Word Format
advertisement
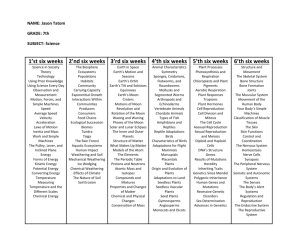
SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE BIOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 12 Copyright © School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document – apart from any third party copyright material contained in it – may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that the Authority’s moral rights are not infringed. Copying or communication for any other purpose can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with prior written permission of the School Curriculum and Standards Authority. Copying or communication of any third party copyright material can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with permission of the copyright owners. Any content in this document that has been derived from the Australian Curriculum may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Australia licence Disclaimer Any resources such as texts, websites and so on that may be referred to in this document are provided as examples of resources that teachers can use to support their learning programs. Their inclusion does not imply that they are mandatory or that they are the only resources relevant to the course. 2015/13034v3 1 Sample course outline Biology – General Year 12 Unit 3 and Unit 4 Semester 1 – Unit 3 – Reproduction and inheritance Week Key teaching points Reproduction 1–2 3 Asexual reproduction asexual reproduction (binary fission, budding, vegetative propagation, cuttings, bulbs, tubers, spores, parthenogenesis) plant propagation by asexual reproduction observation of yeast cells use of the microscope Cell division mitosis use of the microscope to observe growing root cells meiosis Sexual reproduction types of gametes fertilisation (restoring the diploid number) 4–6 Life cycle of a flowering plant alternation of haploid and diploid stages Reproduction in flowering plants structure and function of parts of the flower dissection of a variety of flowers (real or virtual dissections) mechanisms of pollination human facilitation in pollination of native plants seed dispersal – agents for dispersal and adaptations, self-dispersal mechanisms adaptations of Australian plants to regular burning – seed dispersal and recolonisation requirements for germination use of smoke-water to promote germination in native Australian plants Task 1: Science inquiry – Reproduction in flowering plants 7–8 Animal reproduction reproductive structures for external and internal fertilisation timing of reproduction strategies for survival of offspring, including parental care and number of offspring Life cycles of animals life cycle of insects/amphibians and Australian marsupials pest control based on knowledge of life cycles Task 2: Test – Reproduction Sample course outline | Biology | General Year 12 2 Week Key teaching points Inheritance and change 9–11 12–14 15 Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) structure and function of DNA models of DNA genes Mutations gene chromosome (structure and number) Sex determination genetics influence of environmental conditions (temperature, day length) Task 3: Science inquiry – Structure of DNA Variation and Natural selection causes of variation selection pressures survival and reproduction Task 4: Externally set task – A task set by the SCSA based on the following content from Unit 3 – <teacher to insert information provided by the Authority> Task 5: Extended response – Natural selection Selective breeding used in animal husbandry agriculture/horticulture/domestic pets Local ecosystem study introduction to citizen science identification of local environmental project/scientific data collection liaison with relevant groups to form partnerships/involvement in projects Task 6: Test – Inheritance and change Sample course outline | Biology | General Year 12 3 Semester 2 – Unit 4 – Ecosystems and eco-issues Week Key teaching points Local ecosystem study 1 Long-term project planning/links to agency or community organisation Ecosystems definition and characteristics types of ecosystems 2–4 Energy flow flow of energy biogeochemical cycling food chains/webs trophic levels Long-term project data collection 5–7 Communities and populations relationships in communities competition, predation, symbiosis population size, density and carrying capacity community structure and composition Long-term project data collection and collation Task 7: Test – Ecosystems 8–10 Biodiversity unique WA biodiversity World Heritage areas – Shark Bay, Ningaloo Reef, Purnululu National Park biodiversity hotspots keystone species bioindicator species Task 8: Extended response – Case study 11 12–14 15 Long-term project data collection and collation Threats to biodiversity habitat loss, fragmentation and degradation spread of invasive species unsustainable use of natural resources climate change burning/fire aquatic ecosystems and water flows Task 9: Test – Biodiversity Long-term project complete and submit report present findings to local government, agency or community group Task 10: Science inquiry – Long-term project Sample course outline | Biology | General Year 12