Anesthesia case discussion Caleb Coursey, EMT
advertisement

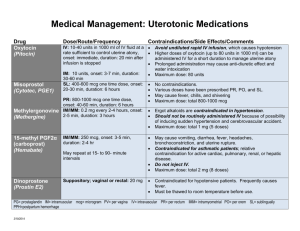
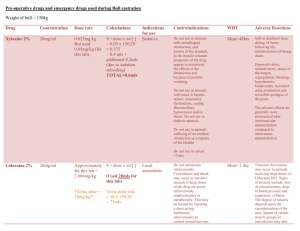
Anesthesia case discussion Caleb Coursey, EMT-P Tina Brunnet, RVT The dosages / charts below will be discussed in the lecture. This is simple a tool to use a reference. While all of the provided information has been reviewed, it is important to remember to double check dosages / concentrations to avoid medication errors. ALPHA 2 AGONIST Dexmedetomidine (DexdomitorR; 0.5 mg/ml) - An alpha-2 agonist (D-isomer) approved for use as a sedative and analgesic in dogs and cats (IV use in dogs, IM use in cats). Approximately twice as potent as medetomidine. Common dose range is 1Xylazine (RompunR; LA preparation = 100 mg/ml; SA preparation = 20 mg/ml) Pre-anesthetic - 0.22 to 2.2 mg/kg IM or SC Lower doses appear to be associated with fewer undesirable side effects than higher doses. 0.22 mg/kg (0.1 mg/lb) IV or 0.55 mg/kg (0.25 mg/lb) IM produces effective sedation in dogs and cats ANTICHOLINERGICS Atropine (0.5 mg/ml) - 0.044 mg/kg (0.02 mg/lb) SC; if an IV anticholinergic is needed, one-third to one-half the dose is usually administered. Glycopyrrolate (Robinul-V®, 0.2 mg/ml); 0.011 mg/kg (0.005 mg/lb) SC or IM; glycopyrrolate is the anticholinergic drug of choice in most (non-emergency) situations. BENZODIAZEPINES Diazepam (Class IV Controlled Substance; Valium® or generic diazepam; 5 mg/ml) - 0.1 to 0.44 mg/kg IV or IM; do not administer diazepam SC. Diazepam IV may cause tranquilization, no apparent effect, or some degree of excitement, especially in healthy mature animals. Its IV administration may reduce the dose of a drug used for induction of anesthesia. Midazolam (Class IV Controlled Substance; Versed® or generic midazolam; 5 mg/ml) - 0.1 to 0.44 mg/kg IV, IM or SQ; as with diazepam, may cause tranquilization, no apparent effect, or some degree of excitement, especially in healthy mature animals. Its IV administration may reduce the dose of a drug used for induction of anesthesia. COMMON INDUCTION AGENTS Etomidate (Amidate®; 2 mg/ml) An imidazole - 1 to 3 mg/kg IV for induction of anesthesia, usually after premedication with an opioid and/or diazepam (to prevent undesirable effects including myoclonus, excitement and vomiting that may occur without premeds). Alfaxalone (Alfaxan®; 10mg/ml) A water-soluble neurosteroidal anaesthetic – Canine 1-3 mg/kg IV & Feline 2-5 mg/kg IV for induction and intubation. Usually after premedication with an opioid and/or a benzodiazepine. It is advisable to stay towards the lower end of the dose range when used in conjunction with opioids & benzodiazepines. Propofol (Propoflo®; PropoFlo28; 10 mg/ml) an alkylphenol - 2 to 6 mg/kg IV for induction and intubation. Usually, administered after premedication with an opioid or tranquilizer. Given by slow injection (60-90 sec) for best effect and to minimize risks of apnea. DISSOCIATIVE AGENT Ketamine (Class III Controlled Substance; Ketaset®; 100 mg/ml) Premedication in healthy cats: 4.4 to 8.8 mg/kg IM; often used with other premeds since it has no intrinsic muscle relaxant properties. 5 mg/kg produces pretty good cooperation (IM) Complete chemical restraint or light anesthesia in healthy cats: 11 to 22 mg/kg IM; often used in combination with other drugs. As an intravenous induction drug: 1. Dose range: 2 to 11 mg/kg 2. Usually administered with an equal volume of diazepam (≈ 0.2 to 0.5 mg/kg); mixed in the same syringe. Practitioner dose is 1 ml/20 lbs IV of 1:1 combination. 