review questions
advertisement

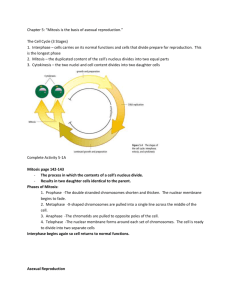
Mrs. O’Brien EXAM REVIEW SCIENCE 10F – 2015 Mrs. O’Brien EXAM DAY: Tuesday June 16th 12:00 RED GYM The following is an outline of topics you should review for the exam. The exam will consist of multiple choice, labeling diagrams, fill in the blanks, true false, short and long answer questions. This review is by no means ‘the exam’. Please refer back to the notes, assignments, labs, tests, projects and quizzes to better prepare yourself! Mrs. O’Brien MAJOR TOPIC CHECKLIST – CHEMISTRY Describe how historical ideas and models furthered our understanding of the nature of matter. Include: Greek ideas, alchemists, philosophers, chemists Investigate the historical progression of the atomic model. Include: Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford, Bohr, quantum model Define element and identify symbols for the elements listed below. Include: the first 18 elements, K, Ca, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, I, Ag, Sn, Au, W, Hg, Pb, U Explain the atomic structure of an atom in terms of the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons, and explain how those numbers define atomic number and atomic mass. Draw Bohr atomic models for the first 18 elements and group them according to the number of outer shell electrons. Investigate the development of the periodic table as a method of organizing elements. Include: periods, families (groups) Investigate the characteristic properties of metals, non-metals, and metalloids and classify elements according to these properties. Examples: ductility, conductivity of heat and electricity, luster, reactivity Relate the reactivity and stability of different families of elements to their atomic structure. Include: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases Compare elements to compounds. Include: atoms, molecules Interpret chemical formulas of elements and compounds in terms of the number of atoms of each element. Examples: He, H2, O2, H2O, CO2, NH3 Differentiate between physical and chemical changes. Know various indicators of chemical change. Examples: color change, production of heat and / or light, production of a gas or precipitate or new substance Investigate technologies and natural phenomena that demonstrate chemical change in everyday situations Example: chemical change from food waste to nutrient rich worm castings Mrs. O’Brien CHEMISTRY – REVIEW QUESTIONS WHMIS & SAFETY 1. Explain what each of the following WHMIS symbols means. 2. How does one test for chemical smells in a test tube or beaker? Trends on the periodic table 1. Examine a blank copy of the periodic table (extras will be provided in class). Label the groups, families and periods. 2. What do the numbers above the groups and the numbers beside the periods represent? 3. Which group is considered the most ‘reactive’ and why? 4. Which group on the periodic table is the least reactive and why? 5. Which group is Sodium found in? 6. Label the following on your periodic table: Hydrogen, Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Halogens, and Noble Gases 7. State the reactivity of the following groups: Hydrogen, Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Halogens, and Noble Gases Bohr Diagrams: 1. Where are neutrons, protons and electrons found in the atom? 2. State the maximum number of electrons found in the first three valence shells. 3. Explain what it means to be an ION. 4. Prepare a Bohr ION diagram for the following: Na+ and O25. Prepare a Bohr diagram showing the ionic bonding between sodium and chlorine. Be sure to include the charge on the ions. Mrs. O’Brien 6. Draw a Bohr diagram of each of the following atoms. Use information provided to help you. Be sure to write the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons for each beside your model. (a.) 8 O Oxygen 15.9 (b.) 18 Ar Argon 39.9 Atomic Mass & Atomic Number: 1. An unknown element has 12 neutrons and 13 protons. What would its atomic mass be? 2. An unknown element has an atomic mass of 14 and 5 electrons. How many neutrons does it have? Combining Capacity: 1. Using a periodic table, give the combining capacity of elements from the following families (groups): The Alkali metals, the Alkaline Earth Metals, the Halogens, the Noble Gases. Mrs. O’Brien Chemical Formulas: 1. What information does a chemical formula tell you? 2. State the number of atoms for each of the following chemical formulas: a. NaCl b. H2O c. C6H12O6 3. A certain chemical compound contains one atom of hydrogen, one atom of carbon and three atoms of oxygen. Write its chemical formula. 