Unit II Sol Review
advertisement

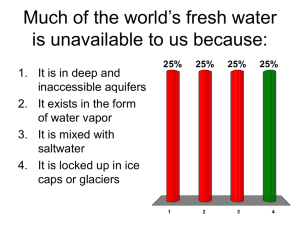
What do I need to know about physical geography? Climate Characteristics Temperature Precipitation Seasons(hot/cold; wet/dry) Climate Elements Influence of latitude (It gets colder the farther north or south of the equator you go) Influence of winds Influence of elevation (It gets colder when you gain elevation) Proximity to water (water has a moderating influence on climate – the summers are cooler and the winters warmer) Mountains Rocky Mountains create rain shadows on leeward slopes Himalayas block rain to create steppes and deserts in Central Asia Effects of Climate Crops – Different crops grow in different climates Clothing Housing – log houses in areas with many trees, adobe houses in dry areas, tiled roof in Mediterranean Natural hazards – droughts, floods World Climate Regions Low latitudes – tropical wet, tropical wet and dry, arid, semiarid, highland Middle latitudes – semiarid, arid, Mediterranean, humid continental, humid subtropical, marine west coast, highland High latitudes – subarctic, tundra, icecap Vegetation Regions Rain forest (Amazon rain forest Brazil) Savanna (tropical grassland in Africa) Desert (Arid) Middle latitude forests Taiga (in subarctic climate, coniferous trees) Tundra (cold grassland with some bushes, lichens, and mosses located in northern Canada, Russia) Weather Phenomena Monsoons – Seasonal wind that brings rain to South and Southeast Asia. Causes flooding but provides water for crops Typhoons – Same as hurricane in Pacific Ocean Hurricanes – Atlantic Ocean Tornadoes – United States Physical and Ecological Processes Earthquakes Floods Volcanoes Erosion Human Impact on Environment Water Diversion Aral Sea – shrinking due to over irrigation, located in Central Asia Colorado River – location of Hoover Dam, used for irrigation in Southwest U.S. Aswan High Dam – located on Nile River, built to stop flooding of river and provide water for irrigation and hydroelectric power Canals, reservoirs, irrigation Changing Landscapes Agricultural terracing (China and Southeast Asia) Polders (reclaimed land from the sea in the Netherlands) Deforestation (Nepal, Brazil, Malaysia) Desertification (expansion of arid conditions into non-arid areas – basically the desert is getting bigger, big problem in North Africa near the Sahara and parts of Asia) Picture of an arid climate zone (desert) Human Impact on Environment Environmental Changes Acid rain (causes by air pollution/problem in Black Forest in Germany and Eastern North America Pollution (air pollution in Mexico City, nuclear pollution near Chernobyl, oil spills Influence of Technology Agriculture (fertilizers, mechanization), people can grow more food now because of tractors and better growing practices Energy usage (most countries use fossil fuels but some countries have nuclear power Automobiles – the automobile has impacted the environment because people have to make roads, parking lots, and cities have grown with suburbs Airplanes – airport expansion/noise Environmental Impact on Humans Settlement patterns (some places are too hot or cold) Housing materials Agricultural activity Types of recreation Transportation patterns Picture of agricultural terracing in Asia Picture showing ship sitting on the bottom of the Aral Sea Picture of Hoover Dam on the Colorado River Map showing the direction of the seasonal wind to South and Southeast Asia (monsoon) Diagram showing how a polder is made in the Netherlands. Note the windmills, a common cultural landscape in the Netherlands. Picture of two cooling towers of a nuclear power plant