3. Effective in both cats and dogs; tends to produce smoother inductions with a lower total dose if animals are premedicated (e.g., butorphanol, hydromorphone, acepromazine, or other tranquilizers or sedatives) Telazol (Class III Controlled Substance;100 mg/ml) Mixture of tiletamine and zolazepam IV induction - 1.1 to 3.3 mg/kg IV Premedication - 2.2 to 6.6 mg/kg IM MIXED KAPPA AGONIST/ MU ANTAGONIST Butorphanol (Class IV Controlled Substance; Torbugesic®; 10 mg/ml); 0.2 to 0.4 mg/kg IV, IM, SC. The maximum dose varies with clinicians' preferences. Some anesthesiologists recommend a maximum dose of 10 mg in large dogs. Short acting analgesia MU OPIOD AGONIST Fentanyl (Class II Controlled Substance; SublimazeR, 50 µg/ml) - 2 to 6 µg/kg IV for pre-anesthetic sedation; generally lower end of range used for cats Hydromorphone (Class II Controlled Substance; 2 mg/ml) - 0.1 mg/kg. May be given IM or SC for premedication. May be used IV for intra-operative analgesia. Dose in cats is 0.05-0.1 mg/kg. Methadone (Class II Controlled Substance; 10mg/mL) – 0.1 – 0.5 mg/kg, IV, IM, or SQ. Typical dose is 0.2mg/kg SQ or IV for pre-med and post-operative pain. Duration of effect is 4 – 6 hours Morphine (Class II Controlled Substance; 0.4-1 mg/kg IM; normally, morphine is not administered IV because it may induce hypotension caused by histamine release. DuramorphR (Class II Controlled substance; 10-ml ampoules; 0.5 mg/ml) has no preservatives and is used for epidural administration (0.1 mg/kg) to provide analgesia. Oxymorphone Class II Controlled Substance; 1 – ml ampoules 1.0 mg/ml) - 0.05 to 0.1 mg/kg IV, IM, or SC; generally a maximum dose of 4 mg. For IV administration, use slow injection technique and lower doses rather than rapid bolus technique. Availability may vary. Oxymorphone has no preservatives and is used for epidural administration (0.1 mg/kg) to provide analgesia. Remifentanil (Class II Controlled Substance; 1mg powder for injection). 3mcg/kg/hr to 36 mcg/kg/hr. Typical starting does is 5mcg/kg/hr. Must be used as a CRI as duration of effect is approximately 3 minutes. PARALYTICS Cisatracurium (Nimbex®, 2mg/ml) – 0.1 mg/kg IV. A nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker, duration of action is approximately 20 minutes. Patient must be under general anesthesia and mechanically ventilated. Pancuronium Bromide (Pavulon®; 1mg/ml & 2mg/ml) - 0.06 mg/kg. A nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker, duration of action is approximately 40 minutes. Patient must be under general anesthesia and mechanically ventilated. PARTIAL MU AGONIST Buprenorphine (Class III Controlled Substance; BuprenexR; 300 µg/ml); 10 to 20 µg/kg IV, IM, or SC. Longer acting analgesia good for mild to moderate pain. Good in cats. PHENOTHIAZINE Acepromazine (PromAceR, 10 mg/ml) – 0.01-0.05 mg/kg IV, IM, or SC; in most cases, the maximum dose is 1 mg. ** Note that the concentration of the commercial preparation of acepromazine is 10 mg/ml. The preparation that we normally have available in the small animal anesthesia area is 1 mg/ml. ** REVERSAL AGENTS Atipamezole (AntisedanR; 5 mg/ml) - An alpha-2 antagonist approved for the antagonism of medetomidine and dexmedetomidine in the dog. Atipamezole has not been evaluated as a routine dexmedetomidine reversal agent in cats. See the package insert for dosage recommendations (usually equal volume to medetomidine dose used). Edrophonium Chloride (Tensilon®, Enlon®; 10 mg/ml) for antagonism of nondepolarizing blocking agents. Preferred treatment. Give 0.5 mg/kg IV give slowly over 2-5 minutes. Bradycardia can be seen if given too quickly. Nalbuphine (NubainR; 20 mg/ml) - for partial opioid antagonism Dosage - 0.55 to 2.2 mg/kg Dilute 1 ml nalbuphine with saline to a total volume of 10 ml, and administer IV slowly and to effect; nalbuphine can be administered SC for a slower onset and longer duration. Naloxone (NarcanR; 0.4 mg/ml) for complete opioid antagonism General dosage: 0.044 mg/kg IV: Dilute 1 ml (0.4 mg) with 9 ml of saline; administer slowly to effect; administer the remainder SC to increase the duration of effect. SC: Administer the appropriate dosage of