2nd Grade Math: 3-Digit Addition Unit Overview
advertisement

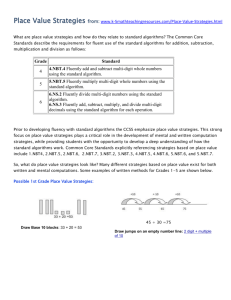
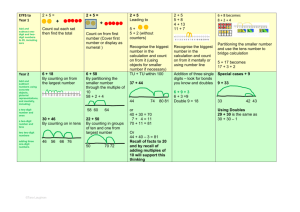
Unit Overview Content Area: Math Unit Title: Addition of 3-Digit Numbers with & w/out Regrouping Unit: 6 Target Course/Grade Level: 2 Timeline: 3 weeks Unit Summary: Students will apply addition regrouping strategies for three digit numerals. Primary interdisciplinary connections: Language Arts NJ Standard 9.1: 21st – Century Life & Career Skills Standard 9.1: All students will demonstrate the creative, critical thinking, collaboration, and problemsolving skills needed to function successfully as both global citizens and workers in diverse ethnic and organizational cultures. Strand: A. Critical Thinking and Problem Solving C. Collaboration, Teamwork and Leadership Content Statement: 9.1.4.A.5: The ability to recognize a problem and apply critical thinking and problem-solving skills to solve the problem is a lifelong skill that develops over time. 9.1.4.C.1: Practice collaborative skills in groups, and explain how these skills assist in completing tasks in different settings such as home, play or school. 21st century themes and skills: Critical Thinking and Problem Solving, Collaboration, Teamwork and Leadership Mathematical Practices: 2.MP.1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2.MP.2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 2.MP.3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 2.MP.4. Model with mathematics 2.MP.6. Attend to precision. 2.MP.7. Look for and make use of structure. 2.MP.8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Learning Targets Domain: Numbers and Operations in Base Ten 2.NBT Measurement and Data 2.MD Operations and Algebraic Thinking 2.OA Cluster: Understand place value. Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract. Work with time and money. Represent and interpret data. Standard # Standards 2.NBT.2 Count within 1000; skip-count by 5s, 10s, and 100s. 2.NBT.4 Compare two three-digit numbers based on meanings of the hundreds, tens, and ones digits, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons. 2.NBT.5 Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction. 2.NBT.7 Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method. Understand that in adding or subtracting three-digit numbers, one adds or subtracts hundreds and hundreds, tens and tens, ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose or decompose tens or hundreds. 2.NBT.8 Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given number 100–900, and mentally subtract 10 or 100 from a given number 100–900. 2.NBT.9 Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work, using place value and the properties of operations. 2.MD.10 Solve simple put-together, take-apart, and compare problems using information presented in a bar graph. 2.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem CPI# Cumulative Progress Indicator (CPI) 9.1.4.A.5 Apply critical thinking and problem-solving skills in classroom and family settings. 9.1.4.C.1 Practice collaborative skills in groups, and explain how these skills assist in completing tasks in different settings (at home, in school, and during play). Unit Essential Questions How can I use what I know about number relationships to add and subtract? Why is recognizing what strategy to use for a specific purpose, helpful? Unit Enduring Understandings A math sentence can be written to solve for unknown information in either addition by utilizing the inverted operation. Numbers follow a pattern that repeat, even when place value changes. Symbols (<, >, =) can be used to compare the value of numbers. Different strategies (mental, paper, drawing) can be used to add numbers fluently. Different strategies (mental, paper, drawing, concrete models) can be applied to add within 1000. Place value affects the other place values when adding. (regrouping, trading, composing/decomposing) When adding two or three digit numbers, knowing the value of that digit, in a given position, determines the next step one must take to solve an equation. Multiples of 10 and 100 can be used as landmark numbers in computation. Words or drawings can be used to explain addition strategies. Picture & Bar graphs charts and tables can be used to solve comparative and addition problems. Unit Learning Targets Students will ... Add 3 digit numbers mentally without regrouping. (2.NBT.8) Use manipulatives to show regrouping of hundreds, tens and ones. (2.NBT.7) Compute addition problems of 3 digit numbers (w/&w/o regrouping) (2.NBT.5) Add two three-digit numbers and record in vertical format.(2.NBT.9) Solve problems involving addition using data from a table.(2.MD.10) Find missing addends of a three digit problem (2.NBT.8) (2.OA.1) Apply knowledge of number patterns to extend existing patterns with numbers within 1000 (2NBT2) Evidence of Learning Summative Assessment Illustrate/explain adding three-digit numbers with/without regrouping. Accurately compute two & three, three-digit numbers with/without regrouping for addition. Give a table with various three-digit numbers and solve addition with/without regrouping. Choose from a list of strategies/tools one could use to solve a given three-digit math addition equation to determine which is the best way to attain the correct answer. Give an equation using 2 three-digit numbers. Solve the problem giving an estimate and exact sum. Accurately extend three-digit number patterns from any given number up to 1,000. Equipment needed: place value blocks, decks of cards, dice, number spinners Teacher Instructional Resources: Everyday Math Math Their Way Scott Foresman Mathematics Program: Chapter 11 Formative Assessments Observe students as they …. work with manipulatives complete work sheets/workbooks play games, complete activities Integration of Technology: SMARTBoard to play online games and utilize on line resources. ELMO to use for demonstration purposes. Utilize resources from Scott Foresman by using Login in: https://www.pearsonsuccessnet.com/snpapp/login/login.jsp Technology Resources: Click the links below to access additional resources used to design this unit: http://www.mrnussbaum.com/draggable/index3.html This is a worksheet to create problems, solve them and computer tells Student if it is correct. http://www.mathplayground.com/wpdatabase/wpindex.html Word problems using three digit numerals. Student is given feedback by computer for answer’s accuracy. Opportunities for Differentiation: Decelerate: Continue using place value blocks and/or beans for longer time so the concept of regrouping is clearly understood. Use the Scott Foresman online tools to give another visual aide for learning the concept. Accelerate: Give students four, five and/or six digit numbers to add. http://www.mathsonline.co.uk/nonmembers/gamesroom/bugs/bugrace3.html Student is expected to add two numbers quickly before bug lands at bottom. http://www.netrover.com/~jjrose/random/container.htm Student puts in an answer to given problem and computer announces if correct or incorrect. Teacher Notes: It is best to approach three digit addition after students are proficient in two digit addition and only after revisiting the use of place value cubes to concretely show how regrouping works.