File
advertisement

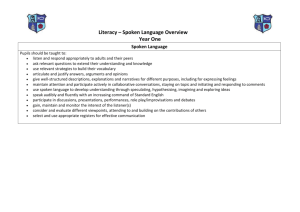
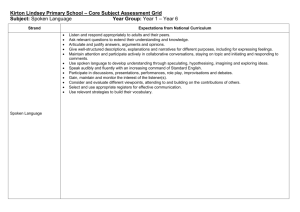
Formative task Student: Total Year 9 Chinese Continuer Listening and Responding Task Description: This task requires students to listen and answer questions in English, it mainly to assess their Chinese listening and understanding skills. The text provided has complex Chinese sentence structures with a range of vocabularies; such as tense markers, time phrases, cohesive devices, question words, adjectives and relative place words. Students are required to identify these items in spoken languages, and also use their analytical thinking skills to answer the questions. It also requires students to use their prior knowledge. Test: Student will hear the text in Chinese. The text will be played three times; there will be a 5 minute break between the first and second playing of the text. Students will have 10 minutes after the third playing of the text. A B C D E Knowledge and understanding Fully understand the text and linguistic features in spoken language. Students are able to fully use their prior knowledge in their response. Understand most key ideas and linguistic features in spoken language. Students are able to use their prior knowledge in their response. Understand some of the key ideas linguistic features in spoken language. Students use some of their prior knowledge in their response. Understand keywords and very basic linguistic features in spoken language. Students able to use limited prior knowledge in their response. Understand very basic keywords in spoken language. Students unable to use their prior knowledge in their response. Interpretation Key ideas and relevant details are identified and explained. Identified a range of linguistic features in spoken language. Most of the key ideas and relevant details are identified and explained. Most of the key linguistic features in the text is described. Some relevant information and linguistic features from text are identified. Most keywords are identified in spoken language. Keywords and some supporting detail are identified in spoken language. One or two basic linguistic features of the text are identified. Keywords are identified in spoken language. Specific information in the text is transcribed rather than interpreted. /