naloxone SC for a slower onset and longer effect. The duration of action of naloxone is relatively short, and its effectiveness will depend on the opioid being antagonized and the time that has passed since the opioid was administered. Pyridostigmine Bromide (Mestinon®; 5 mg/ml) For antagonism of nondepolarizing blocking agents. Give 0.1 – 0.3 mg/kg slowly over 10 minutes IV. Give atropine or glycopyrrolate prior to administration to prevent sever bradycardia. Tolazoline (PriscolineR; 25 mg/ml) (TolazineR; 100 mg/ml) - For antagonism of alpha-2 drugs (e.g., xylazine). Usually dosed at 2 mg/kg slowly IV to effect. Can be diluted with saline to facilitate controlled IV administration. Rapid administration or overdosing can lead to excitement. The dosage needed will vary with the original dose of xylazine and the amount of time that has passed since the xylazine was administered. Yohimbine (YobineR) (2 mg/ml) - For antagonism of alpha-2 drugs (e.g., xylazine). The dose on the label is 0.11 mg/kg (0.05 mg/lb) IV for dogs. The drug should be administered slowly and to effect, and the drug can be diluted with saline to facilitate controlled IV administration. Rapid administration or overdosing may lead to excitement. The dosage needed will vary with the original dose of xylazine and the amount of time that has passed since the xylazine was administered. Ketamine Infusion Dilute Ketamine to 10mg/ml Loading dose: 0.5mg/kg IV Intraop Dose: 10 mcg/kg/min Weight in Kg Dose: 10mcg/kg/min Milliliters per hour 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 0.06 0.12 0.18 0.24 0.30 0.36 0.42 0.48 0.54 0.60 0.66 0.72 0.78 0.84 0.90 0.96 1.0 1.1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.3 1.4 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.6 1.7 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.9 2.0 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 Postop Dose: 2 mcg/kg/min Dose: 2mcg/kg/min Milliliters per hour 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.10 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.16 0.17 0.18 0.19 0.20 0.22 0.23 0.24 0.25 0.26 0.28 0.29 0.30 0.31 0.32 0.34 0.35 0.36 0.37 0.38 0.40 0.41 0.42 0.43 0.44 0.46 0.47 0.48 Lidocaine Infusion Concentration: 20 mgs/ml Loading dose: 1 mg/kg IV Weight in Kg 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Intraop analgesic: 25-50 mcg/kg/min Cardiac Arrythmias: 50 mcg/kg/min – 100mcg/kg/min Dose: 25mcg/kg/min Dose: 50mcg/kg/min Dose: 75 mcg/kg/min Milliliters per hour Milliliters per hour Milliliters per hour 0.08 0.15 0.23 0.30 0.38 0.45 0.53 0.60 0.68 0.75 0.83 0.90 0.98 1.1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.9 3.0 0.15 0.30 0.45 0.60 0.75 0.90 1.1 1.2 1.4 1.5 1.7 1.8 2.0 2.1 2.3 2.4 2.6 2.7 2.9 3.0 3.2 3.3 3.5 3.6 3.8 3.9 4.1 4.2 4.4 4.5 4.7 4.8 5.0 5.1 5.3 5.4 5.6 5.7 5.9 6.0 0.23 0.45 0.68 0.90 1.1 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.3 2.5 2.7 2.9 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4.1 4.3 4.5 4.7 5.0 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.9 6.1 6.3 6.5 6.8 7.0 7.2 7.4 7.7 7.9 8.1 8.3 8.6 8.8 9.0 Dose: 100mcg/kg/min Milliliters per hour 0.30 0.60 0.90 1.2 1.5 1.8 2.1 2.4 2.7 3.0 3.3 3.6 3.9 4.2 4.5 4.8 5.1 5.4 5.7 6.0 6.3 6.6 6.9 7.2 7.5 7.8 8.1 8.4 8.7 9.0 9.3 9.6 9.9 10.2 10.5 10.8 11.1 11.4 11.7 12.0 Fentanyl Infusion Concentration: 50 mcg/ml Loading Dose: 2-5 mcg/kg IV Wt Kg 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Dose: 3 mcg/kg/hr Milliliters per hour 0.06 0.12 0.18 0.24 0.30 0.36 0.42 0.48 0.54 0.60 0.66 0.72 0.78 0.84 0.90 0.96 1.0 1.1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.3 1.4 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.6 1.7 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.9 2.0 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 Anaglesic: 3-10 mcg/kg/hr Dose: 4 mcg/kg/hr