Semester #2 Objectives for ELL English Grammar: Language Strand
advertisement

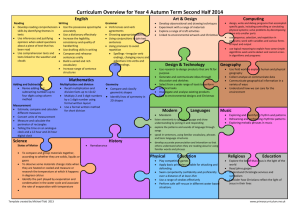
Semester #2 Objectives for ELL English Grammar: Language Strand Standard 1: The student will identify and apply conventions of standard English in his or her communications. Pre-Emergent Emergent Basic Verbs (V) The student will demonstrate knowledge of sentence construction: PE-26: choosing a past E-26: choosing a past B-26: choosing a past perfect tense verb (e.g., perfect tense verb (e.g., “I perfect tense verb (e.g., “I had walked.” versus had walked.” versus “I “I had walked.” versus “I “I walked.”) to complete walked.”) to complete walked.”) to complete declarative, negative, declarative, negative, and declarative, negative, and and interrogative interrogative sentences interrogative sentences sentences with subject- with subject-verb with subject-verb verb agreement. agreement. agreement. PE-27: choosing a future E-27: choosing a future B-27: choosing a future perfect tense verb to perfect tense verb to perfect tense verb to complete declarative, complete declarative, complete declarative, negative, and negative, and interrogative negative, and interrogative sentences sentences with subjectinterrogative sentences with subject-verb verb agreement. (e.g., “I with subject-verb agreement. (e.g., “I will will have walked.” versus “I agreement. (e.g., “I will have walked.” versus “I will walk.”) have walked.” versus “I will walk.”) will walk.”) PE-28: choosing a E-28: choosing a present B-28: choosing a present present perfect perfect progressive tense perfect progressive tense progressive tense verb to verb to complete verb to complete complete declarative, declarative, negative, and declarative, negative, and negative, and interrogative sentences interrogative sentences interrogative sentences with subject-verb with subject-verb with subject-verb agreement. (e.g., “I have agreement. (e.g., “I have agreement. (e.g., “I have been swimming.” versus “I been swimming.” versus been swimming.” versus “I am swimming.”) “I am swimming.”) am swimming.”) Low Intermediate High Intermediate LI-26: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative simple sentences using past perfect tense verbs with subject-verb agreement and with instructional support. LI-27: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative simple sentences using future perfect tense verbs with subject-verb agreement and with instructional support. HI-26: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences using past perfect tense verbs with subject-verb agreement. LI-28: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative simple sentences using present perfect progressive tense verbs (subjectverb agreement) with instructional support. HI-28: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences using present perfect progressive tense verbs with subject-verb agreement. HI-27: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences using future perfect tense verbs with subject-verb agreement. Semester #2 Objectives for ELL English Grammar: Language Strand Standard 1: The student will identify and apply conventions of standard English in his or her communications. Pre-Emergent Emergent Basic Low Intermediate High Intermediate Adjectives Pronouns Verbs (V) The student will demonstrate knowledge of sentence construction: PE-29: choosing a past perfect progressive tense verb to complete declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences with subject-verb agreement. (e.g., “I had been swimming.” versus “I was swimming.”) PE-30: choosing a future perfect progressive tense verb to complete declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences with subject-verb agreement. (e.g., “I had been swimming.” versus “I was swimming.”) PE-4: categorizing personal subjective, personal objective, and personal possessive pronouns. PE-8: listing comparative and superlative adjectives (e.g., -er, -est); selecting a comparative or superlative adjective to complete a given sentence. E-29: choosing a past perfect progressive tense verb to complete declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences with subject-verb agreement. (e.g., “I had been swimming.” versus “I was swimming.”) PE-30: choosing a future perfect progressive tense verb to complete declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences with subject-verb agreement. (e.g., “I had been swimming.” versus “I was swimming.”) E-4: categorizing personal subjective, personal objective, and personal possessive pronouns. E-8: listing comparative and superlative adjectives (e.g., -er, -est); selecting a comparative or superlative adjective to complete a given sentence. B-29: choosing a past perfect progressive tense verb to complete declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences with subject-verb agreement. (e.g., “I had been swimming.” versus “I was swimming.”) B-30: choosing a future perfect progressive tense verb to complete declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences with subject-verb agreement. (e.g., “I had been swimming.” versus “I was swimming.”) B-4: selecting personal subjective, personal objective, and personal possessive pronouns to complete a given sentence. LI-29: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative simple sentences using past perfect progressive tense verbs with subject-verb agreement and with instructional support. LI-30: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative simple sentences using future perfect progressive tense verbs with subject-verb agreement and with instructional support. LI-4: differentiating between personal subjective, personal objective, and personal possessive pronouns and their placement in sentences. B-8: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives with support. (e.g., -er, -est; more/most/ less/least) LI-8: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives; listing irregular comparative and superlative adjectives. (e.g., bad, worse, worst) HI-29: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences using past perfect