4. Complete the following table: Element Symbol Atomic number Atomic Mass # protons # electrons #neutrons 7 7 20 Sodium 10 11 12 5. Complete the following table: ION K+ Ca2+ N3Al3+ PROTONS ELECTRONS Mrs. O’Brien Ionic vs. Molecular Compounds 6. Explain the difference between and ionic and a molecular compound (do they share or swap electrons?). Provide an example of each. Monomers & Polymers 7. Explain the difference between a monomer and a polymer. 8. Why do manufactures ‘cross link’ polymers? What does it mean to ‘cross link’ a polymer? 9. Provide three examples of polymers. Physical vs. Chemical Properties 10.Go over the handout ‘Chemical vs. Physical change’. Extra copies will be provided in class. 11.List some of the indicators of a chemical change. Mrs. O’Brien MAJOR TOPIC CHECKLIST – ASTRONOMY Describe how various cultures used knowledge of the position and motion of visible celestial objects for navigation. Explain the different historical perspectives on the relationship between Earth and space. Include: geocentric model, heliocentric model Explain reasons for the apparent motion of the Sun, stars, planets, and the Moon as seen from Earth. Include: daily rising and setting, seasonal constellations, retrograde motion Be able to define astronomical unit and light year. Describe/explain the major components of the universe. Include: planets, moons, comets and asteroids, nebulae, stars, galaxies, black holes Explain how various technologies have extended our ability to explore and understand space (Astronomy Project – Know your topic). Examples: robotics, Canadarm, Hubble telescope, Lunar Rover, shuttle, space station, Sojourner Rover, International Space Station, SETI, remote sensing, predictions of catastrophic impacts, colonization of space, Pathfinder and Galileo space probes REVIEW QUESTIONS - ASTRONOMY 1. Why was knowledge of celestial motion important to our early ancestors? 2. What is a celestial body? 3. Describe the pattern of motion of the Sun, Moon, and stars as seen by an observer on Earth. 4. Describe the main differences between the Earth-centered (Geocentric) model of the universe and the Sun-centered (Heliocentric) model. 5. Explain the meaning of “retrograde motion”. List the ‘wanderers’ of the night sky. 6. Name the Gas giants. 7. Describe the difference between the each of the following: asteroids, comets, and meteors. 8. What is a nebula – what is it made of, how it is the birth place of stars Mrs. O’Brien ***IMPORTANT DIAGRAM*** Be prepared to include this when answering questions 9. Explain the difference between orbit and rotation as it relates to the Earth’s motion. Explain what causes seasonal changes and changes in daylight time. 10.How does the amount of sunlight we receive in the Northern hemisphere compare to the amount of sunlight received in the Southern hemisphere in the summer vs. winter? 11.Define Solstice and Equinox. 12.Why can’t we see all of the constellations from Winnipeg? 13.Identify the characteristics of the three main types of galaxies. 14.Define the following terms: astronomical units and light-year. 15.Explain the various functions of an astrolabe. 16.Define: Altitude, Azimuth, Zenith. Mrs. O’Brien MAJOR TOPIC CHECKLIST– REPRODUCTION Explain the process of mitosis in plant and animal cells Include: stages of cell division (IPMAT), cytokenisis, cell cycle Explain the reasons for cell division in plant and animal cells Include: growth, repair, reproduction (plants) Describe various types of asexual reproduction that occur in plants and animals Examples: fission, budding, spore formation, fragmentation Describe agricultural applications of asexual reproduction. Examples: cloning, cuttings, grafting, bulbs/ tubers, layering Explain the process of producing gametes through meiosis. Include: sperm and egg production Compare and contrast the functions of mitosis to that of meiosis. Include: diploid cells/haploid cells, number of cells created, number of chromosomes in each cell, number of divisions etc. Compare sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of their advantages and disadvantages for plant and animal species. Investigate and explain adaptations of plant and animal species that enhance reproductive success. Examples: