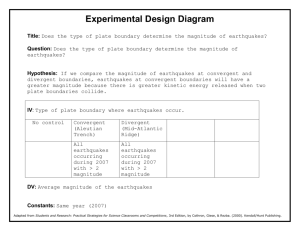
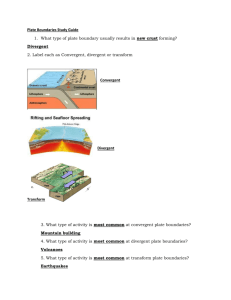
Plate Tectonics Questions: Lithosphere & Earthquakes
advertisement

Unit 30: Plates of the Lithosphere Teacher Questions: 1) Los Angeles city can be found on which tectonic plate? a) Pacific Plate * b) North American Plate c) Juan de Fuca Plate d) Nazca Plate 2) Which evidence did Alfred Wegener NOT propose to support the existence of one large supercontinent, Pangaea, and its subsequent break up? a) fossils of plants and animals found on different continents b) ocean floor drilling exposing remnants of similar continental rocks of two separate continents * c) geographic fit of continents d) glacial features displaying direction of motion 3) Cold, old oceanic crust can be found: a) along convergent plate boundaries near subduction zones * b) at the northernmost section of transform boundaries c) at mid-ocean ridges rift zones * d) none of the above 4) Crust is neither created or destroyed at this boundary a) transform boundaries * b) divergent boundaries c) spreading centers d) convergent boundaries 5) The East Africa Rift Zone is an area of: a) elongated collapse of continental crust b) crustal extension and thinning c) may be the site of a new ocean basin d) all of the above * 6) The area characterized by continental arcs and nearby deep sea trenches occurs along a) ocean-continent convergent boundaries * b) ocean-ocean convergent boundaries c) continent-continent convergent boundaries d) rift zones of divergent boundaries 7) The following statement is true with regard to the Atlantic Ocean: a) The deepest part of the Atlantic Ocean is found right at the center b) Observing the cross-section (side view) will show that the Atlantic Ocean’s profile is shaped like a bowl with the deepest areas are at the center and it gets shallower as you move toward the continents c) The mid-Atlantic oceanic ridge is a chain of volcanoes resulting from a converging plate boundary d) the oldest oceanic crust is found near continents * Depth and size of earthquakes and type of volcanoes help scientists determine the type of plate boundary that exists at certain locations. For questions #8-12, match the type of boundary (a), (b), or (c) with the depth and/or size of an earthquake: a. divergent boundary b. convergent boundary c. transform boundary 8) __a___ shallow earthquakes along the mid-ocean ridge 9) __b___ the foci of earthquakes become deeper moving inland on continental rocks 10) __b___ capable of producing explosive volcanoes and large earthquakes 11) __c___ shallow earthquakes typically not associated with volcanism 12) __a___ shallow earthquakes with relatively quite extrusion of magma