry Proof http://regentsprep.org/Regents/math/geometry/GCG 4/CoordinatepRACTICE.htm Activity Lab: Data Analysis: Interpreting Data Technology Application: Geometer’s Sketchpad: Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to create different size circles. Then, they will measure the degrees of all circles, and set up ratios between. After, they will be able to take the circumference of one and multiply by the scale factor to get the other circle. Students will work with the Geometer’s Sketchpad to construct circles. They will then draw in radii, angles and chords and measure angles formed between to show the relationship between each. Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to draw triangles and measure out midpoints and angle bisectors in order to create inscribed and circumscribed triangles. Students will use Geometer’s Sketchpad to create tangent lines to given circles. Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to create circles. They will then create and shade a sector of a given circle, then draw in to create a triangle within the sector. parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and use them to solve geometric problems. (E.g. find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point. Use coordinates to compute perimeters using the distance formula. Students will then be able to use formulas for area to show that measured area is the same as ones they derived themselves. of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g., using the distance formula. Technolgy Standard Description Performance Task 8.2.12.D.1 Apply the design process. Design and create a prototype to solve a real world problem using a design process, identify constraints addressed during the creation of the prototype, identify tradeoffs made, and present the solution for peer review Explain how material processing impacts the quality of engineered and fabricated products. Develop an innovative solution to a real world problem or issue in collaboration with peers and experts, and present ideas for feedback through social media or in an online community Activity: Student’s will use graph paper to construct circles with given radii. Then, students will be able to draw in right triangles using radii, and show how to find lengths using Pythagorean Theorem. Students will then use this to find the formula for the circle itself. 8.2.12.D.5 Assess the impact of products and systems. 8.1.12.C.1 Contribute to project teams to produce original works or solve problems. Activity: Students will work with the Geometer’s Sketchpad to construct circles. They will then draw in radii, angles and chords and measure angles formed between to show the relationship between each. Data Analysis spiraled with coordinate proofs: Proofs Using Coordinate Geometry: Example: Planning a Coordinate Geometry : Proof http://regentsprep.org/Regents/math/geometry/GCG4/CoordinatepRACTICE.htm Differentiation-GNT/ELL Standard Description Performance Task 4.1.1. Educators maintain high expectations for all students with gifts and talents as evidenced in meaningful and challenging activities Activity: Students wil calculate which is greater, the height or the circumference of a can of three tennis balls. 5.1.1 Educators regularly use multiple alternative approaches to accelerate learning. Activity: Students will calculate the area of chosen circular logos and compare results 5.1.5. Educators regularly use current technologies, including online learning options and assistive technologies to enhance access to high-level programming. Activity: Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to draw triangles and measure out midpoints and angle bisectors in order to create inscribed and circumscribed triangles. Standard Description Performance Task 9.3.ST‐ET.4 Apply the elements of the design process. Activity: Students will use Geometer’s Sketchpad to create tangent lines to given circles. 9.3.ST.2 Use technology to acquire, manipulate, Activity: Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to create circles. They will then Careers and 21st Century analyze and report data. create and shade a sector of a given circle, then draw in to create a triangle within the sector. Students will then be able to use formulas for area to show that measured area is the same as ones they derived themselves. Apply engineering skills in a project that requires project management, process control andquality assurance. Activity: Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to create different size circles. Then, they will measure the degrees of all circles, and set up ratios between. After, they will be able to take the circumference of one and multiply by the scale factor to get the other circle. Standard Description Performance Task CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.2.a Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. Project: Create a Geometry Book that explores the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines including example and illustrations. 9.3.ST.1 Reading / Writing CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.6 Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology's capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. Project: Produce a Quilt Design and Explain & Classify all Quadrilaterals that are utilized in the design process. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.8 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. Project: Create and Design Brochure that presents all the concepts and formulas of polygonal areas. Assessment Geometry Benchmark Exam 4 Mathematics: Geometry Standard G. GMD.3 G.MG.1 G.MG.2 G.MG.3 Description Give an informal argument for the formulas for the circumference of a circle, area of a circle, volume of a cylinder, pyramid, and cone. Use dissection arguments, Cavalieri’s principle, and informal limit arguments. Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects Apply concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations Apply geometric methods to solve design problems Unit # 5: Extending to Three Dimensions 4/27/15-6/19/15 Student Learning Objectives Solve problems using volume formulas for cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres. Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder). Use density concepts in modeling situations based on area and volume. (e.g., persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot). Solve design problems using geometric methods. (e.g., designing an object or structure to satisfy physical constraints or minimize cost; working with typographic grid systems based on ratios). Unit # 5 Interdisciplinary Connections/Critical Thinking Real-World Applications: • Website introduces geometric shapes and their properties using everyday objects. Use classroom objects and household items to discover 3 dimensional shapes and finding volume for those shapes http://www.learner.org/interactives/geometry/index. html Technolgy Standard Description Performance Task 8.2.12.D.1 Apply the design process. Design and create a prototype to solve a real world problem using a design process, identify constraints addressed during the creation of the prototype, identify trade-offs made, and present the solution for peer review Explain how material processing impacts the quality of engineered and fabricated products. Activity: Students are introduced to geometric shapes and their properties using everyday objects by utilizing the following website: http://www.learner.org/interactives/geometry/index.html Develop an innovative solution to a real world problem or issue in collaboration with peers and experts, and present ideas for feedback through social media or in an online community Activity: Students discover Pi and its relationship with circumference. Students use string and scissors to dicover the relationship of circles and Pi. http://www.exploratorium.edu/pi/pi_activities/index.html 8.2.12.D.5 Assess the impact of products and systems. 8.1.12.C.1 Contribute to project teams to produce original works or solve problems. Activity: Students will construct paper models and worksheets to create nets for all 3 dimensional shapes using the following web tool: http://www.korthalsaltes.com/ Differentiation-GNT/ELL Standard Description Performance Task 4.1.1. Educators maintain high expectations for all students with gifts and talents as evidenced in meaningful and challenging activities Area Exploration: To understand area and how to derive a formula. Interactive lesson that dissects shapes to create formulas: http://www.learner.org/courses/learningmath/measurement/session7/part_b/index.html 5.1.1 Educators regularly use Activity: Nets made virtually on the web that will construct themselves. multiple alternative http://www.mathsnet.net/geometry/solid/nets.html approaches to accelerate learning. 5.1.5. Educators regularly use Activity: Density based labs that can be constructed in the classroom to model current technologies, situations. including online http://www.edinformatics.com/math_science/mass_volume_density.htm learning options and assistive technologies to enhance access to high-level programming. Careers and 21st Century Standard Description Performance Task 9.3.ST‐ET.4 Apply the elements of the design process. Activity: Students will use classroom objects and household items to discover 3 dimensional shapes and finding volume for those shapes 9.3.ST.2 Use technology to acquire, manipulate, analyze and report data. Activity: Following website allows student to construct 3-D shapes and calculate and record volumes: http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/SurfaceAreaAndVolume/ 9.3.ST.1 Apply engineering skills in a project that requires project management, process control Real-World Applications: Website introduces geometric shapes and their properties using everyday objects. Use classroom objects and household items to and quality assurance. discover 3 dimensional shapes and finding volume for those shapes http://www.learner.org/interactives/geometry/index.html Reading / Writing Standard Description Performance Task CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.2.a Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. Project: Students will unfold an empty cereal box. Students will use this real life application to develop the concept of nets. Students will measure each attribute: length, width, and height. Students record all measurements in a spreadsheet. Students utilize the formulas to calculate the surface area of a rectangular prism. Students will record all results in spreadsheet and present their results. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.6 Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology's capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. Project: Students will research the different methods of packaging design and create a business presentation that promotes their own packaging design. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.WHST.9-10.8 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering Project: Create and Design an Informational Brochure highlighting all the aspects of three –dimensional solids. the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. Assessment Geometry Final Exam Resources by Standard for Geometry North Arlington Public Schools North Arlington Public Schools Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Unit Overview: In previous grades, students were asked to draw triangles based on given measurements. They also have prior experience with rigid motions: translations, reflections, and rotations and have used these to develop notions about what it means for two objects to be congruent. In this unit, students establish triangle congruence criteria, based on analyses of rigid motions and formal constructions. They use triangle congruence as a familiar foundation for the development of formal proof. Students prove theorems— using a variety of formats—and solve problems about triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They apply reasoning to complete geometric constructions and explain why they work. Standards/ CPI’s G.CO.1 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Points, Lines, and Planes: Activity Lab: How Many Lines Can You Draw To Create A Constellation Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook : 1-3 p.16 Segments, Rays, Parallel Lines and Planes: Example: Naming Segments and Rays Example: Indentifying Parallel and Skew Segments Example: Indentifying Parallel Planes Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Textbook: 1-4 p.23 http://www.homescho olmath.net/teaching/g/ angles.php http://www.homescho olmath.net/teaching/g/ parallel_and_perpendi cular.php Textbook: 1-6 p.36 http://www.homescho olmath.net/teaching/g/ measure_angles.php Measuring Angles: Activity Lab: Using a Protractor to