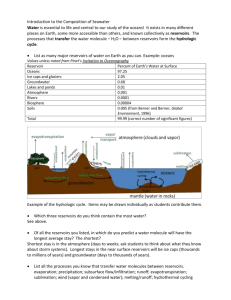
osmosis problems ws

Name_________________________ Osmosis Problems
Diffusion is the spread of a substance from a high concentration to a low concentration. This is important to know when you want to figure out how solutes (sugars, salts, amino acids and other biologically important molecules) will travel from inside a cell to the outside, or the other way around.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water from a high concentration of water to a low concentration of water.
See how the terms ‘of water’ are highlighted? You need to memorize the definition as I have written it, or else the problems will be confusing.
Tonicity is a chemical and physical property of solutions. Name 3 other properties of solutions:_____________,_______________________, and ___________________.
Tonicity refers to the concentration of solutes (the dissolved substances). In cells, these solutes that give the cytoplasm its tonicity include salts, sugars, amino acids and any other molecule which happens to be in the cytoplasm.
The terms hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic refer to the concentration of dissolved solutes in a solution, and cytoplasm is considered a solution.
Write the meanings of these word parts: hyper__________________, hypo____________________, iso_______________________.
Hypertonic refers to a solution that has a greater concentration of solutes. Solutes will diffuse down their concentration gradient to equalize on the other side of the membrane, as long as the mbn is permeable to the solute.
So, define “hypotonic”:
Why is distilled water the ultimate in hypotonic solutions?
Remember that these are relative terms. This means that a solution can be called hypertonic only when it is compared with another solution. When we compare solutions, we use an abbreviation: WRT means
‘with respect to’, or compared with. You need to know this.
We will do problems that include drawings of cells in beakers. Each side will have its own tonicity. You will need to say which way water will diffuse, and which way solutes will diffuse.
The units of solutes are a unit of mass of solute over a unit of volume of solution. (This is like density…)
Often it is mg of solute such as salt over cubic mls of solution.
Procedure:
For each of the following, draw a beaker, and a cell inside of it, and label the tonicity of the cell and its environment (the solution in the beaker)
1.
Cells with a tonicty of 0.04 mg/ml are placed in distilled water, ( standard abbreviation is DW) which by definition has a tonicity of 0.0mg/ml.
Draw and label:
The cell is (hyper, hypo, iso) with respect to (WRT) the solution. The solution is (hyper, hypo, iso)
WRT the cell. Water will ___________________(enter, leave) cell. Solutes will (enter, leave) cell until dynamic equilibrium is reached.
2.
Cells with a tonicity of 0.02 mg/ml are placed in a beaker of sea water, with a tonicity of 0.09 mg/ml.
Draw and label:
The cell is (hyper, hypo, iso) with respect to (WRT) the solution. The solution is (hyper, hypo, iso)
WRT the cell. Water will ___________________(enter, leave) cell. Solutes will (enter, leave) cell until dynamic equilibrium is reached.
3.
Cells with a tonicity of 0.05mg/ml are placed in a solution with a tonicity of 0.05 mg/ml.
Draw and label:
The cell is (hyper, hypo, iso) with respect to (WRT) the solution. The solution is (hyper, hypo, iso)
WRT the cell. Water will ___________________(enter, leave) cell. Solutes will (enter, leave) cell until dynamic equilibrium is reached.
4.
Cells with a tonicity of .03 mg/ml are placed in a solution of 1.1 mg/ml.
Draw and label:
The cell is (hyper, hypo, iso) with respect to (WRT) the solution. The solution is (hyper, hypo, iso)
WRT the cell. Water will ___________________(enter, leave) cell. Solutes will (enter, leave) cell until dynamic equilibrium is reached.