Honors Biology Review Sheet to Chapter 9 Test
advertisement
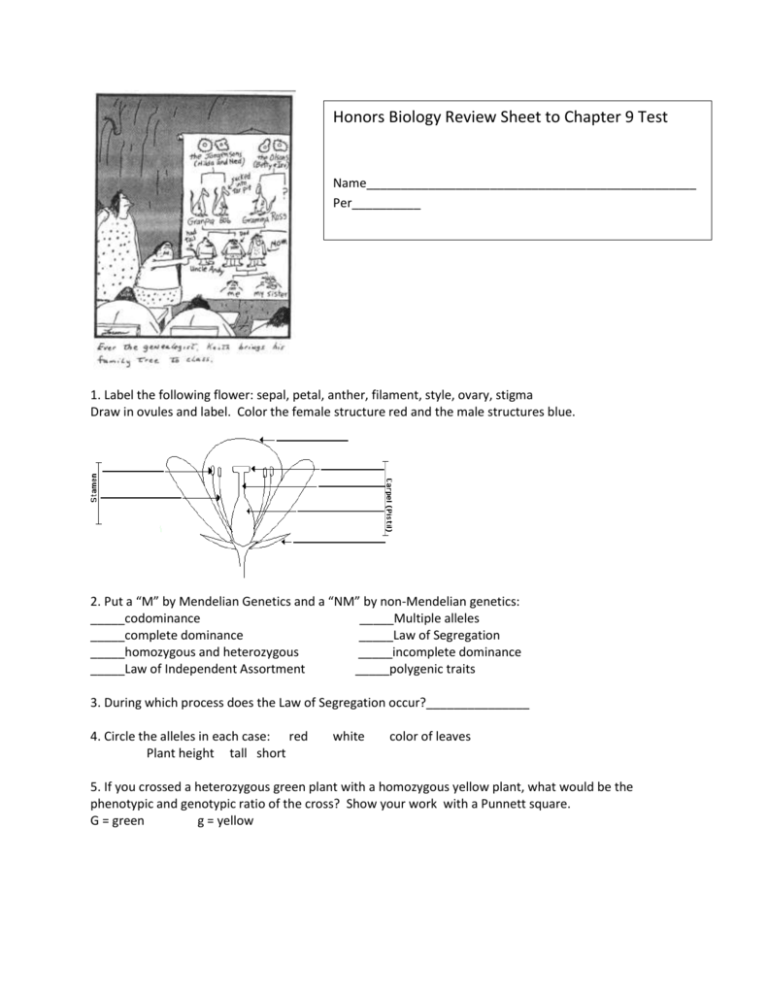
Honors Biology Review Sheet to Chapter 9 Test Name________________________________________________ Per__________ 1. Label the following flower: sepal, petal, anther, filament, style, ovary, stigma Draw in ovules and label. Color the female structure red and the male structures blue. 2. Put a “M” by Mendelian Genetics and a “NM” by non-Mendelian genetics: _____codominance _____Multiple alleles _____complete dominance _____Law of Segregation _____homozygous and heterozygous _____incomplete dominance _____Law of Independent Assortment _____polygenic traits 3. During which process does the Law of Segregation occur?_______________ 4. Circle the alleles in each case: red Plant height tall short white color of leaves 5. If you crossed a heterozygous green plant with a homozygous yellow plant, what would be the phenotypic and genotypic ratio of the cross? Show your work with a Punnett square. G = green g = yellow Honors Biology Chapter 9 Test Review p. 2 6. In a cross of AaBBcc x AaBbCC, what is the probability of producing a genotype of AABbCc? (Hint: Do individual Punnett squares. What is the Law that you use to solve this?____________) 7. Describe how the human blood typing system shows both multiple alleles and codominance. 8. What are the possible genotypes for each blood type? A __________________________ B__________________________ AB_________________________ O__________________________ 9. Cross a male with color-blindness with a heterozygous female with normal vision. C= normal c = color blindness 10. Check which would be used in preparing a karyotype: _____use cells in anaphase _____arrange chromosomes largest to shortest _____stop cells with colchicine _____sex chromosomes are in position 23 _____use cells in metaphase _____use white blood cells _____23 pairs of chromosomes _____a female would have an XY set 11. Circle which is an example of polyploidy: N 2N 3N 12. Fill in the antigens and antibodies of each blood type: BLOOD TYPE Antigens A Antibodies B AB AB 13. If you had a dog with a dominant black coat, how would you find out if it is BB or Bb? 14. Blood type ii is also known as blood type____. 15. What possible blood types could a person with A- blood mating with a person with AB+/- blood have in their children? (Show your work with a Punnett square). Honors Biology Chapter 9 Test Review p. 3 Match the terms with the correct definition: 16._____Both alleles are expressed, such as in AB blood type. 17._____The capital letter allele is always expressed over the recessive 18._____The F1 hybrid phenotype is between the two parents 19._____One gene influences multiple characters 20._____Additive phenotype effect of more than 2 gene locations 21._____ Chromosome pair fail to separate correctly 22._____There are several choices of alleles available for a trait. 23._____The trait is on the X-chromosome. A. polygenic B. sex-linked gene C. codominant D. incomplete dominance E. nondisjunction F. complete dominance G. pleiotropy H. multiple alleles Match the type of mutation with its picture: p. 148 24._____inversion 25._____deletion 26._____translocation 27._____duplication 28. An expected ratio of the offspring of a cross was 25% for each of the following four phenotypes. That was not the case. SO…calculate the recombinant frequency RF of the following cross: 778 - wild type HINT: Total all offspring. 785 - black-vestigial Divide each number by that total for the percent of possible 158 - black-normal recombinant frequency. 162 - gray-vestigial Add the two highest numbers together-those are the nonrecombinant. Add the two lowest numbers together-those are the recombinant. Match the people with their genetic contributions: 29. _____Father of genetics devised principle by studying pea plants. 