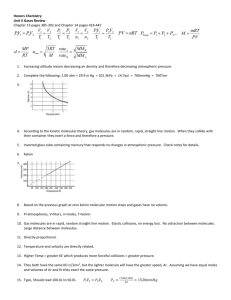
Heating Curve for water Notice the plateaus where temperature
advertisement
Liquids 11.3 – 11.6 Viscosity of Liquids • Viscosity - __________________________________________________________________ • Viscosity depends on the strength of IMF: __________________________________________ • Viscosity decreases with an increase in temperature (think syrup!) – Higher temp means more ____________________________________________________ Surface Tension • • • • • • Bulk molecules in the liquid are equally attracted to all of their neighbors. Surface molecules are only attracted inward towards the bulk molecules. Surface molecules are packed more closely than bulk molecules. This causes the liquid to behave as if it had a “skin”. Surface tension - amount of energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a unit amount (like m2 or in2) Stronger IMFs cause _________________________surface tension. • Higher temperature - __________________________surface tension • Cohesive forces - IMF that bind molecules_____________________________________________ • Adhesive forces - IMF that bind molecules _____________________________________________ Capillary action The rise of liquids up very narrow tubes. The liquid climbs until adhesive / cohesive forces are balanced by gravity. Phase Changes and Energy Sublimation: solid gas Hsub > 0 (endothermic) Melting or fusion: solid liquid Hfus > 0 (endothermic) Vaporization: liquid gas Deposition (crystalization): gas solid Condensation: Freezing: gas liquid liquid solid Hvap > 0 (endothermic) Hdep < 0 (exothermic) Hcon < 0 (exothermic) Hfre < 0 (exothermic) Heating Curves • • Plot of temperature change versus heat added is a heating curve. During a phase change, temp. remains constant even though energy is being added • Added energy _________________________________________________________________ • To calculate the amount of heat absorbed/released from a heating curve: – Use ______________________for increasing/decreasing lines – Use _____________________ for flat lines • Add q values for each line segment to find the total q for the process. Sample Problem Calculate the energy required to convert 25.0 g of ice at -13°C to steam at 125°C. Critical temperature is the highest temperature at which a substance can exist as a liquid - above T molecules c have too much energy to be a liquid Critical pressure is the pressure required for liquefaction at this critical temperature. The greater the IMF_______________________________________________. Vapor Pressure • Some molecules on the surface of a liquid have enough energy to escape the attraction of the bulk liquid and move into the gas phase. • As the number of molecules in the gas phase increases, some of the gas phase molecules strike the surface and return to the liquid. • After some time the pressure of the gas will be constant. – A dynamic equilibrium has been established • Vapor pressure is the _____________________________________________________________ Volatility Liquids with lower IMFs tend to have high vapor pressures – these generally evaporate easily and are are said to be ______________________________. Vapor Pressure and Temperature • Increasing temperature will ____________________________________________________ – Higher temps mean the molecules have more energy to overcome the IMFs that hold them in the liquid phase. – increasing temperature will increase evaporation and will produce more vapor molecules, so more pressure – increasing temperature will increase the pressure of any gas (or vapor) (Charles’ law) Vapor Pressure and Boiling Point • • Boiling occurs when the vapor pressure equals the pressure above the liquid The normal BP is the temperature when the vapor pressure is equals standard pressure (1 atm) Decreasing air pressure (going up in altitude) lowers the temperature at which a liquid will boil – food does not cook as fast (high altitude cooking directions on boxed foods) Two ways to get a liquid to boil: (1) _____________________________________________________________________ (2) _____________________________________________________________________ Clausius-Clapeyron Equation (Relationship between vapor pressure and temperature) more often written for a gas (or vapor) at 2 different P and T as: ln P = -H vap +C RT Graphing 1/T versus ln P The slope of this line = The slope can be used to determine ΔH ΔH vap vap = o o Ether has Pvap = 400 mm Hg at 17.9 C and a normal BP of 34.6 C. What is the heat of vaporization, Hvap , for ether in kJ/mol? o The vapor pressure of ethanol at 34.7 C is 100.0 mm Hg. The heat of vaporization is 38.6 kJ/mole. What is the o vapor pressure of ethanol in mm Hg at 65.0 C? Phase Diagrams • • plot of pressure vs. temperature summarizing all equilibria between phases. Phase diagrams tell us which phase will exist at a given T and P Features of a phase diagram: Vapor-pressure curve: generally as T increases, Pvap increases. Critical point: critical temperature and pressure for the gas. Normal melting point: melting point at 1 atm (101 kPa) Normal boiling point: boiling point at 1 atm (101 kPa) Triple point: T and P at which all three phases are in equilibrium. Any T and P combination on a curve represent 2 phases Any T and P combination not on a curve represents a single phase. Notice that the solid-liquid line for water has a negative slope. This is because solid ice is less dense than liquid water. What phase or phases are present a) at any point on curve YX? b) at any point on curve AD? c) at any point on curve AB? d) at point A or X? e) Looking at the water diagram on the left, what effect would each of the following have on a sample of water at any point on the AD curve. a) increasing T at constant P b) decreasing P at constant T? c) decreasing T at constant P? d) increasing P at constant T? Using the two diagrams above: a) points A and X are called b) point B is called c) point C is called d) point Y is called e) points D and Z are called Good explanation of phase diagrams: http://www.chemguide.co.uk/physical/phaseeqia/phasediags.html Chapter 11 Book Work: 11(2, 7, 18, 20, 26, 40, 44, 52, 58, 60, 61, 73, 84b-d)