Measure and Classify Angles http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activ ities/Angles/ Perimeter, Circumference, and Area: Graphing Calculator Activity: Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Unit Test Participation Class Discussion Textbook: 1-9 p.61 Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Comparing Perimeters and Areas G.CO.2 G.CO.3 G.CO.4 Represent transformations in the plane using, e.g., transparencies and geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). Given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and reflections that carry it onto itself. Translations: Activity: Create your own kaleidoscope http://www.zefrank.com/dtoy_vs_byokal / Reflections: Activity Lab: Paper Folding and Reflections Activity: Reflect the given pattern in a line: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/onlin e/reflection.swf Rotations: Guided Problem Solving: Understanding Math Problems Activity: Rotate shapes either 90 or 45 degrees: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/onlin e/roration.swf 34 Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Study Guide Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Unit Test Textbook: 9-1 p. 470 http://www.mathsnet.n et/transform/index.htm l Textbook: 9-2 p.478 Textbook: p.477 Textbook: 9-3 p.483 Textbook: p.489 http://standards.nctm.o rg/document/eexample s/chap6/6.4/index.htm Textbook: 9-4 p.492 http://www.innovation Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Standards/ CPI’s G.CO.5 G.CO.6 G.CO.7 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. Given a geometric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transformed figure using, e.g., graph paper, tracing paper, or geometry software. Specify a sequence of transformations that will carry a given figure onto another. Use geometric descriptions of rigid motions to transform figures and to predict the effect of a given rigid motion on a given figure; given two figures, use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to decide if they are congruent. Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Symmetry: Example: Identifying Lines Of Symmetry Example; Identifying Rotational Symmetry Symmetry Activity: http://www.haelmedia.com/OnlineActivit ies_txh/mc_txh4_001.html Lesson Activity: Advanced Transformations http://www.misterteacher.com/alphabetg eometry/reflection.html Lesson Activity: Geometric Solids http://illuminations.nctm.org/ActivityDet ail.aspx?ID=70 Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. slearning.co.uk/subject s/maths/activities/year 3/symmetry/shape_ga me.asp Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Check Point Quiz http://www.mathsisfun .com/geometry/symme try.html Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook: p.490 Geometer’s Sketchpad Activity Lab: Tracing Paper Transformations Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Check Point Quiz Use the definition of congruence in 35 http://www.girlsgotech Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Standards/ CPI’s G.CO.8 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent if and only if corresponding pairs of sides and corresponding pairs of angles are congruent. Explain how the criteria for triangle congruence (ASA, SAS, and SSS) follow from the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions. G.CO.9 G.CO.10 Prove theorems about lines and angles. Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. .org/world_around_us. html Use interactive figures to explore geometric transformations (rotations, translations, and reflections and a composition of these): http://standards.nctm.org/document/eexa mples/chap6/6.4/index.htm Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook: p.198 http://www.math.com/ school/subject3/lesson s/S3U3L1GL.html Participation Class Discussion Congruent Figures: Study Guide Activity: Similarity and Congruence Participation http://www.absorblearning.com/mathema Class Discussion tics/demo/units/KCA035.html Study Guide Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Triangle Congruence by SSS and SAS: Activity: Hands On: Building Congruent Triangles 36 Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Textbook: p.205 Textbook: p.204 Textbook: p.213 Textbook: p.220 Textbook: p.36 http://www.shodor.org /interactivate/activities /Angles/ Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Triangle Congruence by ASA and AAS: Activity: Technology: Exploring AAA and SSA Measuring Angles: Activity: Measuring Angles http://www.homeschoolmath.net/teachin g/g/measure_angles.php Properties of Parallel Lines: Activity: Technology: Parallel Lines and Related Angles Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Study Guide Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Check Point Quiz Unit Test G.CO.11 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Guided Problem Solving: Understanding Proof Problems Participation Class Discussion 37 text, etc. Textbook: p.124 http://www.shodor.org /interactivate/activities /angles/index.html Textbook: p.134 Textbook: p.141 Textbook: p.145 Proving Lines Parallel: Activity: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines http://www.homeschoolmath.net/teachin g/g/parallel_and_perpendicular.php Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. Resources Books, articles, Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Study Guide Parallel Lines and the Triangle AngleSum Theorem: Activity Lab: Hands On: Angle Dynamics Activity Lab: Exploring Spherial Geometry Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles: Activity: Equilateral and Isosceles Triangles http://www.homeschoolmath.net/teachin g/g/equilateral_isosceles.php Proportions in Triangles: Activity Lab: Technology: Exploring Proportions in Triangles 38 Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook: p.147 Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Check Point Quiz Textbook: p.228 http://library.thinkques t.org/20991/geo/ietri.h tml Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Unit Test Textbook: p.398 Textbook: p.397 Textbook: p.146 Textbook: p.154 Textbook: p.272 http://www.google.co m/url?sa=t&source=w eb&cd=4&ved=0CC0 QFjAD&url=http%3A %2F%2Fwww.online mathlearning.com%2F side-splitter- Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. G.CO.12 Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Concurrent Lines, Medians, and Altitudes: Activity Lab: Technology: Special Segments in Triangles Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Unit Test Resources Books, articles, text, etc. theorem.html&ei=DD zuTZnPFZL4sAO44N GeAw&usg=AFQjCN HPCCv2vX39xFKl32 Lm8UehQCkA8Q Textbook: p.312 Textbook: p.321 Textbook: p.320 Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods (compass and Properties of Parallelograms: Activity: Dynamic Rectangle and Parallelogram http://standards.nctm.org/document/eexa mples/chap5/5.3/index.htm Proving That a Quadrilateral is a 39 Textbook: p.329 Textbook: p.328 http://www.mathsisfun .com/geometry/quadril aterals-interactive.html Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Standards/ CPI’s G.CO.13 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisecting an angle; constructing perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; and constructing a line parallel to a given line through a point not on the line. Construct an equilateral triangle, a square, and a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle. Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Parallelogram: Activity: Hands-On: Geo-Models Special Parallelograms: Activity: Technology: Diagonals of Parallelograms Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Check Point Quiz Textbook: p.44 http://www.mathsnet.n et/campus/constructio n/index.html http://www.mathsisfun .com/geometry/constru ctions.html 40 Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Congruence, Proof, and Constructions Essential Questions: How do we use Congruence, Proof, and Constructions? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Basic Constructions: Activity: Hands-On: Compass Designs Activity: Technology: Exploring Constructions Activity: Simulations of Ruler and Compass Constructions http://wims.unice.fr/wims/wims.cgi?sessi on=1V77FB9E9B.5&+lang=en&+cmd=i ntro&+module=tool%2Fgeometry%2Fru lecomp.en&+special_parm=1 Activity: Construct an Inscribed Equilateral Triangle: http://www.nvcc.edu/home/tstreilein/con structions/Inscribed/inscribe2.htm Activity: Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon: http://www.nvcc.edu/home/tstreilein/con structions/Inscribed/inscribe4.htm Activity: Construct an Inscribed Square http://www.nvcc.edu/home/tstreilein/con structions/Inscribed/inscribe3.htm 41 Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Geometric Constructions Illustrated with Interactive Java Applets: http://www.nvcc.edu/h ome/tstreilein/construc tions/contents.htm Geometer’s Sketchpad Content Area: Geometry Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: What are the relationships between Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry? Unit Overview: Students apply their earlier experience with dilations and proportional reasoning to build a formal understanding of similarity. They identify criteria for similarity of triangles, use similarity to solve problems, and apply similarity in right triangles to understand right triangle trigonometry, with particular attention to special right triangles and the Pythagorean theorem. Students develop the Laws of Sines and Cosines in order to find missing measures of general (not necessarily right) triangles. They are able to distinguish whether three given measures (angles or sides) define 0, 1, 2, or infinitely many triangles. Standards/ CPI’s SRT.1 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor. Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement http://www.mathsnet.net/transformati ons/index.html Interactive website that allows the basic four transformations Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Teacher Based test Participation Cooperative learning a. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. Actively working on computer models Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Textbook 9-5 Dilations Pg. 498-503 http://www.brightsto rm.com/math/geomet ry/transformations/di lations lesson in dilation and scale factors b. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio c. given by the scale factor. G.SRT.2 Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity http://www.absorblearning.com/mathe matics/demo/units/KCA035.html#Sum mary Interactive lesson with follow up Actively use similar shapes to Textbook 7-2Similar Polygons Pg. 373-379 Content Area: Geometry Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: What are the relationships between Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry? Standards/ CPI’s G.SRT.3 G.SRT.4 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement questions. Evidence of Learning text, etc. create transformations 7-3Proving Triangles Similar Pg. 382-388 http://www.absorblea rning.com/mathemati cs/demo/units/KCA0 24.html Cooperative learning in groups http://www.keymath.com/x3343.xml interactive webpage allowing students Participation to test all similarity triangle postulates. Teacher based test Sketch pad assessments http://education.ti.com/calculators/do wnloads/US/Activities/Detail?id=12318 Active group work Interactive calculator lesson using a TI 83 to experiment with the side splitter Scientific calculator theorem activities 43 Resources Books, articles, Formative and Summative measures Textbook 7-3 Proving Triangles Similar Pg. 382-389 http://www.analyzem ath.com/Geometry/si milar_triangles.html Lesson on similar triangles Textbook 7-4 Similarity in Right Triangles Pg. 391-397 http://www.mathwar ehouse.com/geometry Content Area: Geometry Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: What are the relationships between Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry? Standards/ CPI’s G.SRT.5 G.SRT.6 G.SRT.7 G.SRT.8 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. http://education.ti.com/calculators/tim athnspired/US/Activities/?t=5053&sa= 5024 Multiple TI calculator lessons to explore similar geometric figures Scientific Calculator activities Explain and use the relationship between the sine and cosine of complementary angles. http://www.purplemath.com/modules/ basirati.htm Explores the ratios of trigonometry with problems to solve. Teacher based test Use geometric shapes, their text, etc. /similar/triangles/side -splitter-theorem.php Web page illustrating the side splitter theorem Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems.