worksheet - Mr Science
advertisement

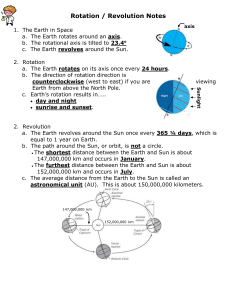
Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. Name _____________________________________________________________ Seasons Text Assignment The Sky Seems to Turn as Earth Rotates (pg. 13) 1. What happens as the Earth rotates at night? (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. Some constellations rise in the East. b. Some constellations set in the East. c. Some constellations rise in the West. d. Some constellations set in the West. 2. The Earth’s axis is always pointed towards this star. a. Polaris b. Thuban c. Vega d. Zuben el Genubi 3. Stars rise and set in the night sky because… a. Earth orbits the Sun. b. Earth rotates. c. the stars are moving in space. Earth’s Rotation Causes Day and Night (pgs. 43-44). 4. As you stand on the Earth’s surface, you are being pulled towards its center. a. True b. False 5. Which is a direction based on the way the Earth rotates? a. East b. North c. South d. West e. All of the above 6. This is the imaginary line around which the Earth rotates. a. Tropic of Cancer axis b. Equator axis c. Axis of Rotation d. Tropic of Capricorn axis 7. The ends of the axis are the… (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. East Pole b. North Pole c. South Pole d. West Pole 1 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. 8. About _____ of the Earth is always in darkness. a. ¼ b. ½ c. ¾ d. None. It is never dark on Earth. 9. If it is noon at one location on Earth, what time is it at a location directly opposite on the other side of Earth? a. Noon b. 6:00 pm c. Midnight d. 6:00 am 10. If the Sun had no gravity, what would happen to Earth? a. Nothing. It would continue traveling around the Sun. b. The Earth would travel into the Sun. c. The Earth would travel in a straight line into deep space. 11. The Earth’s revolution around the Sun is about _____,000,000 miles across. 12. It takes the Earth a _____, to _____ once around the Sun. (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. week b. revolve c. turn d. year 13. The Earth rotates around the Sun at about a _____o angle. 14. Which diagram best shows the Earth orbit around the Sun? a. b. c. d. 2 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. Seasonal Patterns (Pg. 46-47). Match the diagram of the Earth’s tilt with the season. Answers may be used more than once. _____15. Northern Hemisphere Summer _____17. Northern Hemisphere Winter _____18. Northern Hemisphere Spring A. B. Direction of Sunlight _____16. Northern Hemisphere Autumn C. 19. In which month does winter begin in the Southern Hemisphere? a. December b. June c. March d. September 20. On this date, the North Pole is in darkness for 24 hours. a. December Solstice b. June Solstice c. March Equinox d. September Equinox 21. On this date, the sunlight shines equally on both hemisphere. (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. December Solstice b. June Solstice c. March Equinox d. September Equinox 22. The Northern Hemisphere is tilting towards the Sun and it marks the first day of summer. a. December Solstice b. June Solstice c. March Equinox d. September Equinox 3 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. Angles of Sunlight (pg. 48). Use this diagram to answer questions #23, #24, & #25 (Answer may be used more than once). A B C East ____23. Winter Solstice, Noon ____24. Spring Equinox, Noon Looking South West a. A b. B ____25. Summer Solstice, Noon ____26. Autumn Equinox, Noon c. C Match the description with the season. _____27. Shadows are long because sunlight is spread out. The Sun appears low in the sky even at noon. _____28. Shadows are of medium length and the noon Sun appears higher in the sky. _____29. Shadows are short because light is concentrated in a small area. The noon Sun appears high in the Sky. A. Spring Equinox B. Summer Solstice C. Winter Solstice 4 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. Length of Days (pg. 49). 30. Seasons temperatures do not depend on the amount of daylight. a. True b. False 31. In Chicago during winter, there are about _____ hours of daylight. 32. In Chicago during summer, there are about _____ hours of daylight. 33. Near the poles, there can be only daylight for as much as _____ months. 34. Near the equator, there are _____ hours of daylight and darkness. 5 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. Seasons Text Assignment – Key 1. What happens as the Earth rotates at night? (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. Some constellations rise in the East; d. Some constellations set in the West. 2. The Earth’s axis is always pointed towards this star. a. Polaris 3. Stars rise and set in the night sky because… b. Earth rotates. 4. Earth’s gravity is pulling everyone towards the center of the Earth. a. True 5. Which is a direction based on the way the Earth rotates? e. All of the above 6. This is the imaginary line around which the Earth rotates. a. Tropic of Cancer axis b. Equator axis c. Axis of Rotation d. Tropic of Capricorn axis 7. The ends of the axis are the… (There are two or more answers to this question.) a. East Pole b. North Pole c. South Pole d. West Pole 8. About _____ of the Earth is always in darkness. b. ½ 6 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. 9. If it is noon at one location on Earth, what time is it at a location directly opposite on the other side of Earth? c. Midnight 10. If the Sun had no gravity, what would happen to Earth? c. The Earth would travel in a straight line into deep space. 11. The Earth’s revolution around the Sun is about _____,000,000 miles across. 200 12. It takes the Earth a _____, to _____ once around the Sun. (There are two or more answers to this question.) b. revolve; d. year 13. The Earth rotates around the Sun at about a _____o angle. 23 14. Which diagram best shows the Earth orbit around the Sun? d. C 15. Northern Hemisphere Summer B 16. Northern Hemisphere Autumn 7 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. A 17. Northern Hemisphere Winter B 18. Northern Hemisphere Spring 19. In which month does winter begin in the Southern Hemisphere? a. December 20. On this date, the North Pole is in darkness for 24 hours. a. December Solstice 21. On this date, the sunlight shines equally on both hemisphere. (There are two or more answers to this question.) c. March Equinox; d. September Equinox 22. The Northern Hemisphere is tilting towards the Sun and it marks the first day of summer. b. June Solstice C 23. Winter Solstice, Noon B 24. Spring Equinox, Noon A 25. Summer Solstice, Noon B 26. Autumn Equinox, Noon C 27. Shadows are long because sunlight is spread out. The Sun appears low in the sky even at noon. A 28. Shadows are of medium length and the noon Sun appears higher in the sky. B 29. Shadows are short because light is concentrated in a small area. The noon Sun appears high in the Sky. 8 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. 30. Seasons temperatures do not depend on the amount of daylight. b. False 31. In winter, there are about _____ hours of daylight. 9 32. In summer, there are about _____ hours of daylight. 15 33. Near the poles, there can be only daylight for as much as _____ months. 6 34. Near the equator, there are _____ hours of daylight and darkness. 12 9 Objective – Explain that Earth's axis is tilted relative to its yearly orbit around the Sun. Seasons Text Assignment – Scoring Guide 1. a, d 2. a 3. b (3 choices) 4. a (2 choices 5. e (5 choices) 6. c 7. b, c 8. b 9. c 10. c (3 choices) 11. 200 12. b, d 13. 23 14. d 15. C (3 choices) 16. B (3 choices) 17. A (3 choices) 18. B (3 choices) 19. a 20. a 21. c, d 22. b 23. C (3 choices) 24. B (3 choices) 25. A (3 choices) 26. B (3 choices) 27. C (3 choices) 28. A (3 choices) 29. B (3 choices) 30. b (2 choices) 31. 9 32. 15 33. 6 34. 12 Scoring Guide 32-34 – 4 29-31 – 3.5 24-28 – 3 21-23 – 2.5 18-20 – 2 15-17 – 1.5 12-14 – 1 1-11 – .5 0–0 10