bio 131 -lect 1
advertisement
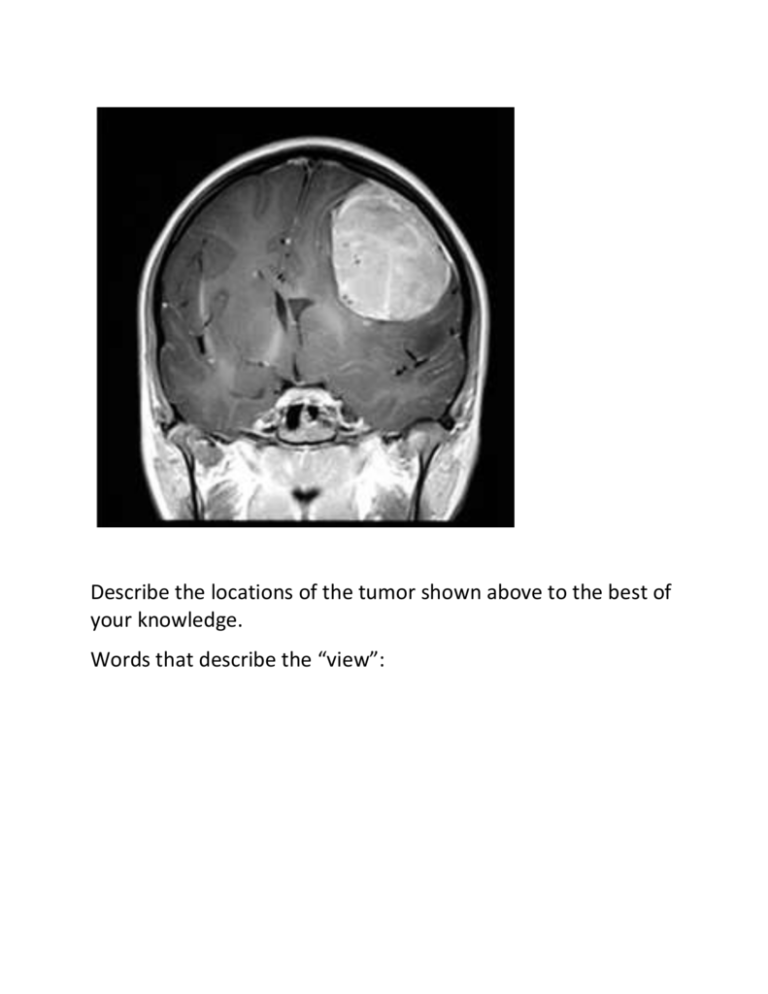
Describe the locations of the tumor shown above to the best of your knowledge. Words that describe the “view”: Fig. 1-9, p. 20 Fig. 1-8, p. 18 Words that describe position: Left/right Ventral/ dorsal Medial/ lateral Palmer/ plantar Anterior/ posterior femoral/ humeral Proximal/ distal frontal/ saggital/ transverse Cranial/ caudal frontal/ supine/ prostrate Words that describe location: System: 11 systems Tissue: nervous, muscular, epithelial, connective Body Cavity: Dorsal Cranial Spinal Cranial bones Vertebral column Brain Spinal cord vs Ventral Thoracic pericardial Abdominopelvic Abdomen- 2 pleural Mediastinum Pelvic Fig. 1-10a, p. 21 Specific location within a cavity: Fig. 1-10c, p. 21 9 Abdominopelvic Regions Right Epigastric Hypochondriac Right Hypochondriac Umbilical Lumbar Fig. 1-7, p. 17 Left Left Lumbar Right inguinal Hypogastric Left inguinal (iliac) (Pubic) (iliac) Membrane, Organ or Appendage: Serous Membranes: pleural, pericardial Describe the location of the fracture. Is a virus “alive”? What characteristics are shared by all living things? Metabolism: sum of all chemical processes Food in and broken down-> catabolism New molecules and structures synthesized -> anabolism Responsiveness: stimulus -> response Movement: internal for all, external for many Growth Differentiation -stem cells Reproduction Homeostasis: The state of staying the same in spite of change. External changes -> temperature Internal changes -> blood pressure, sodium content Homeostasis, Pathology, and Death External changes and homeostasis = thermal regulation Internal changes and homeostasis = physiological regulation Nerves: -rapid and results from nervous impulses =shivering, reflexes Endocrine: -slower -hormones into the blood Feedback Systems -a cycle of events Monitor a controlled condition, any disruption of that condition is a STIMULUS. Body status continually monitored Evaluated Changed Re-monitored Re-evaluated 3 Basic Components of a Feedback System Receptor –monitors changes in the controlled condition. Sends message to the control center. Control Center- sets an acceptable range of values for a particular condition. Evaluates the input from the receptors and executes a change when necessary. Effector-Receives output from the control center and executes a response to change the controlled condition. What would happen in response to this stimulus? Nervous and Endocrine! NEGATIVE FEEDBACK: A mechanism of response in which a stimulus initiates actions that reverse or reduce that stimulus. Using the diagram above how does insulin regulate blood sugar? POSITIVE FEEDBACK: A feedback mechanism in which the response enhances the original stimulus. WATER -H2O Can life exist without water? It is where life began and it is the first habitat of human life. What makes it so special? Dipole A single molecule of water has 2 covalent bonds (shared electrons) and is neutral in net charge BUT it has unequal distribution of charge which gives it special properties. Water is a good solvent and dissolves polar substances. Because each side has a different charge it has electronegativity that allows it to form ionic bonds with ions. Positive ions are attracted to the negative side (oxygen) and negative ions are attracted to the positive side (hydrogen). This characteristic allows it to form solutions in living systems. Hydrophilic substances “like” water and dissolve in it or interact with its polar nature. Living things have “hydrophilic” a. Hydrogen bonding Hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic bonds that form between the hydrogen proton of one molecule with the negatively charged side of another –here its own oxygen. The hydrogen bond is weak by itself but strong in combination with others. Fig. 2-6, p. 33 Water can form 4 hydrogen bonds due to its tetrahedral structure. In ice it forms all 4. In liquid water it forms 3 bonds. These three bonds account for important biological properties and also why a belly flop hurts so much. 1. Solvent -hydrophilic (polar) Ionic bonding in sodium chloride above vs. covalent bonding in glucose below –still both are hydrophilic -hydrophobic (non-polar) oil and water! 2. Cohesion of Water Molecules -surface tension -hydrogen bonding 3. Water as a lubricant 5. High Heat Capacity -can absorb or release large quantities of heat without a large change in its temperature. pH Definition: The negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration. p = negative log (log = an exponent) each pH unit is a 10 fold increase pH scale 0 to 14 acid to base lots of H+ to less H+ (and more OH -) Based on the [H+], (hydrogen ion concentration) At pH 7, the [H+] is 0.0000001 M H+/ liter or 10 –7 The negative log = - (-7) or 7 Strong acids (or bases): ionize easily and contribute many H+ or (OH-). They change pH drastically. Weak acids (or bases): don’t ionize much and contribute less H+ or OH-. They have less of an effect on pH.