Supplementary Material Online: Table 1 Case results Table 1 Case
advertisement
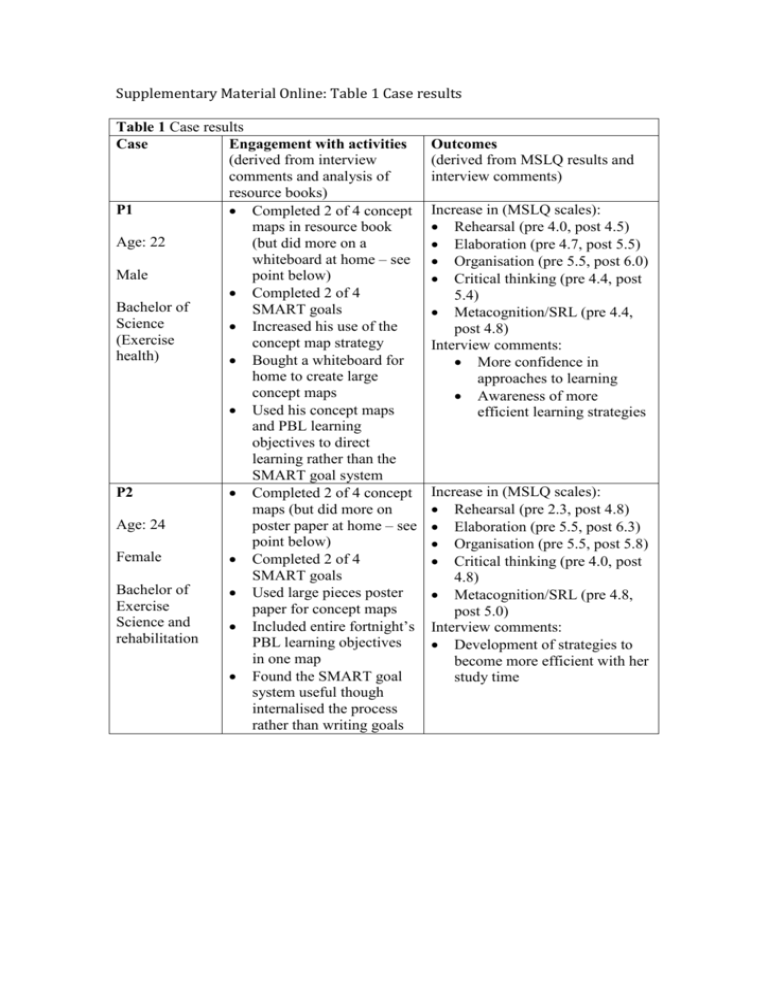
Supplementary Material Online: Table 1 Case results Table 1 Case results Case Engagement with activities (derived from interview comments and analysis of resource books) P1 Completed 2 of 4 concept maps in resource book Age: 22 (but did more on a whiteboard at home – see Male point below) Completed 2 of 4 Bachelor of SMART goals Science Increased his use of the (Exercise concept map strategy health) Bought a whiteboard for home to create large concept maps Used his concept maps and PBL learning objectives to direct learning rather than the SMART goal system P2 Completed 2 of 4 concept maps (but did more on Age: 24 poster paper at home – see point below) Female Completed 2 of 4 SMART goals Bachelor of Used large pieces poster Exercise paper for concept maps Science and Included entire fortnight’s rehabilitation PBL learning objectives in one map Found the SMART goal system useful though internalised the process rather than writing goals Outcomes (derived from MSLQ results and interview comments) Increase in (MSLQ scales): Rehearsal (pre 4.0, post 4.5) Elaboration (pre 4.7, post 5.5) Organisation (pre 5.5, post 6.0) Critical thinking (pre 4.4, post 5.4) Metacognition/SRL (pre 4.4, post 4.8) Interview comments: More confidence in approaches to learning Awareness of more efficient learning strategies Increase in (MSLQ scales): Rehearsal (pre 2.3, post 4.8) Elaboration (pre 5.5, post 6.3) Organisation (pre 5.5, post 5.8) Critical thinking (pre 4.0, post 4.8) Metacognition/SRL (pre 4.8, post 5.0) Interview comments: Development of strategies to become more efficient with her study time Table 1 Case results P3 Completed all 4 concept maps (and more – see Age: 27 point below) Completed 2 of 4 Female SMART goals Demonstrated Bachelor of development in approach Applied to concept mapping science Created extra concept (Physiotherapy) maps, as well as (Honours) completing resource book activities Introduced concept maps to study group Used concept maps to guide learning rather than SMART goals P4 Completed 3 of 4 concept maps (but did more with Age: 23 study group – see point below) Female Completed 1 of 4 SMART goals Bachelor of Used concept maps to Physiotherapy identify connections between content and gaps in her knowledge Used concept maps with study group to demonstrate knowledge to each other Used the SMART goal system with study group to guide group learning Increase in (MSLQ scales): Elaboration (pre 5.3, post 5.7) Organisation (pre 4.0, post 5.5) Critical thinking (pre 3.2, post 3.8) Metacognition/SRL (pre 3.4, post 4.0) Interview comments: Feeling more confident about settling back into study after a five-year break Awareness of more effective learning strategies Increase in (MSLQ scales): Rehearsal (pre 3.8, post 4.5) Critical thinking (pre 3.8, post 4.4) Metacognition/SRL (pre 4.7, post 5.2) Interview comments: Feeling more confident with approaches to learning Table 1 Case results P5 Completed 4 of 4 concept maps (and more at home) Age: 30 Completed 1 of 4 SMART goals Female Adapted the concept mapping strategy by Bachelor of creating large map on Science poster paper to illustrate (Neuroscience) the big picture Concept maps link all learning objectives for the fortnight to see where everything fits Found the SMART goal system useful though internalised the process rather than writing goals P6 Completed 2 of 4 concept maps (but added to each Age: 23 throughout fortnight – see point below) Female Completed 2 of 4 SMART goals Bachelor of Created a basic concept Science map at the beginning of (Microbiology) the fortnight on large piece of poster paper. Continually added new knowledge to it throughout the fortnight Developed colour coding her concept maps to make them easier to organise Adapted to use gaps in concept map to set a ‘todo’ list as her goal-setting strategy rather than SMART goals Formed a group to study with and used the concept maps as a group study strategy Increase in (MSLQ scales): Critical thinking (pre 3.0, post 4.4) Metacognition/SRL (pre 3.7, post 4.7) Interview comments: Greater confidence with approaches to learning Feelings of gaining greater amounts of knowledge in a shorter time As a result of the programme realised the need to form a study group Increase in (MSLQ scales): Elaboration (pre 5.0, post 6.5) Critical thinking (pre 2.8, post 4.2) Metacognition/SRL (pre 4.5, post 5.3) Interview comments: Feeling more positive about her ability to design and execute an effective self-directed learning plan Table 1 Case results P7 Completed 3 of 4 concept maps (but did more on Age: 22 poster paper at home – see point below) Female Completed 2 of 4 SMART goals Bachelor of Created concept maps on Biomedical poster paper and stuck on Science bedroom walls Adapted her SMART goals to only address Attainable and Specific aspects Increase in (MSLQ scales): Elaboration (pre 6.2, post 6.5) Organisation (pre 6.0, post 6.8) Critical thinking (pre 5.2, post 6.0) Metacognition/SRL (pre 5.4, post 5.8) Interview comments: Feeling a reduction in stress and an increase in concentration and well being