Milliliters per 0.08 0.16 0.24 0.32 0.40 0.48 0.56 0.64 0.72 0.80 0.88 0.96 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 3.0 3.0 3.1 3.2 Dose: 5 mcg/kg/hr Milliliters per 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.50 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 4.0 Cardiac TIVA: 48 mcg/kg/hr Dose: 10 mcg/kg/hr Milliliters per 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4.0 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6.0 6.2 6.4 6.6 6.8 7.0 7.2 7.4 7.6 7.8 8.0 Dose: 48 mcg/kg/hr Milliliters per 0.96 1.9 2.9 3.8 4.8 5.8 6.7 7.7 8.6 9.6 10.6 11.5 12.5 13.4 14.4 15.4 16.3 17.3 18.2 19.2 20.2 21.1 22.1 23.0 24.0 25.0 25.9 26.9 27.8 28.8 29.8 30.7 31.7 32.6 33.6 34.6 35.5 36.5 37.4 38.4 Remifentanil Infusion Diluted to a concentration to 50 mcg/ml Wt Kg Dose: 0.05 mcg/kg/min Milliliters per hour 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 0.06 0.12 0.18 0.24 0.30 0.36 0.42 0.48 0.54 0.60 0.66 0.72 0.78 0.84 0.90 0.96 1.0 1.1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.3 1.4 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.6 1.7 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.9 2.0 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 Dose: 0.1 Dose: 0.2 Dose: 0.3 Dose: 0.4 Dose: 0.5 Dose: 0.6 mcg/kg/min mcg/kg/min mcg/kg/min mcg/kg/min mcg/kg/min mcg/kg/min Milliliters per Milliliters per Milliliters per Milliliters Milliliters per Milliliters hour hour hour per hour hour per hour 0.12 0.24 0.36 0.48 0.60 0.72 0.84 0.96 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.8 2.9 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.6 4.7 4.8 0.24 0.48 0.72 0.96 1.2 1.4 1.7 1.9 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.9 3.1 3.4 3.6 3.8 4.1 4.3 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.3 5.5 5.8 6.0 6.2 6.5 6.7 7.0 7.2 7.4 7.7 7.9 8.2 8.4 8.6 8.9 9.1 9.4 9.6 0.36 0.72 1.1 1.4 1.8 2.2 2.5 2.9 3.2 3.6 4.0 4.3 4.7 5.0 5.4 5.8 6.1 6.5 6.8 7.2 7.6 7.9 8.3 8.6 9.0 9.4 9.7 10.1 10.4 10.8 11.2 11.5 11.9 12.2 12.6 13.0 13.3 13.7 14.0 14.4 0.48 0.96 1.4 1.9 2.4 2.9 3.4 3.8 4.3 4.8 5.3 5.8 6.2 6.7 7.2 7.7 8.2 8.6 9.1 9.6 10.1 10.6 11.0 11.5 12.0 12.5 13.0 13.4 13.9 14.4 14.9 15.4 15.8 16.3 16.8 17.3 17.8 18.2 18.7 19.2 0.60 1.2 1.8 2.4 3.0 3.6 4.2 4.8 5.4 6.0 6.6 7.2 7.8 8.4 9.0 9.6 10.2 10.8 11.4 12.0 12.6 13.2 13.8 14.4 15.0 15.6 16.2 16.8 17.4 18.0 18.6 19.2 19.8 20.4 21.0 21.6 22.2 22.8 23.4 24.0 0.72 1.4 2.2 2.9 3.6 4.3 5.0 5.8 6.5 7.2 7.9 8.6 9.4 10.1 10.8 11.5 12.2 13.0 13.7 14.4 15.1 15.8 16.6 17.3 18.0 18.7 19.4 20.2 20.9 21.6 22.3 23.0 23.8 24.5 25.2 25.9 26.6 27.4 28.1 28.8 Dobutamine/Dopamine Infusion Dose: 1-10 ug/kg/min 1 drop/4s = 2ug/kg/min Add dobutamine to a 250mL bag of 5% Dextrose or 0.9% NaCl Administer with 60 drop/ml dripset at 1 drop/4s, then titrate to effect Weight (Kg) 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 35 40 45 50 ug/min 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 52 56 60 70 80 90 100 ug/ml 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240 280 320 360 400 mg/250ml 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 52 56 60 70 80 90 100 Dobutamine (mL) 0.32 0.64 0.96 1.3 1.6 1.9 2.2 2.6 2.9 3.2 3.5 3.8 4.2 4.5 4.8 5.6 6.4 7.2 8 Dopamine (mL) 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.75 2 2.25 2.5 Dopamine Dose Ranges: Dopamine is a mixed dopaminergic, beta agonist and alpha 1 agonist with dose dependant results. At the lower dosage range of 1-3 mcg/kg/min will increase renal and splanchnic vessel dilation due to the dopaminergic effect – resulting in increased renal blood flow. The mid-range dose of 5-8 mcg/kg/min results in mild beta 1 and alpha 1 properties resulting in positive inotropy, chronotropy and vasoconstriction. The high range of 8 – 20 mcg/kg/min of dopamine results in a strong alpha 1 response and acts as a potent vasoconstrictor.