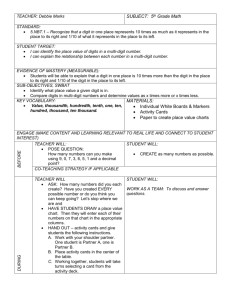
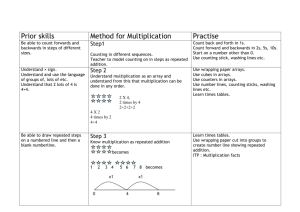
Unpacked Math NBT Standards
advertisement

1234567891234567891234567891 2345678912345678912123456789 1234567893456789123456789123 4567891234567891234567891234 CCSS Numbers and Operations in 5678912345678912345678912345 Base 10 (NBT) 6789qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxc12345 Unpacking the Standards Grade 4 6789123456789mqwertyuiopasdfg hj12345612345678789klzxcvbnmw eruioasd123456789123456789123 4567891234567891234567891234 5678912345678912345678912345 Standard: 4.NBT.1 Math Practices: MP2, MP6, MP7 Cluster (m/s/a) Related CA Standard NEW Recognize that a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. Essential Skills/Concepts Read and write numbers up to 1,000,000 based on the meanings of the digits in each place both in real-life situations and abstractly Understand that each place is 10 times the value of the place to the immediate right Understand that by multiplying by 10, each unit in a place becomes one unit in the next left place Understand the role of commas in large numbers Be able to read each sequence of three digits made by commas as hundreds, tens, and ones followed by the name of the unit (e.g., thousand, million) Academic Vocabulary: Place value standard form Digit word form Unit expanded form Period Value Teaching Notes/Strategies Build larger numbers by using graph paper with very small squares or dot array paper and labeling examples in each place with digits and words (e.g. ten thousand and 10,000) to mimic Base 10 blocks Use Base 10 blocks, dot array paper, or have students make drawings of numbers (mimicking base 10 blocks) to increase understanding of x 10 Use 0-9 digit cards in a place- value pocket chart to read numbers and solve problems. Use clearboards with place value charts inserted and have students write numbers and read them. Play “What’s My Number?” riddles by giving clues about each digit in a number such as: The digit in the thousands place is 10 times the digit in the ones place The digit in the hundred thousands place is 200 times the number in the tens place. Etc. Play “I Have… Who Has...?” card game to practice reading large numbers properly. Ask “If” types of questions about numbers (i.e., “If this digit were to move to the thousands place, it would have a value of__.” OR “If I wanted to move this digit to the ten thousands place, I would need to multiply by ___.” Use cards that show the values of numbers (i.e., 7,000; 800; 90; 6 and have students create numbers by overlapping them—this would be the number 7,896) Resources Manipulatives: Base 10 blocks Graph paper with very small squares or dot array paper Place value charts/mats Clearboards with place value charts to write on Math Journal with place value chart Anchor chart of place value chart showing x10 for each place value to the left. Value Number cards Standard: 4.NBT.2 Cluster (m/s/a) Math Practices: MP2, MP4, MP6, MP7 Related CA Standard 4.NS.1.1, 4.NS.1.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons. Essential Skills/Concepts Teaching Notes/Strategies Read and write numbers up to 1,000,000 based on the meanings of the digits in each place both in real-life situations and abstractly Play “I Have… Who Has...?” card game to practice reading and writing large numbers properly. Manipulatives: Base 10 blocks Use cards that show the values of numbers (i.e., 7,000; 800; 90; 6 and have students create numbers by overlapping them—this would be the number 7,896) Place value charts/mats Use clearboards with place value charts inserted and have students write numbers, read them, and compare them. Math Journal with place value chart Create numbers using drawings or base 10 blocks to compare them. Numeral, Word and Expanded Understand the role of commas in large numbers Be able to read each sequence of three digits made by commas as hundreds, tens, and ones followed by the name of the unit (e.g., thousand, million) Be able to compare large numbers by using the <, =, or > signs. Academic Vocabulary: Place value standard form Digit word form Unit expanded form Period Value Less than and < sign Greater than and > sign Equal and = sign Align numbers in a place value chart to compare them. Resources Clearboards with place value charts to write on Form Place Value Triangle Both available at http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com Math Practices: MP2, MP6 Standard: 4.NBT.3 Cluster (m/s/a) Related CA Standard 4.NS.1.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. Essential Skills/Concepts Know and understand the names of the place values up to the millions place Know and understand the values of each digit in a number up to the millions place in real-life situations and abstractly Build on the skill of rounding from previous grades to round to the nearest 10s , 100s, 1,000s, 10,000s, 100,000s, and/or 1,000,000s place of a multi-digit number Make reasonable estimates of numerical values using the skill of rounding. Academic Vocabulary: Rounding Estimate Place value Digit Teaching Notes/Strategies Sample problem: The population of Midtown, USA, was last recorded to be 76,398. The city council wants to round the population to the nearest thousand for a business brochure. What number should they round the population to? Stack numbers vertically to see the relationships between the rounded number before/after the number to be rounded: Resources Manipulatives: Base 10 blocks Dot arrays Number line counting by 10s Number line counting by 100s Number line counting by 1000s, Etc. 77,000 76,398 76,000 Use a number line counting by 10s, 100s, 1,000s, etc. to help determine which number is closest to the number being rounded. Use dot arrays to represent numbers and the “10” or “100” before/after to determine the closest number. Use