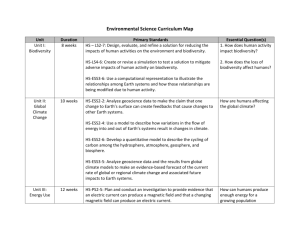
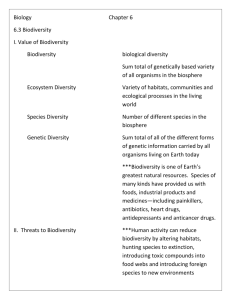
3. Biodiversity & Habitat Loss
advertisement

Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity 1. Which of these climate data is a good predictor of the plant community that might be in an area? 3. What kind of plant community would you expect where the mean annual biotemperature is 9°C and precipitation is 300 mm? 5. What is the conservation status of a species likely to become endangered in the near future througout all or a significant portion of its range? 7. What is the Carolina parakeet an example of? A. mean annual biotemperature B. mean biotemperature of the hottest month C. mean biotemperature of the coldest month A. grassland, steppe or prairie B. temperate forest C. tundra Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 3. Why is a lack of genetic diversity in a population or species considered a problem? 1. What is an international treaty to ensure that global trade in plants and wildlife does not threaten their survival? A. threatened or vulnerable B. near threatened C. least concern A. a species extinction in recent history B. a mass extinction in geologic times C. a potential future extinction event Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 5. Which of these is the biggest threat to species worldwide? 7. What kind of government initiative is arresting a Florida man after finding sea turtle eggs in his backpack? Grades 9-12 Biodiversity A. CITES B. Ramsar C. IUCN A. it reduces a species' ability to adapt to environmental changes B. it increases chances a species will hybridize with other species C. it causes species to disperse before breeding A. loss of habitat B. hunting wildlife out of season C. scientific whaling CORRECT: A, A CORRECT: A, A Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity 2. What kind of plant community would you expect to find at a place with a mean annual biotemperature of 24° C and precipitation around 65 mm? 4. What is the background extinction rate estimated from the fossil record? 6. What is it when a species is no longer able to survive and reproduce in the wild? 8. What is the Hawaian crow an example of? A. 0.001% of species/100 years B. > 50% of species /100 years C. 0.5% of species/ 100 years A. extinct in the wild B. species extinction C. co-threatened species Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 4. The strain of stem rust Ug99 kills 85% of wheat varieties it Africa. What is the best way to stop it? 6. What kind of government initiative is the Puget Sound Marine and Nearshore Grant Program for the purchase of nearshore and upland habitat? A. penalties B. economic incentives C. research CORRECT: A, A CORRECT: A, A A. desert B. tropical rain forest C. grassland, steppe or prairie Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 2. What is a 1916 treaty between the U.S. and Great Britain (for Canada) for the protection of birds that spend time in both the U.S. and Canada? A. a species extinct in the wild B. an historical extinction event C. a mass extinction event Grades 9-12 Biodiversity A. Migratory Bird Treaty B. Ramsar C. CITES A. search for resistant genes in different wheat varieties B. destroy all the plants that are infected C. stop people traveling from Africa to anywhere else. CORRECT: A, A CORRECT: A, A 8. Who sets specific standards for species protection laws, helps people, businesses and agencies follow them and enforces them when they are not followed? A. economic incentives B. education and information C. research A. agencies in the executive branch B. the court system C. congress and legislatures CORRECT: A, A CORRECT: A, A Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity 9. In law, who owns wildlife in the U.S.? 11. The Biotic Index (BI), uses "b", the number of sensitive species, divided by "a",the total number of species. If b = 36 and a = 10, what does BI equal? 13. What kind of plant community would you expect to find at a place with a mean annual biotemperature of 24° C and precipitation around 14,000 mm? 15. What is the conservation status of a species that appears to be stable over most of all of its range for the time being? A. 3.6 B. 36 C. 10 A. temperate rainforest B. tropical rain forest C. desert Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 11. What does fishing down the food web mean? 13. What is a list of plants, animals and fungi facing a risk of extinction or that have gone extinct? A. the U.S. public as a whole B. the person on whose land the wildlife lives C. no one Grades 9-12 Biodiversity A. threatened or vulnerable B. least concern C. near threatened Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 9. Who tallies the number and species of fish kept or discarded on commercial fishing vessels? A. NOAA Fisheries observers B. sniffer dogs and their handlers C. wildlife forensic scientists CORRECT: A, A A. switching to smaller fish lower on the food chain B. switching to plankton C. switching to bottom feeding species A. the Blue List B. the Red List C. the Green List 15. Who decides if a species protection law is being broken? A. agencies in the executive branch B. the court system C. congress and legislatures CORRECT: B, B CORRECT: A, A CORRECT: B, B Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity 10. Who studies species in the wild to learn about life cycles and habitat for managing them for long term survival? 