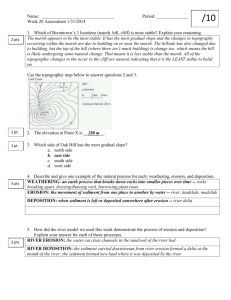
Erosion Notes
advertisement

Recall Notes: 51: TLW understand what creates erosion. 53: TLW will understand new vocabulary associated with soil: weathering, mechanical, chemical, soil, topography, erosion, mass movement, acid rain, creep, slump, deflation, abrasion, runoff, bedrock, clay, glacier, humus, horizon, loam, loess, parent material, permeability, pore spaces, porosity, silt, subsoil, and topsoil 51: Erosion: The process by which water, ice, wind or gravity moves fragments of rock and soil. - Movement of sediment - Carves earth’s surfaces: creating canyons, gorges, and beaches 4 different agents of erosion: 1. wind erosion: wind blows and picks up sediment and abrades away rock. - The intensity of wind erosion is determined by: Sum Speed Slope Surface Abrasion: the sediment or sand blows into roc and causes pits or scratches in the rocks. (Not a Mass Movement) Deflation: Wind erosion can cause the erosion of land and lower the lands surface. Determining the wind direction and direction of migrating sand: - Draw picture of sand dune and compass rose. Loess: accumulation of silt or fine sediment - Created by deposits of sediment and dust from glaciers - Extremely fertile: topsoil 2. Water Erosion: runoff, rivers and streams - creates most of the changes in the earth’s landscape - Runoff pick of piece of rock and runs downhill cutting tiny groove. (rills) Sheet Flow: When water moves downhill in thin sheets (Similar to washing a car) Rills: small channels cut in sediment Gullies: larger channels (.5 meters across) -lead to streams How much water erosion takes place depends on SUM Slope Speed Surface 3. Ice Causes Erosion: Glaciers wear down the landscape by moving and picking up sediment and even boulders. Glaciers: snow accumulates faster than it melts; gravity pulls the massive ice down to a lower elevation. -Continental Glaciers: cover a whole continent (huge) Antarctica, Arctic, and Greenland -Valley Glaciers: Located in high mountains and are smaller glaciers running down between mountains - Glaciers form U-shaped Valleys The amount of erosion that takes place is determined by the SUM Slope Speed Surface What is left behind glaciers when glaciers melt? -till: sediment deposition from melted glaciers: can range from clay to boulders -moraine: landforms made from deposition of till Terminal Moraine: The farthest that the glacier goes; melts quickly and deposits a great amount sediment: Forms ridges. Ground Moraine: The glacier dropped sediment off, but started to recede and results in a small deposit. -When melting occurs from the glacier, streams form and carry and deposit sediment. Outwash: sand and gravel deposits laid down by these melted glacier streams. 3. Gravity causes erosion: Creep, slump, landslide, mudslide, and avalanche -creep: Because of freezing and thawing, slow moving mass movement down a slope; page 324 and 325 -slump: a mass of rock or sediment moves down hill leaving a curved scar; page 324 -rock slides: layers of rock break off and move to the bottom of a slope; page 324 -Mud flow: A mass of wet sediment that flows downhill; page 324 The amount of erosion depends on: SUM Slope Speed Surface 52: TLW understand the effects of erosion. 52: Sediment is removed -forms canyons, valleys and mountain cirques -cirque: A bowl-shaped rock valley on the side of a mountain; often with a glacier or permanent snowfield in it Sediment deposition -forms deltas, sandbars, and sand dunes Preventing Erosion: Plants cause weathering Plants can prevent erosion: Other preventions: -plant roots - tree wind barriers beside fields - Terrace gardening - horizontal plowing - tracking instead of smooth - build walls Deposition: Process which sediments are laid down in new locations: Erosion and Deposition build new landforms. - Deltas, canyons, meanders, and flood plains Delta: where a river and ocean meet is the mouth of the river; sediment builds up and builds-up land Canyon: large valley created by river and streams Meander: Wandering stream in S shapes. Areas of erosion and deposition Flood plains: form along the banks of streams and rivers; low area subject to flooding.