Finance & Business Technology - Effective Presentations
advertisement

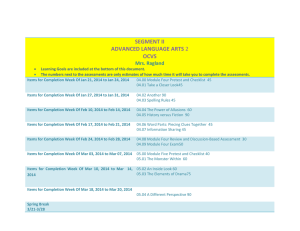
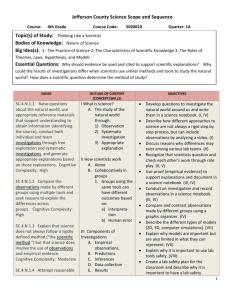
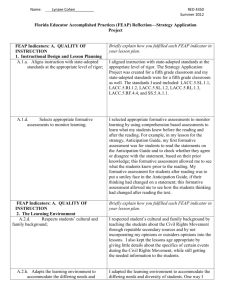
1 PROJECT-BASED LEARNING (PBL) Planning Template Name of Project: Effective Presentations Duration (hrs): 5 CTE Course: Finance & Business Technology Grade Level: 9 Academic Course(s): English I Teachers: Vincent Roeshink Janice Tonger Project-Based Learning Components Project Idea: Summary of the issue, challenge, investigation, scenario, or problem. Knowledge, Skill and Application of Information Processing Systems Driving Question: The question that both engages student attention and focuses their efforts. How can I create an effective presentation? Anchor Event/Project Launch: Introduction and/or background information to set the stage and generate interest. Students will complete a brief study of the different advertising methods, working to recognize each when seen in a real-world example. Inquiry & Innovation: Discuss how the project engages students in innovative research and thought in each curriculum area. Students must create, and fully develop a multi-media campaign, presented via Power Point promoting a product, utilizing the advertising techniques taught. Use Technology to increase and demonstrate communication skills. ADAPTED FROM ©2011 BUCK INSTITUTE FOR EDUCATION 2 Process of Investigation: Develop student guidelines for each phase of project. 1. Introduction and Team Planning: Students are grouped and will determine the scope, depth and breadth of their advertising promotion, via Power Point. Project Calendar 2. Initial Research Phase - Gathering Information: As assigned by group members, students will gather appropriate information pertaining to the promotion of their product. P:roject Teaching & Learning Guide Project Management Log In these beginning steps, students will determine which information is valuable, valid and viable. Next, they will determine the most effective method of broadcasting that information. 3. Creation and Development of Initial Artifacts, Product(s), and/or Prototype(s): 4. Second Research Phase - Additional Information & Revision: Having filtered the original research completed, students will collect any additional information necessary. Collaboration: Discuss collaboration among colleagues in teaching the project. Discuss collaborative instructional strategies utilized by students. Collaboration Rubric Now students are polishing their presentations, practicing the oral aspects, and 5. Final Presentation Development: making final revisions. 6. Publication of Product or Artifacts: Students will present orally their products. Teachers: Roeshink and Tonger compared assigned curriculum maps, identified common lessons, and worked to support each other’s lessons, providing multiple opportunities for students to access instruction, tutoring (if needed) and practice via assignments from each. Students: Students will participate in Think/Pair/Shares and Role assignments in completing the research and development of the Power Point presentations. ADAPTED FROM ©2011 BUCK INSTITUTE FOR EDUCATION 3 Student Voice: Describe how students play a role in project design and implementation. Students will jointly collaborate and determine the topic advertised, the method(s) used to advertise the product, including visual imaging, sound effects, sound bytes and length of presentation. Major Products & Performances: Elaborate on products; Discuss publication and presentation of projects. Products: Students will produce a multi-genre Power Point. Publication/ Presentation: Group: Students will each present a portion of the group project, within the allotted Presentation Rubric Presentation Audience 5-7 minute time frame. Class School Community Individual: Experts Business/Community Web Other: Instructional Technology: Select and discuss the technology-based instructional options embedded in the project. Webquests Course Management System Presentation Hardware Blogs Alternate Reality Games (ARGs) RSS Feeds Wikis Simulation Software Digital Video Tools Social Network Presentation Software Digital Photography Tools Video Conferencing Podcasts Other: (Software or online) (Software or online) Discussion: ADAPTED FROM ©2011 BUCK INSTITUTE FOR EDUCATION 4 Business/Community Involvement: Describe how business partners contribute to project learning. Project Standards Topics of Study: Main areas of project investigation. The main areas of project investigation are advertising techniques. Content Standards: Those taught and assessed in the project: CTE Performance Standards Common Career Technical Core (CCTC) Standards These standards will be released/August 2012 Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards LAC.910.RI.1.1; LACC.910.RI.1.2;LACC.910.RI.1.3; LACC.910.RI.2.4; LACC.910.RI.2.5; LACC.910.RI.2.6; LACC.910.RI.3.7;LACC.RI.3.8; LACC.910.RI.4.10 Common Core Standards 21st Century Skills: Those taught and assessed in the project. LEARNING & INNOVATION SKILLS INFORMATION, MEDIA, & TECHNOLOGY SKILLS LIFE & CAREER SKILLS Creativity & Innovation Information Literacy Flexibility/Adaptability Productivity/Accountability Critical Thinking/Problem Solving Media Literacy Initiative/Self Direction Leadership/Responsibility Communication/Collaboration ICT Literacy Social/Cross-Cultural For descriptions follow web links ADAPTED FROM ©2011 BUCK INSTITUTE FOR EDUCATION 5 Project Assessment, Reflection, Feedback & Revision Assessments: Formative Assessments (During Project) Quizzes/Tests Practice Presentations Journal/Learning Log Notes Preliminary Plans/Outlines/Prototypes Checklists Rough Drafts Concept Maps Online Tests/Exams Other: Written Product(s) w/ Rubric: Other Product(s) or Performance(s) w/ Rubric: Oral Presentation w/ Rubric Peer Evaluation Multiple Choice/Short Answer Self-Evaluation Essay Test Other: Individual Journal/Learning Log Focus Group Group Whole Class Discussion Fishbowl Discussion Whole Class Survey Other: Grades Written Comments Group Feedback Peer Feedback Individual Feedback Self-Assessment Summative Assessments (End of Project) Reflection Methods: Feedback & Revision: Scaffolded feedback and “check points” should be routinely provided by the teacher within the collaborative instructional process. Feedback can be based on either teacher and/or peer evaluations. ADAPTED FROM ©2011 BUCK INSTITUTE FOR EDUCATION