Vocabulary Cheat Sheet
advertisement

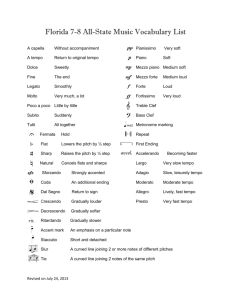
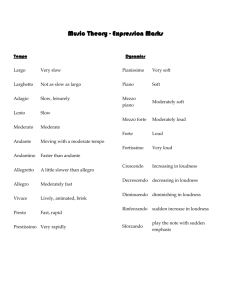
Vocabulary Cheat Sheet A capella: Without accompaniment A tempo: Return to original tempo Dolce: Sweetly Fine: The end Legato: Smoothly Molto: Very much, a lot Poco a poco: Little by little Subito: Suddenly Tutti: All together Fermata: Hold Flat: Lowers the pitch by ½ step Sharp: Raises the pitch by ½ step Natural: Cancels flats and sharps Coda: An additional ending Dal Segno: Return to sign Crescendo: Gradually louder Decrescendo: Gradually softer Ritardando: Gradually slower Accent mark: Emphasis on a certain note Staccato: Short and detached Slur: A curved line joining 2 or more notes of different pitches Tie: A curved line joining 2 notes of the same pitch Pianissimo: Very soft Piano: Soft Mezzo Piano: Medium soft Mezzo Forte: Medium loud Forte: Loud Fortissimo: Very loud Treble Clef Bass Clef Metronome marking Repeat First Ending Accelerando: Becoming faster Largo: Very slow tempo Presto: Very fast tempo Allegro: Lively, fast tempo Moderato: Moderate tempo Blend: Mixing the same vowels and tones together equally in a correct manner. Balance: The volume of each voice part is equally distributed throughout. Rhythm: Controlled movement of music in time. Meter: Measure of time. Melody: Dominant tune of the composition. Voicing: When music splits into parts. Lyrics: Words in a piece of music. Harmony: Combination of notes sounded at the same time to produce chords. Form: The structure of a piece of music, frame upon which it is constructed. Solo: A single performer or a passage that is to be performed by a single performer. Duet: A piece of music that is to be performed by TWO musicians. Trio: Piece of music performed by 3 solo voices. Quartet: A piece of music performed by four solo musicians. Choir: A group of singers who usually sing in parts with several voices on each part. Ensemble: A group of musicians that perform as a unit. Soprano: The highest pitched female part. Alto: A female voice of low range. Tenor: Highest pitched male part. Baritone: The most common range of male voice pitched between the tenor and bass. Bass: The lowest male part. Function of Vocal Mechanism: Soft Palate: Fleshy part toward the back roof of mouth. Lift for an un-nasally sound. Pharynx: Throat. Using pharyngeal voice creates and bright, loud sound. Larynx: Voice Box. Try to keep neutral to avoid straining of chords and neck. Tongue: Tongue position assists with reaching certain notes and creating certain tones.