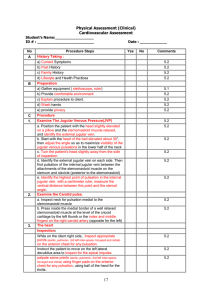
Case fatality rate
advertisement
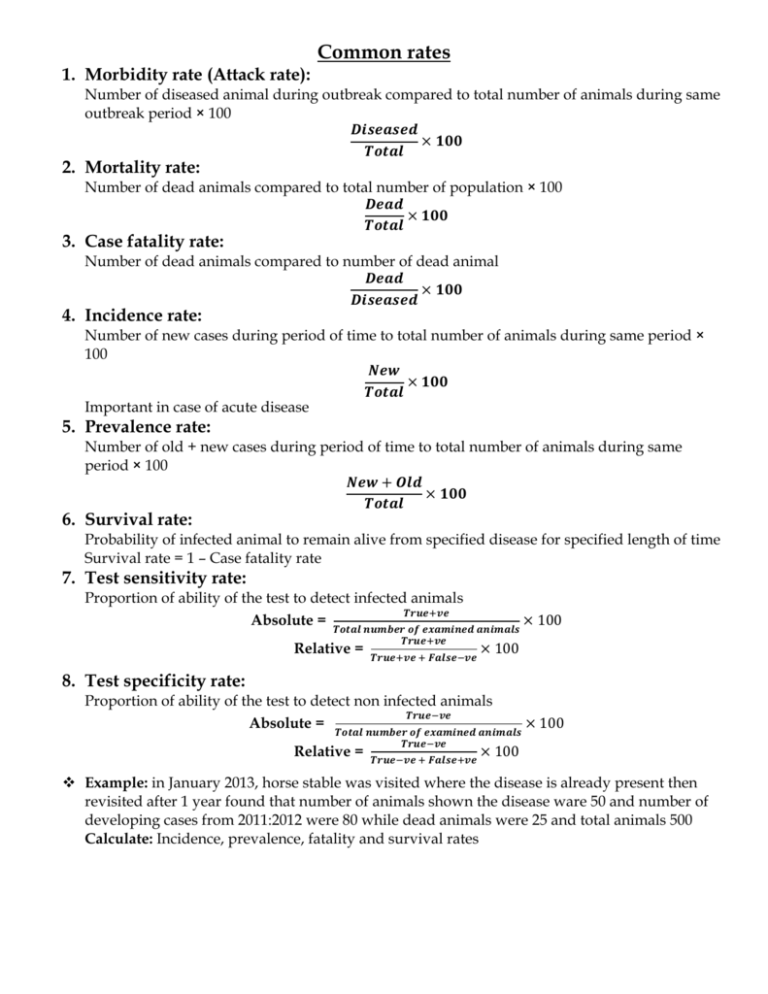
Common rates 1. Morbidity rate (Attack rate): Number of diseased animal during outbreak compared to total number of animals during same outbreak period × 100 𝑫𝒊𝒔𝒆𝒂𝒔𝒆𝒅 × 𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝑻𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 2. Mortality rate: Number of dead animals compared to total number of population × 100 𝑫𝒆𝒂𝒅 × 𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝑻𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 3. Case fatality rate: Number of dead animals compared to number of dead animal 𝑫𝒆𝒂𝒅 × 𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝑫𝒊𝒔𝒆𝒂𝒔𝒆𝒅 4. Incidence rate: Number of new cases during period of time to total number of animals during same period × 100 𝑵𝒆𝒘 × 𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝑻𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 Important in case of acute disease 5. Prevalence rate: Number of old + new cases during period of time to total number of animals during same period × 100 𝑵𝒆𝒘 + 𝑶𝒍𝒅 × 𝟏𝟎𝟎 𝑻𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 6. Survival rate: Probability of infected animal to remain alive from specified disease for specified length of time Survival rate = 1 – Case fatality rate 7. Test sensitivity rate: Proportion of ability of the test to detect infected animals 𝑻𝒓𝒖𝒆+𝒗𝒆 Absolute = 𝑻𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝒏𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒆𝒙𝒂𝒎𝒊𝒏𝒆𝒅 𝒂𝒏𝒊𝒎𝒂𝒍𝒔 × 100 Relative = 𝑻𝒓𝒖𝒆+𝒗𝒆 𝑻𝒓𝒖𝒆+𝒗𝒆 + 𝑭𝒂𝒍𝒔𝒆−𝒗𝒆 × 100 8. Test specificity rate: Proportion of ability of the test to detect non infected animals 𝑻𝒓𝒖𝒆−𝒗𝒆 Absolute = 𝑻𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝒏𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒆𝒙𝒂𝒎𝒊𝒏𝒆𝒅 𝒂𝒏𝒊𝒎𝒂𝒍𝒔 𝑻𝒓𝒖𝒆−𝒗𝒆 Relative = 𝑻𝒓𝒖𝒆−𝒗𝒆 + 𝑭𝒂𝒍𝒔𝒆+𝒗𝒆 × 100 × 100 Example: in January 2013, horse stable was visited where the disease is already present then revisited after 1 year found that number of animals shown the disease ware 50 and number of developing cases from 2011:2012 were 80 while dead animals were 25 and total animals 500 Calculate: Incidence, prevalence, fatality and survival rates Clinical Examination Definition: Get my hand on the affected system of the body to approach accurate diagnosis. N.B: Care must be taken by the examiner during examination to protect himself from dangerous animal by control of the animal and from zoonotic diseases by wearing gloves and disinfection of the hand. Control of the animal: 1. Equine: Ear Twitch – Lip Twitch – Raise one of fore limbs. 2. Canine and Feline: Owner – Muzzle – Narcotic agent in case of vicious animal. 3. Camel: Tying all legs and mouth by ropes. Temperature – Pulsation - Respiration: How to take temperature: 1. Control animal and raise tail 2. Shake thermometer till 35℃ or bellow (not handle it at bulb part) 3. Lubricate it especially in case of equine and small ruminants. 4. Introduce thermometer through anal opening then tilt it to be in contact with rectal mucosa. 5. Wait for 1 to 1.30 minutes 6. Remove thermometer and clean it by cotton piece or water 7. Record temperature. Items Temperature Pulsation Respiration Site Rate Type Rate 1-External maxillary artery: Equine 37:38 at medial aspect of 28:40 Horse 37:38 mandible. 45:65 Donkey Costoabdominal 10:14 37.5:38.5 2-Median artery: at medial 70:80 Foal aspect of upper extremity of fore limb. Dog Pet animal 1-Femoral artery: at medial 15:30 38.9 90:120 Dog small breeds: aspect of femur Costal Cat 37.5:38.5 65:90 Dog large breeds: 20:30 37.5:39.2 110:130 Cat 30:50 Camel 1- Posterior tibial artery: at Abdominal 5:12 36.8 Adult medial aspect of tibia 39.2 Calf Area of auscultation and percussion: Triangular area lies between: Posterior angle of scapula – 2nd last intercostal space – Olecranon process of ulna Lines of area: 1. Dorsal line between posterior angle of scapula and 2nd last intercostal space 2. Anterior line between posterior angle of scapula and olecranon process of ulna 3. Ventral line between 2nd last intercostal space and olecranon process of ulna Ventral line mid: 1. 