KEY GMO Web Quest - NAAE Communities of Practice
advertisement

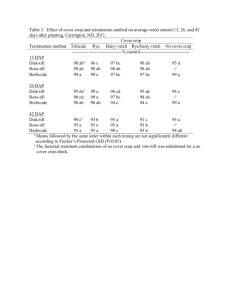
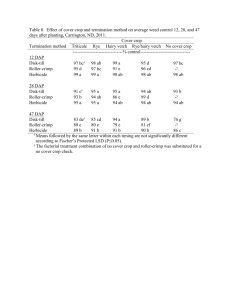
GMO Web Quest Name:_______________________________ Go to the website: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/harvest/ Next you will select different tabs to complete activities. Good Luck! GUESS WHAT’S COMING TO DINNER? When you click on each item on the dinner table, a short explanation on what new modifications are being made with this item will be displayed. Click your way around the table to explore what is changing on our dinner table! What is changing with how we can cook French fries? We are engineering potatoes that do not absorb as much of the oil they are fried in. Which food may one day replace getting a vaccine in the traditional form of a shot? The banana, because its peel protects the inside from any outside contamination. Where (in the world) will the vaccination technology be the most beneficial? In third world countries (developing countries) where transportation and storage of regular vaccines is very difficult. Into what three crops are we trying to add vitamins and minerals not normally found in the crop? Wheat, corn and rice. How would the change in coffee production be a benefit to the coffee producer? We are engineering coffee that is naturally decaffeinated. This would leave one less step in the production, allowing them to produce a cheaper product. ENGINEER A CROP First you must read the introduction paragraphs on the left side of the screen. This explains the difference between selective breeding and transgenic breeding. There are two lab activities that you will conduct. First click on Selective Breeding After reading the first slide, what trait are you trying to selectively breed for? We are trying to breed for the largest cob of corn. Click begin, and try to select the cob that will pass on the best genetics for the trait we are breeding for. How many generations did it take before you got to the optimum crop? 4-5 generations What are the negatives for this type of plant breeding? Takes more time or more generations. Not very selective, you are crossing more genes that you need to, getting more variety of offspring. Click on Engineer a Crop again, and this time select Transgenic Manipulation First you must read the introduction paragraphs on the left side of the screen. What type of transgenic plant are you going to create in this lab? A Bt tomato plant. What does Bt stand for? What does it do? Bt is Bacillus thuringiensis is a toxin that is harmful to certain insects, but harmless to mammals. Click on Begin. Step 1 Take the toxin gene from a stretch of Bt DNA and combine it with a vector. What is a vector? A short piece of DNA tht can replicate on its own when inside a bacteria cell. What gene besides Bt has been added to the vector? A gene that makes it resistant to herbicide. Step 2 Add the vector to the bacterium. Why do we put the vector into the bacterium? Agrobacterium can transfer its DNA into plants, normally this is to cause disease. However, we can also use it to get the Bt DNA into the plant. The vector also uses the bacterium to replicate its self, making a Bt factory! Step 3 Move the bacteria to the growth medium. How fast do bacteria grow? Fast! There will soon be a million of the bacterium. In this case it’s a good thing, but in what cases can it be bad? In general bacteria spread disease and sickness, and this speed of replication makes the spread much faster. Step 4 Add pieces of the tomato plant’s leaf to the bacteria. What genes are being added to the tomato leaf pieces? Bt and Herbicides resistance What is the nucleus of a cell? Where the DNA of a cell is housed. Step 5 Move the plant cells to the growth medium for plants. Why did we move the plant cells to a different media? Plants require a different type of environment to grow compared to bacterium. Step 6 Spray herbicide on the plant cuttings. Why do we spray the plant cells with herbicide? What are we left with? We spray the plant cells to kill off any that do not contain the herbicide resistant genes. Any plant without the herbicide resistance also does not have the Bt gene. We are then left with all plants that have Bt. Step 7 & 8 Transfer the plant to the growth chamber. Examine the plant to determine if it has the desired trait. How do we know if our plant has the Bt genes? We introduce the insects that should be killed. If they died after eating the leaf, the plant has Bt.