Text Structures: Internal & External Guide | Informational Texts
advertisement
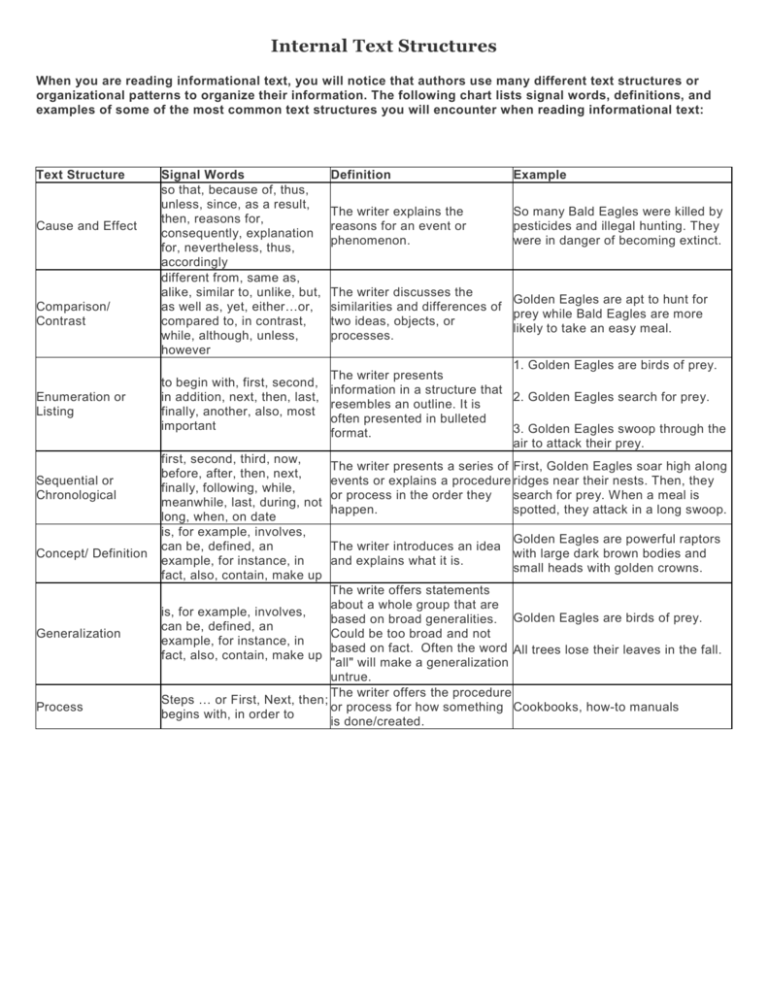
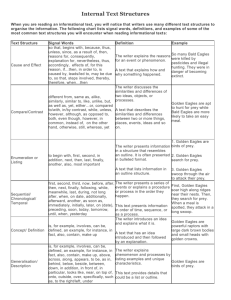
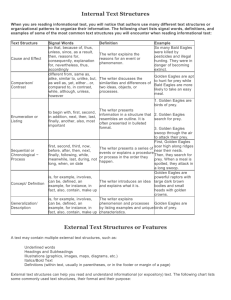
Internal Text Structures When you are reading informational text, you will notice that authors use many different text structures or organizational patterns to organize their information. The following chart lists signal words, definitions, and examples of some of the most common text structures you will encounter when reading informational text: Text Structure Cause and Effect Comparison/ Contrast Enumeration or Listing Sequential or Chronological Concept/ Definition Generalization Process Signal Words so that, because of, thus, unless, since, as a result, then, reasons for, consequently, explanation for, nevertheless, thus, accordingly different from, same as, alike, similar to, unlike, but, as well as, yet, either…or, compared to, in contrast, while, although, unless, however Definition Example The writer explains the reasons for an event or phenomenon. So many Bald Eagles were killed by pesticides and illegal hunting. They were in danger of becoming extinct. The writer discusses the Golden Eagles are apt to hunt for similarities and differences of prey while Bald Eagles are more two ideas, objects, or likely to take an easy meal. processes. 1. Golden Eagles are birds of prey. The writer presents to begin with, first, second, information in a structure that in addition, next, then, last, 2. Golden Eagles search for prey. resembles an outline. It is finally, another, also, most often presented in bulleted important 3. Golden Eagles swoop through the format. air to attack their prey. first, second, third, now, The writer presents a series of First, Golden Eagles soar high along before, after, then, next, events or explains a procedure ridges near their nests. Then, they finally, following, while, or process in the order they search for prey. When a meal is meanwhile, last, during, not happen. spotted, they attack in a long swoop. long, when, on date is, for example, involves, Golden Eagles are powerful raptors can be, defined, an The writer introduces an idea with large dark brown bodies and example, for instance, in and explains what it is. small heads with golden crowns. fact, also, contain, make up The write offers statements about a whole group that are is, for example, involves, based on broad generalities. Golden Eagles are birds of prey. can be, defined, an Could be too broad and not example, for instance, in based on fact. Often the word All trees lose their leaves in the fall. fact, also, contain, make up "all" will make a generalization untrue. The writer offers the procedure Steps … or First, Next, then; or process for how something Cookbooks, how-to manuals begins with, in order to is done/created. External Text Structures or Features A text may contain multiple external text structures, such as: Underlined words Headings and Subheadings Illustrations (graphics, images, maps, diagrams, etc.) Italics/Bold Text Definitions (within text, usually in parentheses, or in the footer or margin of a page) Footnotes Sidebars External text structures can help you read and understand informational (or expository) text. The following chart lists some commonly used text structures, their format and their purpose: External Text feature Format Purpose–How does it help me read and understand the information? Table of contents Chapters This provides me with a list of information included in the text. Headings Headings and Subheadings I can read a brief phrase that tells me what information I will find in the paragraph below it. Bold or italicized words Bold or italicized words These words are important terms that I must be able to define so I can understand the information. Graphics/illustrations Graphics/illustrations A picture, graph, or chart that provides me more information OR arranges the information in a visual format so I might understand it better. Footnotes Appear at the bottom of a page or at the end of a document Footnotes give credit to the source material from which a writer derives information. In addition, footnotes can be included to provide additional information that will help the reader to understand the meaning of words/phrases that may be unclear. Sidebar Information presented at the side of the main text Sidebars provide additional information, e.g., information about the life of an author or a related detail, to complement the main text of an article.