★ Resources Books, articles, Sketchpad activities http://www.cut-theknot.org/pythagoras/cosine2.shtml Proofs and mathematical problems demonstrating the relationship between sine and cosine 44 Participation Textbook 7-2 Similar Polygons Pg. 373-379 Textbook 7-4 Similarity in Right Triangles Pg. 391 Textbook 8-4 The sine and cosine Ratio Pg. 439-443 Content Area: Geometry Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: What are the relationships between Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder).* G.MG.1 Apply concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations (e.g., persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot).* G.MG.2 Apply geometric methods to solve design problems (e.g., designing an object or structure to satisfy physical constraints or minimize cost; working with typographic grid systems based on ratios).* Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Cooperative learning http://www.themathpage.com/aTrig/tri gonometry.htm Lessons and activities covering right triangles and Actively working trigonometry ratios on computer models http://www.learner.org/interactives/ge ometry/index.html Website introduces geometric shapes and their properties using everyday objects. Use classroom objects and household items to discover 3 dimensional shapes and finding volume for those shapes http://www.edinformatics.com/math_s cience/mass_volume_density.htm Density based labs that can be constructed in the classroom to model situations 45 Textbook Chapter 8 Pg. 417-465 Textbook Chapter 11Surface area and Volume Pg. 598-656 Participation Cooperative learning in groups Exploring geometric shapes outside the classrooom Participation Textbook Chapter 11 Surface area and Volme Pg. 597-659 Content Area: Geometry Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: What are the relationships between Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. G.MG.3 Cooperative learning in groups Derive the formula A = 1/2 ab sin(C) for the area of a triangle by drawing an auxiliary line from a vertex perpendicular to the opposite side. http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks2bitesi ze/maths/shape_space/ apply geometric shapes to solve puzzles Prove the Laws of Sines and Cosines and use them to solve problems. Exploring geometric shapes outside the classrooom Textbook 11-7 Areas and Volumes of Similar Solids Pg. 646-651 Cooperative learning in groups http://www.ecalc.com /mathhelp/worksheet/geom etry Reference sheet G.SRT.9 (+) Participation G.SRT.10 (+) Understand and apply the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines to find unknown measurements in right and non-right triangles (e.g., surveying problems, resultant forces). http://jwilson.coe.uga.edu/EMAT6680/ Simmons/6700/Unit%20Lesson1W.pdf file explaining how to use geometer sketchpad to use and derive the Teacher Based test formula A=1/2 ab sin © Participation 46 Textbook 8-4 The sine and cosine Ratio Pg. 439-443 Content Area: Geometry Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: What are the relationships between Similarity, Proof, and Trigonometry? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Cooperative learning G.SRT.11 (+) http://www.brightstorm.com/math/trig onometry/basictrigonometry/trigonometric-ratios-sine http://www.brightstorm.com/math/trig Actively working onometry/basictrigonometry/trigonometric-ratios-sine on computer models Math videos text, etc. Textbook 8-4 The sine and cosine Ratio Pg. 439-443 Textbook 8-4 The sine and cosine Ratio Pg. 439-443 http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonD etail.aspx?ID=L704 Lesson teaching trigonometry in non right triangles Teacher based test Geometer sketchpad activities 47 Resources Books, articles, Content Area: Geometry Extending to Three Dimensions Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: Extending to Three Dimensions Unit Overview: Students’ experience with two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects is extended to include informal explanations of circumference, area and volume formulas. Additionally, students apply their knowledge of two-dimensional shapes to consider the shapes of cross-sections and the result of rotating a two-dimensional object about a line. Standards/ CPI’s G.GMD.1 G.GMD.3 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Give an informal argument for the formulas for the circumference of a circle, area of a circle, volume of a cylinder, pyramid, and cone. Use dissection arguments, Cavalieri’s principle, and informal limit arguments. Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures http://www.exploratorium.edu/pi/pi_a ctivities/index.html To discover Pi and its relationship with circumference. Students use string and scissors to dicover the relationship of circles and Pi. Participation http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/ac tivities/SurfaceAreaAndVolume/ Allows student to construct 3-D shapes and calculate volumes Actively constructing models Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Text book 10-6 Circles and Arcs Cooperative Pg.566-571 learning 11-3 Surface Areas of pyramids and cones Actively working Pg. 617-623 on computer http://www.mathgoo http://www.learner.org/courses/learnin models dies.com/lessons/vol2/ gmath/measurement/session7/part_b/i circumference.html Teacher made tests lesson on ndex.html To understand area and how to derive a formula. Interative circumference lesson that disects shapes to create formulas Use volume formulas for cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres to solve problems.★ Text book Chapters 10 Area Chapter 11Surface Area and Volume Pages 539-656 Content Area: Geometry Extending to Three Dimensions Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: Extending to Three Dimensions Standards/ CPI’s G.GMD.4 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Identify the shapes of twodimensional cross-sections of threedimensional objects, and identify three-dimensional objects generated by rotations of two-dimensional objects. Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder).* Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement http://mathforum.org/alejandre/mathf air/pyramid2.html Constructing pyramids to find volume and surface area. Use circular and square blocks to create volume formulas for three dimensional figures. http://www.mathsnet.net/geometry/soli d/nets.html Nets made virtually on the web that will construct themselves. http://www.korthalsaltes.com/ Paper models and worksheets to create nets for all 3 dimensional shapes Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Cooperative learning in groups Finding volume for everyday materials Constructions Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Handouts using paper cutouts http://www.brightsto rm.com/math/geomet ry/volume/volume-ofprisms Textbook 11-1 Space Figures and cross Sections Pg. 598-603 Research constructions of different polyhedrons G.MG.1 http://www.learner.org/interactives/ge ometry/index.html Website introduces geometric shapes and their properties using everyday objects. 49 Participation Cooperative learning in groups Textbook Chapter 11Surface area and Volume Pg. 598-656 Content Area: Geometry Extending to Three Dimensions Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Essential Questions: Extending to Three Dimensions Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Use classroom objects and household items to discover 3 dimensional shapes and finding volume for those shapes 50 Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Exploring geometric shapes outside the classrooom Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Content Area: Geometry Coordinates Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Connecting Algebra and Geometry through Essential Questions: How do we Connect Algebra and Geometry through Coordinates? Unit Overview: Building on their work with the Pythagorean theorem in 8th grade to find distances, students use a rectangular coordinate system to verify geometric relationships, including properties of special triangles and quadrilaterals and slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines. Students continue their study of quadratics by connecting the geometric and algebraic definitions of the parabola. Standards/ CPI’s G.GPE.4 G.GPE.5 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). Prove the slope criteria for parallel and perpendicular lines and uses them to solve geometric problems (e.g., find the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line that passes through a given point). Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Placing Figures in the Coordinate Plane: Example:Real-World Connection TShirt Design Example:Naming Coordinates Proofs Using Coordinate Geometry: Example: Planning a Coordinate Geometry Proof http://regentsprep.org/Regents/math/geo metry/GCG4/CoordinatepRACTICE.htm Activity Lab: Data Analysis: Interpreting Data Lines in the Coordinate Plane: Example: Graphing Lines In SlopeIntercept Form http://www.khanacademy.org/video/grap Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook: 6-6 p.343 Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook: 6-7 p.348 http://www.mathwareh ouse.com/coordinategeometry/ http://regentsprep.org/r egents/math/geometry/ GCG6/LCir.htm Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook: 3-6 p.166 http://www.math.com/ school/subject2/lesson s/S2U4L2GL.html#sm 1 http://www.algebra- Content Area: Geometry Coordinates Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Connecting Algebra and Geometry through Essential Questions: How do we Connect Algebra and Geometry through Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Find the point on a directed line segment between two given points that partitions the segment in a given ratio. G.GPE.6 Use coordinates to compute perimeters of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g., using Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement hing-a-line-in-slope-interceptform?playlist=Algebra+I+Worked+Exam ples Example: Using Point-Slope Form http://www.phschool.com/atschool/acade my123/english/academy123_content/wlbook-demo/ph-213s.html Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines: Example: Checking for Parallel Lines Example: Writing Equations of Parallel Lines http://www.phschool.com/atschool/acade my123/english/academy123_content/wlbook-demo/ph-219s.html Example: Checking for Perpendicular Lines Example: Writing Equations for Perpendicular Lines http://www.phschool.com/atschool/acade my123/english/academy123_content/wlbook-demo/ph-221s.html 52 Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. class.com/slopeintercept-form.html Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Unit Test Textbook: 3-7 p.174 http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=u3zvkzkQW4 http://www.wtamu.edu /academic/anns/mps/m ath/mathlab/col_algebr a/col_alg_tut28_parpe n.htm Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook: 1-8 p.54 Algebra Lab: http://www.algebralab. org/lessons/lesson.asp Content Area: Geometry Coordinates Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Connecting Algebra and Geometry through Essential Questions: How do we Connect Algebra and Geometry through Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures the distance formula.★ G.GPE.7 The Coordinate Plane: Finding the Midpoint of a Segment: Example: Finding the Midpoint Example Finding an Endpoint http://www.purplemath.com/modules/mi dpoint.htm http://cs.selu.edu/~rbyrd/math/midpoint/ Derive the equation of a parabola given a focus and directrix. G.GPE.2 The Coordinate Plane: Finding Distance on the Coordinate Plane: Example: Finding Distance http://www.purplemath.com/modules/dis tform.htm http://www.mathwarehouse.com/algebra/ distance_formula/index.php Perimeter, and Area: Example: Finding Perimeter in the Coordinate Plane Activity Lab: Technology: Comparing Perimeters and Areas 53 Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Unit Test Resources Books, articles, text, etc. x?file=geometry_coor dmidpoint.xml http://regentsprep.org/r egents/math/geometry/ GCG2/Lmidpoint.htm Textbook: 1-8 p.53 http://www.teachersch oice.com.au/maths_lib rary/analytical%20geo metry/alg_15.htm Textbook: 1-9 p.61 http://hotmath.com/hel p/gt/genericalg1/sectio n_8_5.html Check Point Quiz Participation Class Discussion Study Guide Textbook: p.69 Graphing Calculator http://colalg.math.csus b.edu/~devel/precalcd emo/conics/src/parabol a.html http://www.brightstor m.com/math/algebra- Content Area: Geometry Coordinates Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Connecting Algebra and Geometry through Essential Questions: How do we Connect Algebra and Geometry through Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Parabolas: Finding the Equation from Information http://www.purplemath.com/modules/par abola3.htm http://www.physicsforums.com/showthre ad.php?t=69327 http://www.valleyview.k12.oh.us/vvhs/d ept/math/agparabhelp.html 54 Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. 