appearance, behavior, number of gametes or offspring, chemical cues Project: butterfly project Describe the function of the male and female human reproductive systems. Include: role of hormones, labeling various parts, function of each part, Outline human development from conception through birth. Include: X and Y chromosomes, zygote, embryo, fetus, 1st 2nd 3rd trimester, 3 stages of birth, risk factors during pregnancy Explain the difference between dominant and recessive genes. Include: genotype, phenotype, genotypic ratio, phenotypic ratio, homozygous recessive, homozygous dominant, heterozygous, hybrid, purebred etc. Describe the difference between DNA, chromosomes and genes Explain the inheritance of sex-linked traits in humans and use a pedigree to track the inheritance of a sex linked trait. Examples: color blindness, hemophilia Include: symbols for pedigree, genotypes for sex linked traits, male vs. female sex chromosomes. Describe environmental factors and personal choices that may lead to a genetic mutation or changes in an organism's development. Examples: fetal exposure to alcohol Mrs. O’Brien REVIEW QUESTIONS - REPRODUCTION Genetics & Heredity 1. Define the following: DNA, chromosome, gene, phenotype, genotype, dominant allele, recessive allele, sex linked trait, pedigree, karyotype. 2. A man who is heterozygous for brown eyes has a child with a woman who is homozygous recessive for blue eyes. a. Create a punnett square to predict the genotypes of their offspring. b. State the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of their offspring. 3. A man and a woman who are both heterozygous for widow’s peak have a child. a. Create a punnett square to predict the genotypes of their offspring. b. State the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of their offspring. 4. Examine the karyotype below and determine whether the individual is a boy or girl. 5. Create a pedigree using the following information (remember to shade the recessive trait - color blindness). A color blind man marries a woman with normal vision. They have three children. The first child is a boy with normal vision. Their second child is a girl who is color blind. Their third child is a boy with normal vision. Their first child marries a woman with color blindness. 6. State the genotype for the sex chromosomes in a man vs. a woman. 7. Provide two examples of sex linked traits. Explain why sex linked traits are found more often in men than in women. 8. State the difference between an “Autosome” and a “Sex Chromosome”. Then LIST the number of autosomes and sex chromosomes a human cell has. Mrs. O’Brien Asexual & Sexual Reproduction (Mitosis & Meiosis) 1. Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis by completing the table below, be prepared to fill out a similar table on the exam: MITOSIS MEIOSIS Occurs in asexual reproduction Occurs in sexual reproduction Results in four haploid cells Results in two diploid cells Is used to generate regular human cells (tissues, bones etc.) Is used to generate sperm and eggs Creates cells that are genetically IDENTICAL to the parent cell Creates cells that are genetically different than the parent cells Occurs in the gonads Crossing over occurs in prophase I 2. Explain what asexual reproduction is. Does it use mitosis or meiosis? Provide an example of asexual reproduction and how it works. 3. Define gonads and gamete. Then state where gametes are produced in males and females. Is this done through mitosis or meiosis? 4. Sate the advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproduction. 5. Define the following: budding, spore formation, fragmentation, layering, grafting, cuttings, binary fission. Reproduction & Development 1. Define: gestation period, embryo, fetus, oxytocin, zygote, mitosis, meiosis, puberty 2. Explain the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. Mrs. O’Brien 3. State the main functions of the following hormones: FSH, LH, Estrogen, Testosterone, Progesterone. 4. Explain the difference between primary and secondary sexual characteristics . State several primary and secondary characteristics in males and females. 5. What is the menstrual cycle and why is it important for reproduction? 6. State the functions of the placenta and umbilical cord in the development of a fetus. 7. State and explain the 3 birth stages. 8. Why is alcohol so dangerous to consume during pregnancy? 9. What is thalidomide and why is it dangerous to a developing fetus? 