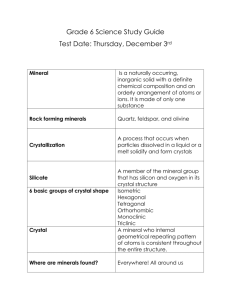
What is a Mineral? Pages 45-47 Mineral – a naturally occurring
advertisement

What is a Mineral? Pages 45-47 Mineral – a naturally occurring, inorganic solid with a definite chemical composition (same matter throughout) and an orderly arrangement of atoms or ions Naturally Occurring -only 30 common minerals (10 minerals are rock forming) Definite Chemical Composition --same chemical formula (make-up) throughout -some made of only one element throughout & some made of a combination of elements Crystalline Form -minerals form predictable crystal patterns due to repeating atom arrangement -internal arrangement of atoms determines crystal shape (ex. salt crystals are cubes) Solid -all minerals are solid (tightly packed atoms w/definite shape and volume), but not all solids are minerals Inorganic -not from biologic (living) origins The Structure of Minerals pages 47-49 Crystal Shape -occur in many different shapes -often too small to identify shape -can use high powered microscopes to reveal orderly arrangement of atoms Common Minerals -common rock forming minerals are made of combinations of elements that are abundant in Earth’s crust -2 most abundant elements in crust are oxygen and silicon -2 main families of rock-forming minerals are silicates and non-silicates -silicate is a member of the mineral group that has silicon and oxygen in its crystal structure (ex. olivine & mica) -non-silicates do not contain silicon (ex. calcite & halite) How do Minerals Form? 49-51 -form through process called crystallization (particles dissolved in a liquid or a melt solidify and form crystals) -can form from hot or cold solutions Minerals from Cool Solutions -water dissolves minerals from rocks in soil and picks up elements that become dissolved solids -as water evaporates the solids crystallize out of the water and form minerals (ex. salt from salt water) -some organisms remove minerals (salts) from water to make shells/reefs Minerals from Hot Solutions -water flows through crust into hot environments carrying dissolved solids & some of the dissolved solids form mineral deposits inside the Earth (ex. gold) Minerals from Magma -magma is molten rock stored under Earth’s surface. -lava and ash are magma that has erupted onto Earth’s surface -as lava and magma cool, atoms arrange themselves to make mineral crystals -small crystals form when lava cools quickly on or near surface -large crystals form as magma cools slowly below surface Changes in Minerals -minerals from deep in the crust & mantle are only stable under high temp and pressure -when brought to surface, changes in temp and pressure, along with erosion cause minerals to break down and form new minerals Mineral Resources pages 63-66 -average person uses 22,000kg of mineral resources yearly -ore – is a mined rock that contains enough concentrations of a desired substance, such as a metal, so that it can be mined for a profit Metallic Mineral Resources -ores of iron and aluminum are some of the most abundant metallic mineral resources -iron is main ingredient in steel -metals are used in food industry, such as metal cans -aluminum is abundant in crust Rare Metals -gold occurs in ratio of 1 part gold to 4 billion parts rock (still concentrations large enough to mine for a profit) -gold is a good conductor and doesn’t corrode -platinum used in cars to regulate harmful gas emissions Nonmetallic Mineral Resources -used for road construction, ceramics, building stone and fertilizers Gemstones -gemstone is a rare and attractive mineral that can be worn as jewelry -ex diamonds & rubies -Hardness of some gemstones make them useful in abrasives and as cutting tools