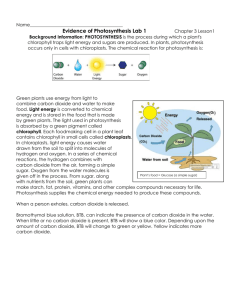
PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION
advertisement
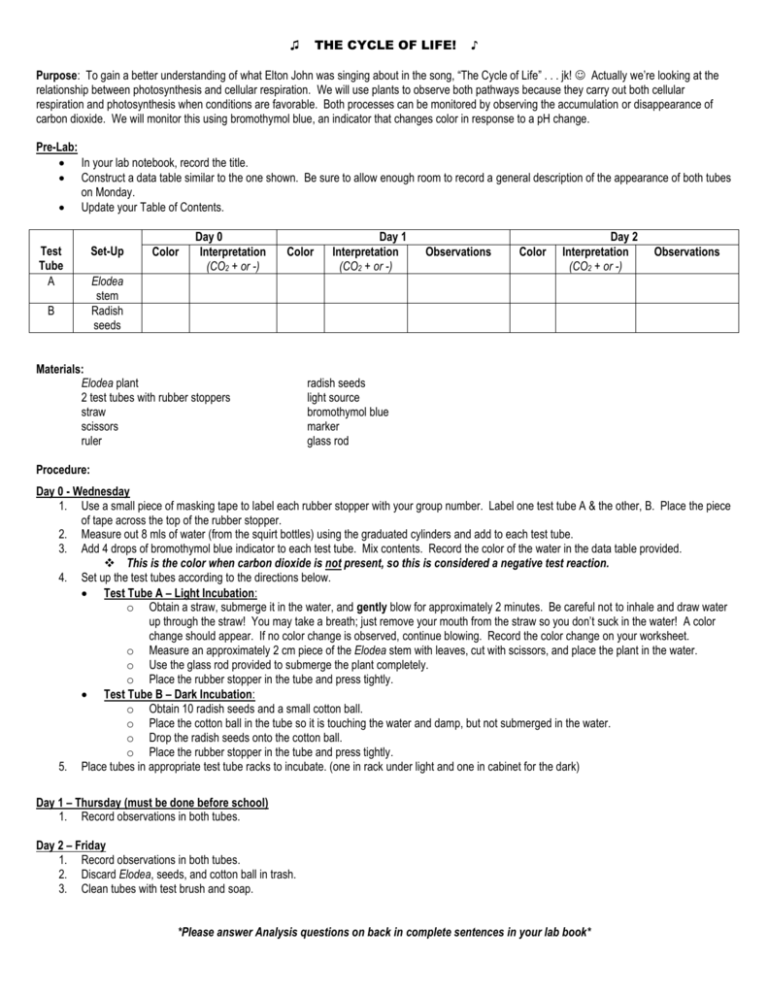
THE CYCLE OF LIFE! ♫ ♪ Purpose: To gain a better understanding of what Elton John was singing about in the song, “The Cycle of Life” . . . jk! Actually we’re looking at the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. We will use plants to observe both pathways because they carry out both cellular respiration and photosynthesis when conditions are favorable. Both processes can be monitored by observing the accumulation or disappearance of carbon dioxide. We will monitor this using bromothymol blue, an indicator that changes color in response to a pH change. Pre-Lab: In your lab notebook, record the title. Construct a data table similar to the one shown. Be sure to allow enough room to record a general description of the appearance of both tubes on Monday. Update your Table of Contents. Test Tube A B Set-Up Color Day 0 Interpretation (CO2 + or -) Color Day 1 Interpretation (CO2 + or -) Observations Color Day 2 Interpretation (CO2 + or -) Observations Elodea stem Radish seeds Materials: Elodea plant 2 test tubes with rubber stoppers straw scissors ruler radish seeds light source bromothymol blue marker glass rod Procedure: Day 0 - Wednesday 1. Use a small piece of masking tape to label each rubber stopper with your group number. Label one test tube A & the other, B. Place the piece of tape across the top of the rubber stopper. 2. Measure out 8 mls of water (from the squirt bottles) using the graduated cylinders and add to each test tube. 3. Add 4 drops of bromothymol blue indicator to each test tube. Mix contents. Record the color of the water in the data table provided. This is the color when carbon dioxide is not present, so this is considered a negative test reaction. 4. Set up the test tubes according to the directions below. Test Tube A – Light Incubation: o Obtain a straw, submerge it in the water, and gently blow for approximately 2 minutes. Be careful not to inhale and draw water up through the straw! You may take a breath; just remove your mouth from the straw so you don’t suck in the water! A color change should appear. If no color change is observed, continue blowing. Record the color change on your worksheet. o Measure an approximately 2 cm piece of the Elodea stem with leaves, cut with scissors, and place the plant in the water. o Use the glass rod provided to submerge the plant completely. o Place the rubber stopper in the tube and press tightly. Test Tube B – Dark Incubation: o Obtain 10 radish seeds and a small cotton ball. o Place the cotton ball in the tube so it is touching the water and damp, but not submerged in the water. o Drop the radish seeds onto the cotton ball. o Place the rubber stopper in the tube and press tightly. 5. Place tubes in appropriate test tube racks to incubate. (one in rack under light and one in cabinet for the dark) Day 1 – Thursday (must be done before school) 1. Record observations in both tubes. Day 2 – Friday 1. Record observations in both tubes. 2. Discard Elodea, seeds, and cotton ball in trash. 3. Clean tubes with test brush and soap. *Please answer Analysis questions on back in complete sentences in your lab book* Analysis: Please answer in complete sentences. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Compare the appearance of test tube A on Day 1 to the appearance of test tube A on the final day of incubation. Explain your results. Compare the appearance of test tube B on Day 1 to the appearance of test tube B on the final day of incuabtion. Explain your results. Which pathway (cellular respiration or photosynthesis) is exergonic? Endergonic? Which is catabolic? Anabolic? Include an explanation of these terms. In the equation for cellular respiration, what reactant is reduced? To form what product? What reactant is oxidized? To form what product? In the equation for photosynthesis, what reactant is reduced? To form what product? What reactant is oxidized? To form what product? Explain why a seed does not carry out photosynthesis. Seeds require energy to grow and therefore, contain a supply of the storage form of glucose. Identify this biomolecule. Can humans metabolize this biomolecule? Explain. Most seeds must take up water, a process known as imbibition, in order to germinate and grow. Given they are not photosynthesizing, why does the seed need water? Explain.