10.Label the male and female reproductive anatomy and state the role of each part. Mrs. O’Brien MAJOR TOPIC CHECKLIST – ELECTRICITY Explain various electrostatic scenarios discussed in class by showing the movement of negative charges in an object (go over the various statics labs we did in class: magic wand, balloons, bending water, electroscope, pith ball etc.) Include: conservation of charge, conduction, grounding, attraction of a neutral insulator, induction Define electric current as charge per unit time and solve related problems. Include: I=Q/t Define voltage (electric potential difference) as the energy per unit charge between two points along a conductor and solve related problems. Include: V=E/Q Describe resistance in terms of the particle model of electricity. Construct electric circuits using schematic diagrams. Include: series, parallel Compare and contrast voltage and current in series and parallel circuits. Include: cells, resistance Investigate and describe the relationship among current, voltage (electric potential difference), and resistance in a simple electric circuit. Relate the energy dissipated in a circuit to the resistance, current, and brightness of bulbs. Mrs. O’Brien REVIEW QUESTIONS – ELECTRICITY 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain the law of attraction and repulsion. Explain why a charged rod attracts a neutral object. State the difference between induction and conduction. Be able to diagram and explain various electrostatic scenarios from the labs we completed in class. Draw the charges in the following scenarios Problem 1: Draw where the negative and positive charges will move when a negative rod is brought near a neutral pith ball. Problem 2: Show the movement of charge when a positive rod is brought near an electroscope. What would happen if the rod were to touch the electroscope? Electrical Circuits 5. Define : voltage, resistance, current, ammeter, voltmeter, resistance, charge, circuits, load 6. Provide an example of a resistor. 7. State the four factors that impact resistance. 8. In each diagram there is an identical battery, bulb and switch. In which will the light bulb light up when the circuit is closed? 9. Draw a circuit with three bulbs, a switch, and a battery. Construct your circuit so that when the switch is open only two of the bulbs go out. The third bulb should stay on regardless of whether the switch is open or closed. Use the appropriate symbols. Mrs. O’Brien 10.Explain the difference between series and parallel circuits. Be able to draw series and parallel circuits. 11.Examine the four circuit diagrams shown below. Each diagram shows three light bulbs connected in parallel. Each diagram has a switch in a different location. Which circuit would be able to turn on or turn off all of the light bulbs at the same time? Why? Resistance & Current Calculations 12.Calculate the resistance in the following scenarios using the formula R=V/I: a. Calculate the resistance of a heating coil of an electric heater if a current of 12.5A runs through it when it is connected to 120V wall outlet. b. A light bulb passes a current of 0.83A when the potential difference across the bulb is 120V. What is the electrical resistance of the bulb in Ohms? 13.State the units used to measure charge, current, resistance and voltage. 14.Explain the difference between potential energy and potential difference. 15.List FOUR things that will change the resistance of a WIRE. 16.Be able to use the following equation to calculate current: I=Q/t a. How long does it take 650 coulombs of charge to pass a specific spot on a circuit if the current at that spot is 12.5 A? Mrs. O’Brien b. An ammeter reads 13.5A at a point in a circuit. If it takes 55 seconds for a charge to passing that point in the circuit what is the charge passing through that point? Questions based on Projects 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. List three MAJOR elements found in soil. List a food source for three of the major elements. How would you neutralize an acidic compost bin? Describe sexual reproduction in worms. Describe sexual reproduction in plants. Provide an example. Describe the various types of asexual reproduction in plants (meristems, cuttings, cloning, layering etc.) 7. Describe some strategies plants have for reproductive success (seed coat, embryo etc.) 8. Describe how mitosis and meiosis is used in plants. END OF REVIEW