progressive tense verbs with subject-verb agreement. HI-30: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences using future perfect progressive tense verbs with subject-verb agreement. HI-4: differentiating between personal subjective, personal objective, and personal possessive pronouns and their placement in sentences. HI-8: producing declarative, negative, and interrogative sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives, including irregular adjectives. Semester #2 Objectives for ELL English Grammar: Language Strand Standard 1: The student will identify and apply conventions of standard English in his or her communications. Pre-Emergent Emergent Basic Adverbs The student will demonstrate knowledge of sentence construction: PE-5: selecting E-5: selecting comparative B-5: using comparative comparative and and superlative adverbs to and superlative adverbs superlative adverbs to complete a given with instructional support. complete a given sentence. sentence. PE-8: producing sentences with a subject, verb, indirect object, and direct object (S-V-IO-DO) with subject-verb agreement, using a sentence frame. Sentence Construction PE-10: producing sentences with a subject, verb, object and prepositional phrase (SV-O-P) with subject-verb agreement, using a sentence frame. PE-11,12,13: inserting an adverb within a given sentence to modify the verb, an adjective, and/or an adverb. PE-14: producing compound sentences with two given independent clauses. (independent clause + conjunction + independent clause) PE-24: completing a sentence frame consisting of a dependent clause + comma + independent clause to form a complex sentence. Low Intermediate High Intermediate LI-5: using comparative and superlative adverbs. HI-5: using comparative and superlative adverbs, including irregular adverbs. E-8: producing sentences with a subject, verb, indirect object, and direct object (S-V-IO-DO) with subject-verb agreement, using a sentence frame. B-8: producing sentences with a subject, verb, indirect object, and direct object (S-V-IO-DO) with subject-verb agreement. LI-8: producing complete sentences with a subject, verb, indirect object, and direct object (S-V-IO-DO) with subject-verb agreement. HI-8: producing complete sentences with a subject, verb, indirect object, and direct object (S-V-IO-DO) with subject-verb agreement. E-10: producing sentences with a subject, verb, object and prepositional phrase (S-V-O-P) with subjectverb agreement, using a sentence frame. B-10: producing sentences with a subject, verb, object and prepositional phrase (S-VO-P) with subject-verb agreement, using a sentence frame. LI-10: producing sentences with a subject, verb, object, and prepositional phrase (S-V-O-P) with subjectverb agreement. HI-10: producing sentences with a subject, verb, object, and prepositional phrase (S-V-O-P) with subjectverb agreement. E-11,12,13: inserting an adverb within a given sentence to modify the verb, an adjective, and/or an adverb. B-11,12,13: producing sentences with an adverb to modify the verb, an adjective, and/or an adverb. LI-11,12,13: producing sentences with an adverb to modify the verb, an adjective, and/or an adverb. HI-11,12,13: producing sentences with an adverb to modify the verb, an adjective, and/or an adverb. E-14: producing compound sentences with two given independent clauses. (independent clause + conjunction + independent clause) E-24: completing a sentence frame consisting of a dependent clause + comma + independent clause to form a complex sentence. B-14: producing compound sentences. (independent clause + conjunction + independent clause) LI-14: producing compound sentences. (independent clause + conjunction + independent clause) HI-14: producing compound sentences. (independent clause + conjunction + independent clause) B-24: completing a sentence frame consisting of a dependent clause + comma + independent clause to form a complex sentence. LI-24: completing a sentence frame consisting of a dependent clause + comma + independent clause to form a complex sentence. HI-24: producing a complex sentence consisting of a dependent clause + comma + independent clause. Semester #2 Objectives for ELL English Grammar: Language Strand Standard 1: The student will identify and apply conventions of standard English in his or her communications. Pre-Emergent Emergent Basic Questions Sentence Construction The student will demonstrate knowledge of sentence construction: PE-26: completing a E-26: completing a B-26: completing a compound-complex compound-complex compound-complex sentence frame sentence frame consisting sentence frame consisting consisting of two of two independent of two independent independent clauses clauses and one or more clauses and one or more and one or more dependent clauses. dependent clauses. dependent clauses. Low Intermediate High Intermediate LI-26: producing a compound-complex sentence frame consisting of two independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses. HI-26: producing a compound-complex sentence frame consisting of two independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses. HI-15-22: producing interrogative sentences beginning with “who, what, when, where, why, how, which, whose.” PE-15-22: completing interrogative sentences frames beginning with “who, what, when, where, why, how, which, whose.” E-15-22: producing interrogative sentences beginning with ““who, what, when, where, why, how, which, whose.” B-15-22: producing interrogative sentences beginning with “who, what, when, where, why, how, which, whose.” LI-15-22: producing interrogative sentences beginning with “who, what, when, where, why, how, which, whose.” PE-24: producing Yes/No questions beginning with a modal auxiliary verb by using sentence frames. E-24: producing Yes/No questions beginning with a modal auxiliary verb by using sentence frames. B-24: producing Yes/No questions beginning with a modal auxiliary verb by using sentence frames. LI-24: producing Yes/No HI-24: producing Yes/No questions beginning with questions beginning with a modal auxiliary verb. a modal auxiliary verb.