Unit 4 - Leona QSI Math Site
advertisement

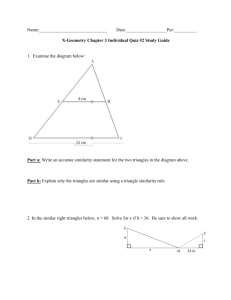
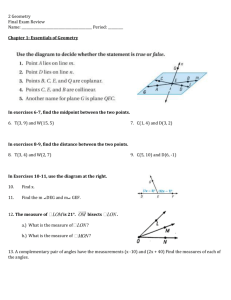
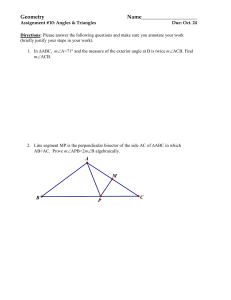
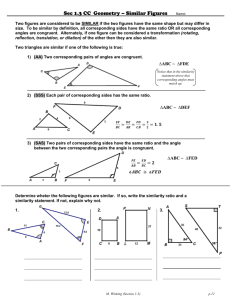
LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Geometry B 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A Course: Geometry B Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 Unit 4: Similarity (10 days) Essential Questions: What properties can be identified between similar geometric figures? How can similar geometric figures be used to solve real world problems? AZCCRS Standards = Major □ = Supporting ○= Additional ★= Modeling Core Content (High School Standards) Key Vocabulary: Transformations, Reduction, Enlargement, Corresponding Parts, Postulate, Theorem, Prove, Given, Two-Column Proof, Paragraph Proof, Conjecture, Counterexample, Deductive, Inductive, Contradiction, Symmetric Property, Reflexive Property, Transitive Property, Scalene, Isosceles, Equilateral, Trapezoid, Parallelogram, Rectangle, Square, Rhombus, Kite, Dilation, Center, Proportional, Ratio, Scale Factor, Similarity, Center of Dilations, Mid-Segment Tier 3 Support Assessment Resources Formal Dilations Triangle and Polygon Similarity Applications and Proofs of Similarity G.SRT.A.1a Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor: a. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged. b. The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor.and G.SRT.A.2 Given two figures, use the definition of similarity in terms of similarity transformations to decide if they are similar; explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles as the equality of all corresponding pairs of angles and the proportionality of all corresponding pairs of sides. G.SRT.A.3 Use the properties of similarity transformations to establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar. Describe the effects and the properties of figures that have been dilated about the origin and other points. Given a ratio identify a point on a line segment between two given end points that partitions the segment in a given ratio. Recognize and identify that the corresponding sides of the dilated objects are parallel and that line going through the center of the figures are unchanged. G.SRT.B.4 Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. G.SRT.B.5 Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Understand and apply scale factor through dilations of geometric figures. Prove that two figures are similar using dilations. G.GPE.B.6 Find the point on a directed line segment between two given points that partitions the segment in a given ratio. Mathematical Practices MP.1-8 Understand and determine that corresponding sides are proportional and corresponding angles are congruent in similar figures. Make connections between dilations Draw dilated figures using a scale factor. Identify corresponding parts of geometric figures. Write ratios and simplify. 1. Pre Test 2. Quizzes 3. Unit Test http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_296 _g_4_t_3.html?open=activities&from=topic _t_3.html http://tube.geogebra.org/student/m157262 http://tube.geogebra.org/student/m449131 Informal 4. 5. Checking for Understanding 6. http://www.absorblearning.com/media/attac hment.action?quick=hr&att=1270 7. http://www.absorblearning.com/media/attac hment.action?quick=hq&att=1268 8. http://www.nctm.org/standards/content.aspx ?id=26770 http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id =3165 Questioning Set up proportions and solve for a variable. Dilations http://www.cpm.org/flash/technology/panto graphv1.2.swf https://share.ehs.uen.org/node/12485 Completion of Project/Activity/ Assignments Summarization of Learning Daily Exit Slip 9. 10. http://math.kendallhunt.com/documents/dg4/ condensedlessons/dg4cl_895_11.pdf 11. http://www.cpm.org/pdfs/information/sampl eChapters/CCG%20Ch%203%20TV.pdf Similarity in Polygons 12. http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id =2469 13. http://fawnnguyen.com/listerine-fuji-water2/ Updated: 2/9/2016 Course: Geometry B Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Geometry B 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A and angle properties between similar figures. Prove that the congruence of two angles leads to similarity in two triangles. Prove that two triangles are similar by AA, SAS, and SSS criteria. Prove a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two sides of the triangle proportionally. Use properties of similar figures to solve problems and applications of similarity. Similarity in Triangles 14. http://cpm.org/technology/general/similarity / 15. http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ATriang leFormedByTheCentersOfThreeCircles/ 16. http://www.cpm.org/technology/CCG/Ch3/ AAA_Similarity.html 17. http://www.cpm.org/technology/CCG/Ch3/S AS_Similarity_v3.html 18. http://www.cpm.org/technology/CCG/Ch3/S SA_Similarity.html 19. http://www.cpm.org/technology/CCG/Ch3/S SS_Similarity.html 20. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/download .php?fileid=1257 21. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/download .php?fileid=1372 22. http://www.mathopenref.com/similartriangle s.html 23. http://threeacts.mrmeyer.com/besttriangle/ 24. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.p hp?taskid=429#task429 25. http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/TheRati oTheorem/ 26. http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id =1672 27. EngageNY https://www.engageny.org/resource/geometr y-module-2 28. http://www.mathematicsvisionproject.org/up loads/1/1/6/3/11636986/sec2_mod6_simtrig _tn_83113.pdf 29. Discovery Geometry Website with minilessons Updated: 2/9/2016 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Geometry B 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A Course: Geometry B Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 http://math.kendallhunt.com/x19812.html 30. http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/ Unit 5: Key Vocabulary: Essential Questions: What unique properties are found in right triangles? Right Triangles What are trigonometric ratios and how are they related to similar right triangles? How can right triangles and their properties be used to solve problems? (12 days) Right Triangle Similarity Trigonometry Applications and Proofs with Right Triangles AZCCRS Standards = Major □ = Supporting ○= Additional ★= Modeling G.SRT.B.4 Prove theorems about triangles. Theorems include: a line parallel to one side of a triangle divides the other two proportionally, and conversely; the Pythagorean Theorem proved using triangle similarity. G.SRT.B.5 Use congruence and similarity criteria for Core Content (High School Standards) G.SRT.C.6 Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. G.SRT.C.7 Explain and use the relationship between the sine and cosine of complementary angles. G.SRT.C.8 Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. (★) Mathematical Practices MP.1-8 Tier 3 Support Resources Assessment Formal Use properties of right triangles to solve problems. Including special right triangle properties in triangles of 45-45-90, and 30-60-90. triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. Transformations, Corresponding Parts, Postulate, Theorem, Prove, Given, TwoColumn Proof, Paragraph Proof, Conjecture, Counterexample, Deductive, Inductive, Contradiction, Symmetric Property, Reflexive Property, Transitive Property, Right Triangle, Distance Formula, Dilation, Proportional, Ratio, Scale Factor, Similarity, Pythagorean Theorem, Hypotenuse, Opposite Side, Adjacent Side, Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Trigonometry, Trigonometric Ratios, Inverse Trigonometry Show that the relationship between the side ratios of similar right triangles are the same and related to their corresponding angles, which leads to the definition of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. Prove the Pythagorean theorem using the properties of similar right triangles. Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean theorem to solve problems and applications of right triangles. Understand and explain the relationship between trigonometric Define complementary and supplementary, obtuse, acute, and right angles. Identify the parts of a right triangle (hypotenuse, legs). Use the Pythagorean theorem to solve for a side length of a right triangle. Use the Pythagorean theorem to identify if a triangle is a right triangle. 1. http://www.nbclearn.com/nfl/cuecard/51220 Pre Test Quizzes 2. Unit Test 3. Informal 4. Checking for Understanding 5. Questioning Completion of Project/Activity/ Assignments 6. 7. 