12. Which of these climate data is a good predictor of the plant community that might be in an area? 14. What kind of plant community would you expect to find where mean annual biotemperature is 3° C and precipitation ranges from 60 to 1000 mm. A. wildlife scientists B. captive breeders C. restoration ecologists A. precipitation in the driest month B. total annual precipitation C. mean monthly precipitation A. temperate forest B. tundra C. desert Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 12. What is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands? 14. Svalbard, Norway, is home to what iconservation tool? 16. Who encourages the passage of species protection laws and supports their enforcement? A. a lab to study algae at the base of polar food chains B. a global seed vault to back up other seed vaults C. a zoo for breeding arctic mammals A. congress and legislatures B. non-governmental organizations C. the court system Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 10. Which of these is the biggest threat to large African mammals like elephants and rhinos? A. illegal hunting for ivory and horns B. loss of habitat when rivers are diverted for irrigation C. harvesting gizzards for the traditional medicine market 16. What is the conservation status of a species that is likely to become extinct in the near future throughout all or a significant portion of its range? A. least concern B. endangered C. threatened or vulnerable Grades 9-12 Biodiversity A. IUCN B. Ramsar C. CITES CORRECT: B, B CORRECT: B, B CORRECT: A, A CORRECT: B, B Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity 17. What is it when over 50% of living species disappear in 100 years? 19. Which act do the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Agency both administer? 21. Who brings back natural habitats damaged by humans or weather by active management (weeding, planting, flooding, draining, burning, etc.) ? 23. Biotemperature is the temperature at which plants can grow. What is the range of biotemperatures for most plants? A. the Clean Air Act B. the Endangered Species Act (ESA) C. the Clean Water Act (CWA) A. wildlife scientists B. restoration ecologists C. captive breeders A. species extinction B. a mass extinction event C. background extinction Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 17. What kind of government initiative is the "Get to Know Your Species", an interactive website from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service that lets you find out what endangered species live in your state? A. between 0° C and 24° C B. between 32° C and 104° C C. between 0° C and 30° C Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 19. Who finds wildlife products (like ivory) or wildlife that are being illegally shipped across international borders? A. research B. education and information C. economic incentives A. NOAA Fisheries observers B. sniffer dogs and their handlers C. wildlife forensic scientists CORRECT: B, B CORRECT: B, B 21. Which of these is the biggest threat to marine species in waters near the mouth of the Mississippi river? 23. What is a global nongovernmental organization whose mission is to conserve nature and ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable? A. diseases from farmed fish B. nutrient pollution from fertilizer and manure runoff C. habitat loss when wetlands are filled in A. Ramsar B. CITES C. IUCN CORRECT: C, C CORRECT: B, B Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity 18. What is the disappearance of thousands of marine species at the end of the Cretacous an example of? 20. Which of these is an effect of gray wolves being re-introduced into Yellowstone in the 2000s? 22. The Biotic Index (BI) tells whether a stream is healthy enough to support aquatic life. Which way should BI values go if stream health improves? A. a potential future extinction B. a mass extinction in geologic times C. an historical extinction A. elk increased B. beaver numbers increased C. willow numbers decreased Grades 9-12 Biodiversity A. they should stay the same B. up C. down 24. What kind of plant community would you expect to find at a place with a mean annual biotemperature of 9° C and precipitation around 750 mm? A. tropical rain forest B. grassland, steppe or prairie C. temperate forest Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 