2/quadratic-equationsand-inequalities/focusand-directrix-of-aparabola/ Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Unit Overview: In this unit, students prove basic theorems about circles, with particular attention to perpendicularity and inscribed angles, in order to see symmetry in circles and as an application of triangle congruence criteria. They study relationships among segments on chords, secants, and tangents as an application of similarity. In the Cartesian coordinate system, students use the distance formula to write the equation of a circle when given the radius and the coordinates of its center. Given an equation of a circle, they draw the graph in the coordinate plane, and apply techniques for solving quadratic equations to determine intersections between lines and circles or parabolas and between two circles. Standards/ CPI’s G.C.1 G.C.2 Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Prove that all circles are similar. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. Evidence of Learning Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Activity: Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to create different size circles. Then, they will measure the degrees of all circles, and set up ratios between. After, they will be able to take the circumference of one and multiply by the scale factor to get the other circle. Activity: Students will work with the Geometer’s Sketchpad to construct circles. They will then draw in radii, angles and chords and measure angles formed between to show the relationship between each. G.C.3 Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Formative and Summative measures Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Geometer’s Sketchpad http://www.cpm.org/p dfs/state_supplements/ Similar_Circles.pdf Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Geometer’s Sketchpad http://mstudley.com/ geosketch/geosketcha ndcirclespt2.pdf http://archives.math. utk.edu/ICTCM/VO L16/C020/paper.html Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Geometer’s Sketchpad http://www.nvcc.edu/ home/tstreilein/const ructions/Inscribed/in scribe2.htm Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle. experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Activity: Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to draw triangles and measure out midpoints and angle bisectors in order to create inscribed and circumscribed triangles. G.C.4 (+) Derive the equation of a circle of given center and radius using the Pythagorean Theorem; complete the square to find the center and radius of a circle given by an equation. [Type text] Activity: Students will use Geometer’s Sketchpad to create tangent lines to given circles. text, etc. Quiz on material presented. Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Geometer’s Sketchpad http://mstudley.com/ geosketch/geosketcha ndcirclespt2.pdf Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Geometer’s Sketchpad http://jwilson.coe.uga .edu/EMAT6680Fa08 /Wisdom/EMAT6690 /Circles%20And%20 Spheres/Circles%20a nd%20SpheresUnit.htm Student response in class. Questions from textbook. Quiz on material 12.5 – Circles in the Coordinate plane, pg. 695. Worksheets Activity: Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to create circles. They will then create and shade a sector of a given circle, then draw in to create a triangle within the sector. Students will then be able to use formulas for area to Resources Books, articles, Formative and Summative measures Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. G.C.5 Evidence of Learning Lessons and Activities The learning Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Evidence of Learning Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Formative and Summative measures presented. show that measured area is the same as ones they derived themselves. G.GPE.1 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). G.GPE.1 Activity: Student’s will use graph paper to construct circles with given radii. Then, students will be able to draw in right triangles using radii, and show how to find lengths using Pythagorean Theorem. Students will then use this to find the formula for the circle itself. Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder).* G.MG.1 [Type text] Activity: Students will use the Geometer’s Sketchpad to create figures with given coordinates. They will then use the distance formula and slopintercept form of a line to prove lines are perpendicular, thus being able to define the given shape algebraically. Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Geometer’s Sketchpad http://go.hrw.com/re sources/go_mt/ca/c2 /c2_8-7tl.pdf Geometer’s Sketchpad Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Activity: Students will use Geometer’s Sketchpad to create their own pictures using only the shape tools provided within the program. Students must list all polygons and shapes used within their drawings. [Type text] Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Describe events as subsets of a sample space (the set of outcomes) using characteristics (or categories) of the outcomes, or as unions, intersections, or complements of other events (“or,” “and,” “not”). S.CP.1 Understand that two events A and B are independent if the probability of A and B occurring together is the product of their probabilities, and use this characterization to determine if they are independent. S.CP.2 S.CP.3 Understand the conditional probability of A given B as P(A and B)/P(B), and interpret independence of A and B as saying that the conditional probability of A given B is the same as the probability of A, and the conditional probability of B given A is the same as the probability of B. S.CP.3 S.CP.4 Construct and interpret two-way frequency tables of data when [Type text] Evidence of Learning Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Activity: Students will create “trees” of given samples (e.g. “You are going to buy a new snowboard, bindings, and boots. You have a choice of Burton, Forum, Foursquare, and Stepchild boards; Burton, DC and Forum boots, and Altec, Union, or Rome bindings.” Activity: Students will take turns rolling dice and recording their results. Numbers 4 and 6 are worth 1 point, 1 is 1, and the rest are 0. Students will each take 10 rolls and record the results. After, we will discuss and find the probability of all events, and see if previous throws change later outcomes. Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Formative and Summative measures Activity: Students will be given decks of cards and asked to draw cards at random. They will do this with an without replacement. Each time, they will be asked to find the probability that their card was drawn. We will use this to Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. http://www.hgs.k12.va .us/Bruce_Norton_fold er/MISC/Probability_ Trees.pdf Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. http://www.mathgoodi es.com/lessons/vol6/in dependent_events.html http://www.mathgoodi es.com/lessons/vol6/co nditional.html http://office.microsoft. Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Student generated frequency tables and interpretation Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… two categories are associated with each object being classified. Use the two-way table as a sample space to decide if events are independent and to approximate conditional probabilities. For example, collect data from a random sample of students in your school on their favorite subject among math, science, and English. Estimate the probability that a randomly selected student from your school will favor science given that the student is in tenth grade. Do the same for other subjects and compare the results. S.CP.4 experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Find the conditional probability of A given B as the fraction of B’s outcomes that also belong to A, and interpret the answer in terms of the model. [Type text] Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Formative and Summative measures of data. show that conditional probability can change outcomes of events if the cards are common. com/en-us/excelhelp/explorehistogramsHA001110948.aspx Activity: Given in description of Learning Target. Recognize and explain the concepts of conditional probability and independence in everyday language and everyday situations. For example, compare the chance of having lung cancer if you are a smoker with the chance of being a smoker if you have lung cancer. S.CP.5 Evidence of Learning Lessons and Activities The learning Lesson: Class discussion about the difference between conditional statements. Change of having cancer Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Student response in class. Worksheet on Statistics textbook – pg 169-173 Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Evidence of Learning Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement being a smoker is different then being a smoker and having cancer. Show differences using charts and graphs. S.CP.6 Apply the Addition Rule, P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A and B), and interpret the answer in terms of the model. Activity: Students will be given decks of cards and asked to draw cards at random. They will do this with an without replacement. Each time, they Apply the general Multiplication Rule in a will be asked to find the probability that uniform probability model, P(A and B) = P(A)P(B|A) = P(B)P(A|B), their card was drawn. We will use this to show that conditional probability can and interpret the answer in terms of the model. change outcomes of events if the cards are common. S.CP.7 S.CP.8 (+) [Type text] Use permutations and combinations to compute probabilities of compound events and solve problems. Activity: Students will take decks of cards and go through the probability of pulling different pairs of cards out, showing how depending if the cards have something in coming, this will change our probability. Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Formative and Summative measures material presented. Quiz on material presented. Student response in class. Worksheet on material. Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. http://www.mathgoodi es.com/lessons/vol6/co nditional.html http://www.algebralab. org/lessons/lesson.asp x?file=Algebra_Proba bilityAdditionRule.xm l http://people.richland.e du/james/lecture/m170 /ch05-rul.html http://www.mathsisfun Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s S.CP.9 (+) Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Use probabilities to make fair decisions (e.g., drawing by lots, using a random number generator). experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement Activity: Students will create probability trees, which will show all possible results from a given experiment. With these trees, students will be able to show how to find the probability of a given event using the multiplication rule. Analyze decisions and strategies using probability concepts (e.g., product testing, medical testing, pulling a hockey goalie at the end of a game). S.MD.6 (+) Activity: Students will be given ingredients for a sandwich. Students must show all possible ways in which 4 items can be placed on the sandwich out of 6 possible items. We will then discuss if it’s the same sandwich if the same ingredients are on in the different order. Activity: Students will use the TI-83/89 calculators to generate 100 random digits from 2-12. After, they will use this to Resources Books, articles, text, etc. Formative and Summative measures Quiz on material presented. Worksheet on material. Quiz on material presented. S.MD.7 (+) [Type text] Evidence of Learning Lessons and Activities The learning Student response in class. Worksheet on material presented. Quiz on material presented. .com/combinatorics/co mbinationspermutations.html http://www.random.or g/ Statistics textbook – pgs. 387-407 Content Area: Geometry Target Course/Grade level: 10 Unit Title: Circles With and Without Coordinates Essential Questions: Essential Questions: How do we explore Circles With and Without Coordinates? Standards/ CPI’s Unit Learning Targets As a result of this segment of learning, students will… Lessons and Activities The learning experiences that will facilitate engagement and achievement determine if this is representative of all possible dice rolls. Lesson: Students will use their knowledge of probability to determine if they should continue producing a product with given results. Using probability, standard deviation, and hypothesis testing, students will be able to determine if they are making a correct decision. [Type text] Evidence of Learning Formative and Summative measures Resources Books, articles, text, etc.