8. Summarization of Learning 9. Daily Exit Slip Proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/me pres/book8/y8s3act.pdf http://map.mathshell.org/materials/tasks.php ?taskid=276&subpage=expert http://www.cpm.org/flash/technology/pytha goreanv1.2.swf http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_164 _g_4_t_3.html?open=instructions&from=to pic_t_3.html Trigonometric Functions http://illuminations.nctm.org/hsactivity/ http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id =2493 http://www.teachengineering.org/view_activ ity.php?url=http://www.teachengineering.or g/collection/cub_/activities/cub_navigation/c ub_navigation_lesson03_activity2.xml http://www.teachengineering.org/view_lesso n.php?url=collection/uno_/lessons/uno_hand held/uno_handheld_lesson01.xml 10. http://www.cpm.org/technology/CCG/Ch4/L eaning_Tower_of_Pisa.html Updated: 2/9/2016 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Geometry B 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A Course: Geometry B Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 functions (especially with the sine and cosine of complementary angles). Unit 6: Circles (8 days) Similarity and Circles Inscribed Angles, Radii, and Chords Constructions with Circles Essential Questions: What unique properties are found in circles? How can circles and their properties be used to solve problems? AZCCRS Standards = Major □ = Supporting ○= Additional ★= Modeling □G.CO.D.13 Construct an equilateral triangle, a square, and a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle. ○G.C.A.1 Prove that all circles are similar. ○G.C.A.2 Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. ○G.C.A.3 Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle, and prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle. ○G.GPE.A.1 Derive the equation of a circle of given Circles in a Coordinate Plane center and radius using the Pythagorean Theorem; complete the square to find the center and radius of a circle given by an equation. G.GPE.B.4 Use coordinates to prove simple Core Content (High School Standards) Prove that all circles are similar. Solve problems using the relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle. Constructions with circles Write equations of circles given the center and radius. Prove or disprove a given point lies on the circles. Relate it to the Pythagorean theorem. 11. http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/HowFar CanOneSeeFromAHeight/ 12. EngageNY https://www.engageny.org/resource/geometr y-module-2 13. http://www.cpm.org/pdfs/information/sampl eChapters/GC_Ch4_2006_TV.pdf 14. http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/ Key Vocabulary: Postulate, Theorem, Prove, Given, Two-Column Proof, Paragraph Proof, Conjecture, Counterexample, Deductive, Inductive, Contradiction, Symmetric Property, Reflexive Property, Transitive Property, Dilation, Proportional, Ratio, Scale Factor, Similarity, Pythagorean Theorem, Circle, Center, Diameter, Radius, Semi-Circle, Circumference, Area, Chord, Secant, Tangent, Minor Arc, Major Arc, Arc Length, Arc Measure, Inscribed, Circumscribed, Central Angle, Intercepted Arc, Point of Tangency Tier 3 Support Know where Pi came from (as a ratio of circumference to diameter) Define the parts of a circle (radius, diameter, circumference, center) Resources Assessment Circle Parts and Properties Formal Pre Test 1. Quizzes 2. Unit Test 3. Informal Checking for Understanding Questioning Completion of Project/Activity/ Assignments http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/Geometr icElementsOfACircle/ http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id =2417 http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id =3777 Circles and Triangles 4. 5. 6. 7. Summarization of Learning 8. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.p hp?taskid=403&subpage=problem http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id =2219 http://map.mathshell.org/materials/download .php?fileid=696 http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id =2374 Circles in Coordinate Plane http://map.mathshell.org/materials/download .php?fileid=1202 Updated: 2/9/2016 Course: Geometry B Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). Mathematical Practices MP.1-8 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Geometry B 2014-2015 Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A Tier 1+ Introduce unit circle relating trig functions and converting from degrees to radians. Daily Exit Slip 9. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/download .php?fileid=1247 10. EngageNY https://www.engageny.org/resource/geometr y-module-5 11. http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/ Updated: 2/9/2016