FCAT REVIEW Earth Science Worksheet
advertisement
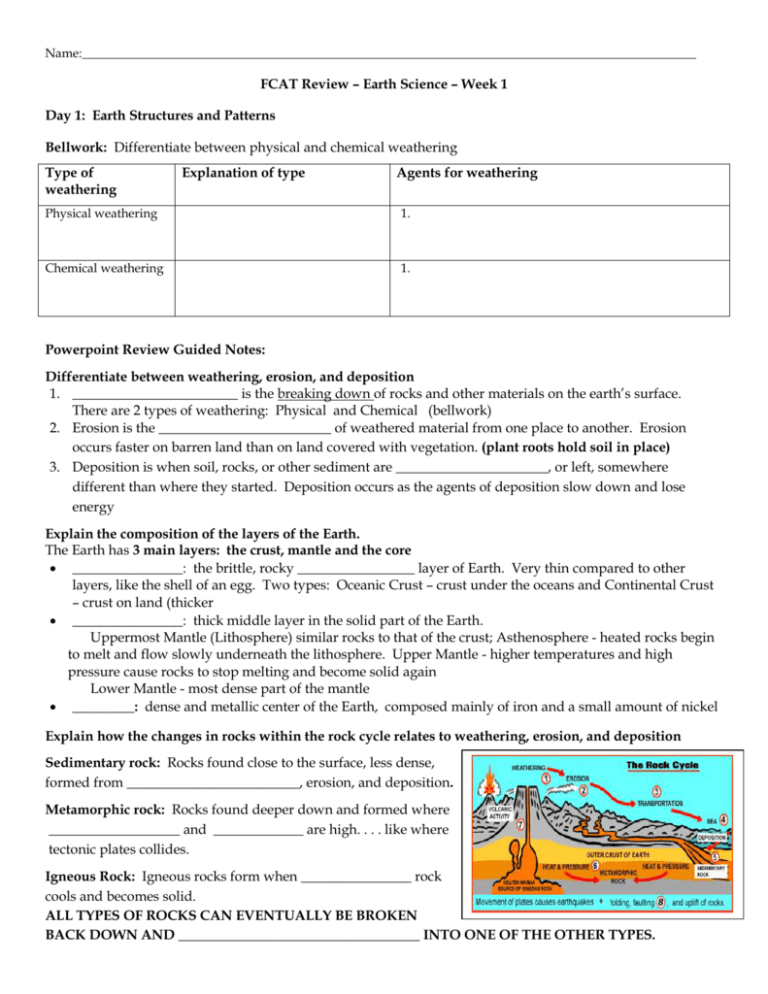
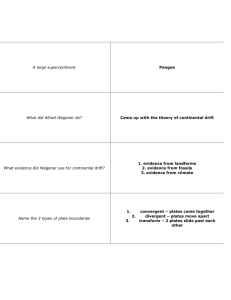
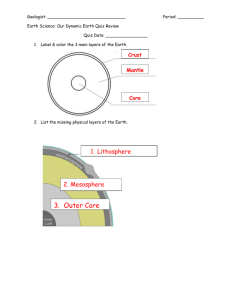
Name:__________________________________________________________________________________________________ FCAT Review – Earth Science – Week 1 Day 1: Earth Structures and Patterns Bellwork: Differentiate between physical and chemical weathering Type of weathering Explanation of type Agents for weathering Physical weathering 1. Chemical weathering 1. Powerpoint Review Guided Notes: Differentiate between weathering, erosion, and deposition 1. ________________________ is the breaking down of rocks and other materials on the earth’s surface. There are 2 types of weathering: Physical and Chemical (bellwork) 2. Erosion is the _________________________ of weathered material from one place to another. Erosion occurs faster on barren land than on land covered with vegetation. (plant roots hold soil in place) 3. Deposition is when soil, rocks, or other sediment are ______________________, or left, somewhere different than where they started. Deposition occurs as the agents of deposition slow down and lose energy Explain the composition of the layers of the Earth. The Earth has 3 main layers: the crust, mantle and the core ________________: the brittle, rocky _________________ layer of Earth. Very thin compared to other layers, like the shell of an egg. Two types: Oceanic Crust – crust under the oceans and Continental Crust – crust on land (thicker ________________: thick middle layer in the solid part of the Earth. Uppermost Mantle (Lithosphere) similar rocks to that of the crust; Asthenosphere - heated rocks begin to melt and flow slowly underneath the lithosphere. Upper Mantle - higher temperatures and high pressure cause rocks to stop melting and become solid again Lower Mantle - most dense part of the mantle _________: dense and metallic center of the Earth, composed mainly of iron and a small amount of nickel Explain how the changes in rocks within the rock cycle relates to weathering, erosion, and deposition Sedimentary rock: Rocks found close to the surface, less dense, formed from _________________________, erosion, and deposition. Metamorphic rock: Rocks found deeper down and formed where ___________________ and _____________ are high. . . . like where tectonic plates collides. Igneous Rock: Igneous rocks form when ________________ rock cools and becomes solid. ALL TYPES OF ROCKS CAN EVENTUALLY BE BROKEN BACK DOWN AND ___________________________________ INTO ONE OF THE OTHER TYPES. Explain how we use the law of superposition and radioactive dating to date fossils. Law of Superposition Radioactive Decay Dating of Fossils The Law of Superposition – says that the ________________________ rocks are on the top and the ________________________ rocks are on the bottom. Radioactive dating of fossils: ________________________ is one of the basic elements of life. Carbon atoms decay at a constant rate, so scientists use the ________________ of carbon in life forms to date when these fossils lived. Explain how the theory of plate tectonics is used to describe how the Earth’s surface is built up and torn down. The theory of Plate Tectonics is based on Wegeners theory of Continental Drift which stated that the continents were once all connected (Pangea). The movement of the _____________________ __________________ caused the continents to separate and move apart. The evidence of what happens at plate boundaries and the formation of new crust helps support this theory. Fossil evidence where organisms of the same species were found on different continents also help support it. Explain how the convecting mantle causes earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and creates mountains and ocean basins. The earth’s mantle is where ________________________ currents happen that provide the energy for tectonic plates to move. This movement of plates happens at the __________________and each type of boundary movement can cause a different type of landform or event. Convergent boundary: two plates move _______________ each other – This can cause subduction where one plate slides underneath another and is destroyed or it can slowly form a ______________________. Divergent boundary: where two plates move __________________from each other resulting in _____________ ________________ (ocean basins) being formed. Transform boundary: where two plates move __________________________ each other - although crust is neither created or destroyed here, they can get caught and cause earthquakes Online interactive and video practice: Rock cycle: http://www.learner.org/interactives/rockcycle/index.html Earth’s structure and plate tectonics: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/ Test your Earth structure skills: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/testskills.html Law of Superposition: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EadTLGMu3LI Radiocarbon dating: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2io5opwhQMQ Study the information above for a 10 question quiz tomorrow QUIZ SCORE_____/10 Day 2: Earth’s Atmosphere and Weather Bellwork: Quiz on Day 1 materials Powerpoint Review Guided Notes: Differentiate between conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction: heat transfer through __________________ Convection: heat transfer from a ___________to a gas or a gas to a liquid Radiation: heat transfer through__________________________ radiation Explain how the water cycle affects weather patterns and climate. The ___________________ cycle plays a key role in weather patterns and local climate. For example: Cities near the ocean will have higher humidity levels and higher chances of rain because they are closer to the area where water evaporates off the oceans. Locations farther from where evaporation happens will have drier ____________________. Explain how the jet stream and ocean currents affect local weather. Jet Stream Ocean Currents A jet stream forms high in the upper troposphere between two ____________ __________________ masses of very different temperature. The greater the temperature difference between the air masses, the faster the ________________________ blows in the jet stream. Ocean Currents: Varying ocean _________________________ affect local atmospheric pressure, which creates regional _____________________patterns that, in turn, drive oceanic currents that affect surface ocean temperatures. Explain the interactions between the geosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. Atmosphere: Earth’s __________ _____________________: Earth’s nonliving structures Biosphere: Earth’s _____________ organisms Hydrosphere: Earth’s _______________ Cryosphere: Earth’s ______________ masses Even a small ____________________ in one system can change one or more of the other systems. How does the Sun’s energy influence weather and climate? The Earth ‘s ____________________________ shape causes it to be heated ___________________. The equator region receives more direct sunlight (thermal energy) The warmer air at the equator caused by more __________________ sunlight causes ___________________ currents to form in Earth’s atmosphere. These currents are what drive _____________________ patterns. Differentiate between weather and climate. Weather is the _______________________ atmospheric conditions in an area. Climate is the __________________ ______________________ conditions in an area over a long period of time. Describe how the composition and structure of the atmosphere protects life and insulates the planet. Our atmosphere does three main things: helps _________________ some of the radiation from the Sun holds _____________ in so that the temperature can sustain life Holds in the _________________ needed for life; CO2, O2, and N Online interactive practice: Conduction, convection, and Radiation: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pnVVJfUMkAo Convection Currents and humidity: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nQ0GAib-X0U Convection in ocean currents: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7xWWowXtuvA Earth Systems: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ciV6Uaeobxk Layers of the atmosphere: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0vcHBNMw2h0 Study the information above for a 10 question quiz tomorrow QUIZ SCORE_____/10 Day 3: Energy and Transformations Bellwork: Explain the electromagnetic spectrum and the types of radiation that make it up. Powerpoint Review Guided Notes: Differentiate between reflection and refraction. (VOCAB) Explain how different types of waves travel through different mediums Explain how the Law of Conservation of Energy is supported in different energy transfer situations. How can you change the state of a state of matter? From solid to liquid to gas or from Gas to liquid to solid. Describe the transformation of energy from one form to another in various situations. Give evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. Describe and give examples that heat flows in predictable ways, moving from warmer objects to cooler ones until they reach the same temperature. Practice and vocabulary: Online interactive practice: Energy Flow: http://www.alliantenergykids.com/FunandGames/OnlineGames/KIDS_GAME_FLOW_OF_ENERGY http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/energy-skate-park Waves: http://www.tryscience.org/experiments/experiments_japan_online.html Study the information above for a 10 question quiz tomorrow QUIZ SCORE_____/10 Day 4: Force, Motion, and Graphing motion Bellwork: Use the data in the table to create a graph that charts the motion of each object listed. Explain whether the object is increasing speed, decreasing speed, or traveling at a constant speed. Powerpoint Review Guided Notes: Differentiate between contact and non-contact forces. Explain how non-contact forces like electrical, magnetic, and gravitational force act on an object. What two things does the law of gravity depend on? Explain how gravity changes when mass or the distance between two objects changes. Explain how motion happens. Describe how unbalanced forces acting on an object will affect its speed and/or direction of motion. Practice and vocabulary: Online interactive practice: Roller Coaster Force and Motion: http://www.funderstanding.com/slg/coaster/ Graphing Motion: http://www.learner.org/workshops/force/mouselab.html Study the information above for a 10 question quiz tomorrow QUIZ SCORE_____/10