7th rib in pet animal 2. 11th rib in equine (number of ribs in equine 18 except Arabian horse 16) 3. 8th rib in camel Examination of Lung: 1. Auscultation: Normal vesicular sound 2. Percussion: Resonant sound (Gas filled organ) Examination of heart: at area of cardiac dullness at bottom of left side of triangular area 1. Auscultation: Lubb-Dupp sound 2. Percussion: Dull sound (Gas free organ) Examination of rumen in camel at paralumbar fossa (behind last rib): Auscultation: Booming or gurgling sound (3:5 Times/minute) Percussion: Resonant Palpation: Resilient (Return after removal of pressure) Examination of Paranasal sinuses(Frontal and Maxillary sinus) Normal percussion: Tympanic sound Abnormal percussion: Dull sound in case of sinusitis or empyemia Examination of mucous membrane: 5 in female (oral – nasal – conjunctival – rectal – vaginal) 4 in male (oral – nasal – conjunctival – rectal) Normal Characters: rosy red – free from wound, ulcer, vesicles and discharges – shinny. Abnormal Characters (Color) 1. Congested: Fever – inflammation 2. Pale: Anemia – heavy parasitism 3. Cyanosed: Cardiovascular & respiratory diseases 4. Yellowish: Jaundice – Fascioliasis – late stage of hemolytic anemia 5. Petechial haemorrhage: Septicemic Cases 6. Dirty: Toxicity 7. Contain ulcer, vesicle, wound or discharges Examination of skin: Normal: free from wound, erosions, alopecia, ectoparasites with shiny appearance Abnormal: Wound Alopecia (if regular Ring Worm If irregular Mange) Examination of superfacial lymph nodes: 1. Pre-scapular: in-front of scapula just above shoulder Absent in camel and replaced by inferior cervical lymph node 2. Pre-femoral: in front of femur just above stifle joint Absent in dog and cat 3. Sub-maxillary: in inter-mandibular space If enlarged: in cattle Actinomycosis In horse Glanders or Strangles 4. Supra-mammary: at base of udder If enlarged Mastitis 5. Superfacial inguinal: at base of scrotum If enlarged Brucellosis 6. Sub-Parotid: at base of the ear 7. Retropharyngeal: behind pharynx Items Points of Examination Size Consistency Normal Larger in young animal than old animal Firm Pain Lobulation Temperature Movement Painless Lobulated of body temperature Movable Abnormal Enlarged Flactuating abscessiation Hard Caseation and Calcification Painful Non-Lobulated Hot Immobile Jugular vein pulsation: Jugular V present in jugular furrow with carotid A and this pulsation normally not present. Types: 1. False: Physiological: in lean or emaciated animal (pulsation originate from carotid artery) 2. True: Pathological due to pericarditis – atrioventricular valve insufficiency How to differentiate: 1. Make digital pressure at base of neck at jugular furrow. 2. If pulsation disappear True 3. If pulsation persist False Sites of Injection: I/M: Gluteal – Neck – Thigh – Buttock S/C: at area of more skin (infront of shoulder and flank region) Catch fold of skin – introduce needle in triangular area (free movement of needle) I/V: Jugular vein – Milk vein – Tail vein in cattle Tibial vein –jugular vein in equine and camel Dog and cate fore limb in radial or cephalic vein Hind limb in saphenous and recurrent tarsal vein I/D: Like S/C but no free movement of needle. Capillary refilling time Press by finger on upper and lower gum then remove your finger and estimate time of returning of gum to normal color Normal: 1:2 seconds Abnormal: above 2 seconds in case of dehydration or cardiovascular disturbance Skin Fold Test: (Skin Tent Test): Catch skin of neck, eye or tail fold and estimate time of returning to normal position Normal: return at once Abnormal: delayed in case of dehydration and according to time the degree of dehydration is recorded