18. What are specific areas occupied by a species at the time of listing, that contain the physical or biological features essential to its conservation? A. tropical rain forests B. critical habitat C. wetlands 20. Which of these is the biggest threat to migratory ducks and geese? A. nutrient pollution from fertilizer and manure runoff B. habitat loss when wetlands are filled in C. harvesting gizzards for traditional medicine markets CORRECT: B, B CORRECT: B, B Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 22. What ususally happens to the number of species an area can support when the area becomes smaller? A. it stays the same B. it goes down C. it goes up CORRECT: B, B 24. What is an event that reduces the genetic diversity of a popluation or species? A. genetic modification B. mutations C. a genetic bottle neck CORRECT: C, C Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity 25. What is the death, without any surviving offspring, of all the individuals in a species? 27. What is a U.S. law passed by congress in 1973 to conserve the ecosystems that endangered and threatened species depend on? 29. Which of these is an inventory of the global conservation status of a species 31. Who helps wild animals reproduce in safe enviroments like zoos or reserves and then releases them into the wild? A. local extinction B. a genetic bottle neck C. global species extinction A. the Migratory Bird Treaty B. the Basel Convention C. the Endangered Species Act A. the Toxics Release Inventory B. the U.S. Endangered Species List C. the IUCN Red List A. wildlife scientists B. restoration ecologists C. captive breeders Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 27. Which of these is a governmental factor that can affect enforcement of laws to protect species? 29. What is any act which actually kills or injures wildlife, including significant habitat modification or degradation that significantly impairs essential behavior patterns? 31. Which of these led to the decline and extintion of many native plants in Australia? Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 25. Which crop disaster was caused by a lack of genetic diversity in the crop? A. the midwester Grasshopper Swarm of 1931 B. the spread of the Boll Weevil in cotton states 1915-1917 C. Irish Potato Famine of 1845 1847 A. whether a judge likes the law B. whether a landowner cares about the species C. how much funding congress provides A. deforestation B. over fishing C. harm CORRECT: C, C CORRECT: C, C A. habitat loss when rivers were channelized and wetlands were filled in B. nutrient pollution from manure and fertilizer runoff C. the introduction of non-native European rabbits CORRECT: C, C CORRECT: C, C Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity Grades 6-8 Biodiversity 26. What is the conservation status of species whose numbers are reduced over its range or which is dependent on conservation efforts to persist? 28. What are species that depend on a species that has gone extinct called? 30. What can the Endangered Species Act require of landowners, developers and businesses if an endangered species if found on their property? 32. Which of these is the main cause of extinction worldwide? A. that they give their land up B. nothing C. that they take reasonable steps to protect them Grades 9-12 Biodiversity A. least concern B. endangered C. near threatened Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 26. Who passes laws protecting species, assigns protection to an ageny and provides funding for the agency? A. the court system B. agencies in the executive branch C. congress and legislatures A. extinct in the wild B. a mass extinction event C. co-threatened Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 28. What kind of government initiative is developing Habitat Conservation Plans that allow landowners to continue to use their land while minimizing harm to endangered species? A. economic incentives B. education and information C. research Grades 9-12 Biodiversity 30. Who can identify the species a fish fillet came from to tell if it was illegally harvested? A. sniffer dogs and their handlers B. NOAA Fisheries observers C. wildlife forensic scientists CORRECT: C, C CORRECT: C, C CORRECT: C, C A. pollution B. legal hunting C. habitat loss 32. Which of these caused the collapse of orange roughy, Chilean seabass and bluefin tuna fish populations? A. habitat loss whenwetlands were filled in B. nutrient pollution from fertilizer and manure runoff C. overfishing CORRECT: C, C Biodiversity & Habitat Loss 6-12 EARTH QUEST Biodiversity & Habitat Loss 6-12 EARTH QUEST Biodiversity & Habitat Loss 6-12 EARTH QUEST Biodiversity & Habitat Loss 6-12 EARTH QUEST Biodiversity & Habitat Loss 6-12 EARTH QUEST Biodiversity & Habitat Loss 6-12 EARTH QUEST Biodiversity & Habitat Loss 6-12 EARTH QUEST Biodiversity & Habitat Loss 6-12 EARTH QUEST