Formation of Sedimentary Rocks - Tanque Verde Unified School
advertisement
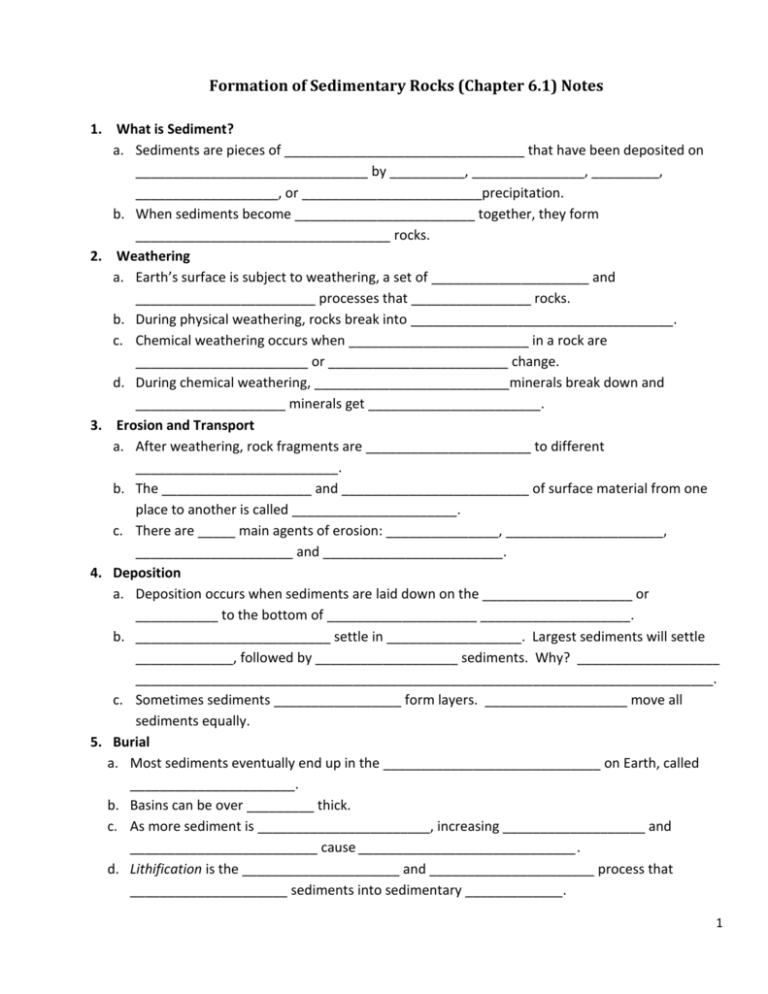
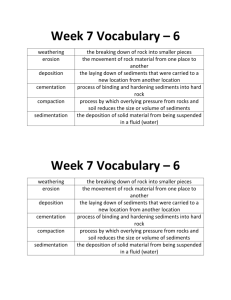
Formation of Sedimentary Rocks (Chapter 6.1) Notes 1. What is Sediment? a. Sediments are pieces of ________________________________ that have been deposited on _______________________________ by __________, _______________, _________, ___________________, or ________________________precipitation. b. When sediments become ________________________ together, they form __________________________________ rocks. 2. Weathering a. Earth’s surface is subject to weathering, a set of _____________________ and ________________________ processes that ________________ rocks. b. During physical weathering, rocks break into ___________________________________. c. Chemical weathering occurs when ________________________ in a rock are _______________________ or ________________________ change. d. During chemical weathering, __________________________minerals break down and ____________________ minerals get _______________________. 3. Erosion and Transport a. After weathering, rock fragments are ______________________ to different ___________________________. b. The ____________________ and _________________________ of surface material from one place to another is called ______________________. c. There are _____ main agents of erosion: _______________, _____________________, _____________________ and ________________________. 4. Deposition a. Deposition occurs when sediments are laid down on the ____________________ or ___________ to the bottom of ____________________ ____________________. b. __________________________ settle in __________________. Largest sediments will settle _____________, followed by ___________________ sediments. Why? ___________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. c. Sometimes sediments _________________ form layers. ___________________ move all sediments equally. 5. Burial a. Most sediments eventually end up in the _____________________________ on Earth, called ______________________. b. Basins can be over _________ thick. c. As more sediment is _______________________, increasing ___________________ and _________________________ cause _____________________________. d. Lithification is the _____________________ and ______________________ process that _____________________ sediments into sedimentary _____________. 1 6. Lithification a. Lithify comes from the ______________ word lithos, meaning ____________. b. Lithification begins with ________________________. The ________________ of over-lying sediments forces the grains ________________________________, causing ______________________________________. Draw compaction below. c. Sediments buried deep enough (__________) experience _________________________ that are high enough for ____________________________________ to occur. d. Cementation occurs when mineral growth ____________________ (glues) sediment grains ___________________________. e. ________________ and __________________________ are common cements. 7. Features of Sedimentary Rocks a. Bedding – ____________________________ layering of sediments. b. Graded bedding – When bedding becomes progressively _____________________ and _____________________ towards _______________________ layers. c. Cross-bedding – horizontal layers that are ____________________ and __________________ each other. Sketch examples of each: Horizontal bedding Graded bedding Cross-bedding d. Fossils – the _________________________________, impressions, or other evidence of onceliving _________________________. e. When an organism _________, it may be ________________ before it ___________________. If remains are undisturbed, it might become preserved as a ___________________. f. During lithification, all or parts of the organism can be replaced with _____________________ and turn into ______________. 2