Strong and Weak Syllables in English Phonetics
advertisement

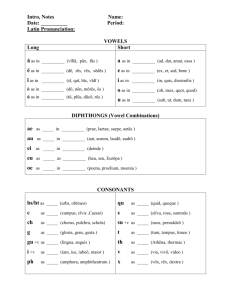
Lecture 1 Strong and Weak Syllables The Nature of Syllable Syllable consist of a centre which has little or no airflow obstruction and hence sound comparatively loud. Before and after the centre (at the beginning and end of the syllable), there is a greater airflow obstruction and/or less sound. From the phonetic POV: _______________________ is a single vowel in isolation, e. g.: are [ɑː], or [ɔː] etc. Such syllables are preceded and followed by silence. Some syllables have an __________ – instead of silence, they have one or more consonants preceding the centre of the syllable, e. g.: key [kiː], more [mɔː] etc. Syllables may have no onset, but they may have a __________ – they end with one or more consonants, e. g.: am [æm], ease [iːz] etc. Some syllables have both onset and coda, e. g.: fill [fɪl], sat [sæt] etc. The Structure of English Syllable Roach, 2009, p. 60 Strong and Weak Syllables Some syllables are strong and some weak Weak syllables have a tendency to be _______________________________________________ and ________________________________. For example the word data [ˈdeɪtə] The most important thing to know is that Weak Syllables Weak syllables only have one of a very small number of possible peaks. At the end of a word, weak syllable ends with a vowel (with no coda): 1. vowel [ə] 2. vowel [i] 3. vowel [u] e. g.: e. g.: e. g.: Vowel [ə] is ___________________________________________________________________ and ___________________________________________________________!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! [ə], [i], [u] [ə] example words: The [i] vowel is neither the [i:] of beat [bi:t] nor the [ɪ] of bit [bɪt]. The [u] vowel is neither the [u:] of shoe [ʃuː] nor the [ʊ] of book [bʊk]. It is no longer a true phonemic transcription if [i:] and [u:] are used. However, native speakers ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________. [i] [i] can be found: 1. 2. 3. 4. [u] Words containing [u] are not so common. [u] occurs most frequently in words such as ___________ ___________________________________________________________________. Furthermore, [u] can be found before another vowel within words such as in evacuation [ɪˌvækjuˈeɪʃn] or influenza [ˌɪnfluˈenzə]. Syllabic Consonants There are syllables which do not have a vowel sound. In this case, consonant such as [l], [r], or a nasal stands as the peak of the syllable instead of a vowel. It is important to remember that these are regarded as weak syllables. It is normal to indicate a syllabic consonant with a small vertical mark For example: List of resources: Cruttenden, A. Gimson’s Pronunciation of English. Hodder Education, 2008. Crystal, D. A Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics. Blackvell Publishing, 2008. Davenport M. – Hannahs S. Introducing Phonetics and Phonology. Hodder Arnold, 2005. Richards, J. – Schmidt, R. Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics. Longman, 2010. Roach, P. English Phonetics and Phonology. Cambridge University Press, 2009. Underhill, A. Learning and teaching pronunciation. Macmillan, 2005.