a rounding “algorithm” or song (Example: put a box around the place to round to, circle the numbers after it to become zeros, draw an arrow to the number to the right of the box—4 or less stays the same, 5 or more add one more.) Present “real-life” situations to give context to rounding and have students practice giving reasonable estimates. Have partner discussions/journal writes about why estimates are reasonable or not. Place value chart to stack numbers vertically Round to the nearest ten Round to the nearest hundred Both available at http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com Standard: 4.NBT.4 Cluster (m/s/a) Math Practices: MP2, MP5, MP7, MP8 Related CA Standard 4.NS.3.1 Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. Essential Skills/Concepts Fluency in basic addition/subtraction facts (not essential, but desired) Know the steps of the standard algorithm to add and subtract multidigit numbers to 1,000,000 Teaching Notes/Strategies Use Base 10 blocks to demonstrate one-forten trades between adjacent places in a number they are adding or subtracting Direct Instruction on the steps of the algorithm. Resources Manipulatives: Base 10 blocks Graph paper Board math Understand and can explain or demonstrate what the steps of the standard algorithm mean mathematically Have students explain to a partner or write in a journal the steps of the algorithm and what they mean mathematically Touchmath Use one-for-ten trades between adjacent places in a number they are adding or subtracting Use different colors during the steps of the algorithm for emphasis on each step White boards or clearboards Academic Vocabulary: Trades, regrouping, or exchanging Use graph paper to keep numbers aligned as students rewrite problems from a book. This can reduce errors and emphasize place value. Use Touchmath counting and worksheets for students who are having difficulty remembering/understanding the steps or make frequent errors (ask Kirsten Werk for these resources). White board or clearboard practice Small group instruction/practice Error analysis of problems Colored pencils/pens Place value charts to align numbers Adding and Subtracting Multi-Digit Numbers Addition and Subtraction Number Stories Both available at http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com Standard 4.NBT.5 Cluster (m/s/a) Math Practices: MP2, MP3, MP4, MP5, MP7 Related CA Standard 4.NS.3.2, 4.NS.3.3 Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models. Essential Skills/Concepts Extend learning from previous grades to multiplying and dividing with numbers greater than 100 using methods the student understands and can explain. Use visual representations such as area and array models to draw and connect to equations to support reasoning and explanation of methods. After extensive work and mastery of understanding with the above, students can come to learn the standard algorithms as abbreviations or summaries of their previous reasonings. Academic Vocabulary: Area Array Factoring Teaching Notes/Strategies Use various methods to teach multiplying with numbers greater than 100. Some of these may include: Area models with and without base 10 blocks Rectangular array models Use of base 10 blocks Use factoring Use repeated addition Use expanded notation Use real-life scenarios to give meaning to multiplication/division. Estimate for reasonableness. Have students write their explanations in a math journal or chat with a partner to discuss their method. Resources Manipulatives: Base 10 blocks Graph paper Clearboards Math journals Multiplication Strategy: Doubling and Halving Multiplication Strategy: Partial Products (1) Multiplication Strategy: Partial Products (2) Multiplication Race (1 x 3 digit) Multiplication Race (2 x 2 digit) Multiplication Number Story Breaking Apart a Factor Multiplication Bump (x100) Make the Largest Product Make the Smallest Product Expanded notation All available at http://www.k- Reasonable 5mathteachingresources.com Estimate Standard: 4.NBT.6 Cluster (m/s/a Math Practices: MP2, MP3, MP4, MP5, MP7 Related CA Standard 4.NS.3.2, 4.NS.3.4 Find whole-number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and one-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models. Essential Skills/Concepts Relate area models used to teach multiplication to teach the related division problem. Begin teaching standard division algorithm, but it will continue in 5th grade and mastery by 6th grade. Find whole number quotients with remainders and know the appropriate way to write the result (ex: 195÷9 = 21 with 6 leftover can be written as 195 = 21(9) + 6. Equations should be given context for understanding and can be related to 195÷9 = 21 6/9 which students will write in later grades. Avoid 195÷9 = 21 R 6. Teaching Notes/Strategies Resources Use various methods to teach dividing with numbers greater than 100. Some of these may include: Using properties of operations Using the relationship between multiplication and division Using equations Using rectangular array models Using area models Use factoring Use repeated subtraction Use expanded notation “Divvy Out” Stacking Method for division Manipulatives: Base 10 blocks Use real-life scenarios to give meaning to division. Division Strategy: Partition the Estimate for reasonableness. Estimate the Quotient Have students write their explanations in a math journal or chat with a partner to discuss their method. Ver.1 Graph paper Clearboards Math journals At http://www.k5mathteachingresources.com Division Strategy: Partial Quotients (1) Division Strategy: Partial Quotients (2) Dividend Remainders Who Has the Largest Quotient? Who Has the Largest Quotient? Ver. 2 Academic Vocabulary: Area estimate Various Math symbols for division array remainders , /, ¼, ÷ expanded notation reasonable divisor quotient