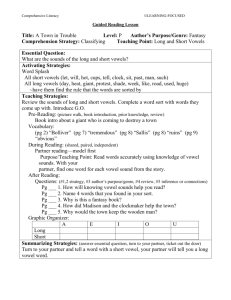
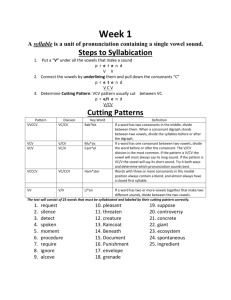
How the sounds of English are translated into
advertisement

How the sounds of English are translated into our written language Or in other words – Phonics! Phonemic awareness – hearing sounds, distinguishing b from p, etc. Alphabetic principle -- that letters represent sounds -- learn the sounds of each letter CVC words : words with consonant, vowel consonant such as cat Work on short vowel sounds, e and i cause the most confusion Ccvc and cvcc : words such as jump and flip Silent e rule introduces long vowels : vowels say their names in these words like, cake, cute Digraphs to learn : th, sh, ch, wh, rarely ph (the h brothers) also at end of words such as ck, ng Long vowels in words with special patterns such as: ild, old, all, alk, oll, ind Two vowels go walking rule: two vowels often make a long vowel of the first one -- seat, coat, rain The R sisters rule or r controlled vowels: ar, er, ir, ur, or Vowel dipthongs: these crazy ones just need to be memorized Ay, oi, oy, ow, ou, ew, eu, ea, ie, igh, ue, eigh, aw, au Soft g and soft c when followed by e, i, or y Syllables compound words, common endings such as ful, ing, ed, ness divide between double consonant (dinner ) and divide between different consonants (winter) divide when there is only one consonant in the middle: pilot vs. lemon don’t divide up dipthongs such as ee, oa, ow, etc. watch for syllables ending in le and y Then we move away from phonics toward semantics or the meaning of chunks of words Examples are a study of prefixes and suffixes such as: ness, less, ous, or, ity, ture, ment, tion etc.