Dragon Genetics Lab
advertisement

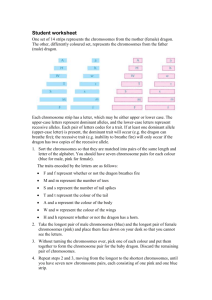
Pre Lab Dragon Genetics Lab – Introduction to Genetics Define the following terms in your own words: Homologous – Phenotype – Genotype – Homozygous – Heterozygous – Dominant – Recessive Background Information Traits are encoded on structures called chromosomes. When a sperm fertilizes an egg, the resulting offspring should receive an equal number of chromosomes from mom and dad. A pair of homologous dragon chromosomes is show below. Determine the genotype and phenotype that would result in the offspring of these two dragons, and fill in the missing information in the data table below. FIRE BREATHING (F) BODY COLOR (G) not fire breathing (f) body color (g) TRAIT Fire breathing or not Body Color Spikes (present or absent) GENOTYPE Ff spikes absent (s) SPIKES PRESENT (S) PHENOTYPE Fire breathing Procedure In this activity, you will “mate” with a dragon of the opposite gender to create a “baby dragon.” You will then use your knowledge of genetics to determine the genotype and phenotype for each of 13 traits in your baby dragon. You will also construct a picture of your baby dragon. Steps 1. Select either a dragon egg or sperm from the front of the classroom. 2. Find your mate (the person who as the egg or sperm with the matching number) 3. Remove all of the chromosomes from your respective egg and sperm. 4. Find chromosome #1 (C#1) from both the mates. Pair these two homologous chromosomes together. 5. Repeat step 3 for each of the remaining homologous chromosomes. At the end of this step you should have all 4 homologous chromosome pairs that make up your baby dragon. 6. Using the DRAGON KEY, determine your baby’s genotype and phenotype for all of the traits listed on the chromosomes. Record this information in the proper spaces of the DRAGON DATA TABLE. 7. Refer to the phenotypes listed on your data table and include each phenotype on your drawing of your baby dragon. Be sure to use colors as well. 8. Please return all your materials at the end of this lab activity. DRAGON KEY Upper case letters represent dominant alleles; Lower case letters represent recessive alleles N – long neck B – black tail spikes R – red wings n – short neck b – red tail spikes r – yellow wings H – horn present h – horn absent E – Red eye e – white eye W – yellow body w – white body S – spikes on end of tail s – no spikes on end of tail F – fire breathing f – not fire breathing K – freckles k – no freckles T – three toes t – four toes L – long tail l – short tail XX – Female with no ear frills XY – Male with ear frills G – Green Body color g – Blue Body color Chromosome pair number 1 2 3 Trait Neck length Eye Color Horn? Spikes? Tail length Body color Color of wings Number of toes Belly color Color of spikes DRAGON DATA TABLE Genotype Homozygous/ Heterozygous Phenotype Freckles? 4 Fire breathing? Ear frills?