30._____Along with Punnett noticed some genes were linked. 31._____Found a recombination frequency with fruit flies. 32._____Devised a chart to predict the possible offspring of parents. 33._____Used crossover data to map gene loci. A. Reginald Punnett B. Gregor Mendel C. Alfred Sturtevant D. Thomas Hunt Morgan E. William Bateson Honors Biology Chapter 9 Review p. 4 MATCH THE GENETIC DISORDER WITH ITS DESCRIPTION: 34. _____failure to produce an enzyme to break down mucus in lungs 35._____Trisomy 21, trident hands, skin fold at inner eye lid flat nose 36._____X0, female disorder, web of skin at neck, infertile 37._____XXY, male disorder, infertile, small testes, female characteristics 38._____Unable to distinguish certain colors, sex-linked trait 39._____A gap where the spinal cord should close. 40._____usually a disorder among Eastern European Jews, child did young. 41._____lacking a blood clotting factor; disorder among European royalty 41._____The red blood cells collapse; heterozygotes resistant to malaria. 42._____Affects young boys, loss of muscle strength 43._____The lip and the arch in mouth fail to properly close. 44._____Taller than usual, heart problems, pigeon chest. 45._____Dwarfism, trident hands, homozygous dominant is lethal. 46._____failure to break down phenylalanine, build up on brain 47._____lack pigment in skin, hair, eyes 48._____dementia, nerve cell in brain build up plaque and destroys brain 49._____cannot break down cholesterol and it hardens arteries 50._____uncontrollable muscle spasms, 40+ CAG’s, happens in adults Interpret the following pedigree: A. Huntingtons B. Klinefelters C. Duchenne MD D. Color-blindness E. Alzheimers F. Turner syndrome G. Cystic fibrosis H. Down Syndrome I. Achondroplasia J. Spina bifida K. Cleft lip/cleft palate L. Tay Sachs M. Hemophilia N. hypercholesterolemia O. albinism P. Marfans Q. PKU R. sickle-cell-anemia 51. If person I-1 is Autosomal dominant disease HH and person I -2 is hh: a. fill in the genotypes of the rest of the people. b. How many children did the original parents have?_______ c. Who is the oldest child of the original parents (number)?______ d. How does this pedigree show that this is a dominant disorder (HINT: how often do you see it? 52. Are all wild types the dominant ones? Give an example to validate your answer. (see p. 161) 53. How do the Blue People of Kentucky show in-breeding? (p. 163) 54. Cross an Achonroplasia parent Aa with a normal parent aa. What is the genotypic and phenotypic ratio? Honors Biology Chapter 9 Review p. 5 55. Match the following methods for obtaining samples for genetic testing: A. Ultrasound imaging B. Amniocentesis C. CVS (chorionic villus sampling) D. karyotype _____needle into abdomen of mother with ultrasound to obtain amniotic fluid _____white blood cells photographed in metaphase _____sample of tissue from the placenta _____high-frequency sound waves produce a picture of the fetus 56. By making a Punnett square determine the possible blood types of a mother of blood type AO and a father of blood type AB. 57. What is the universal donor blood type?____________________universal recipient?___________ Match the sex determination methods in each of the following organisms: 58. _____XY A. turtles 59._____X-O (females XX, males only X) B. Birds, fish, butterflies 60._____ZW (males ZZ, females ZW) C. humans 61._____temperature the eggs hatch D. grasshoppers and roaches EXTENDED RESPONSE: -You will be given one dominant-recessive Punnett square (four box) to determine the genotypic and phenotypic ration. 5 pts -You will be given one blood type or one genetic disorder (four box) Punnett square to determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios. 5 points -You will be given one dihybrid (16 box) Punnett square to determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios. 10 points