File - Nanette Brown Portfolio
advertisement

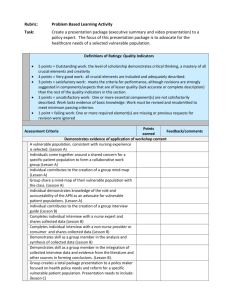
Running head: VULNERABLE POPULATIONS Vulnerable Populations Nanette Brown NURS 340 Ferris State University 1 VULNERABLE POPULATIONS 2 Vulnerable Populations Vulnerable populations in healthcare are defined as those individuals or groups of people that there is a noted gap or difference in the healthcare they receive as opposed to the general public (Harkness and DeMarco, 2012 p. 32). There are a variety reasons that individuals or populations fall into the vulnerable or underserved populations in healthcare. Race and culture are not the only factors, for example gender, sexual orientation, particular diseases, lower socioeconomical status or geographic location can play a role in healthcare disparities (Healthy People 2020, 2013). The vulnerable population focused on in this paper are Spanish speaking Hispanics. It is an exploration of my own personal bias and information on their healthcare gathered from research on this population. Providing nursing care to Spanish speaking patients has been a struggle for myself in my nursing career. I find it frustrating primarily due to the fact that the language barrier interferes with my ability to give the best care that I can. I am not confident that the patient understands their illness, treatments and care given. I do not feel as though I understand what all of their needs are. It gives me a feeling of inadequacy; that I am not able to care for my patient the way I would like to. Another issue for me is that it takes much more time to care for them thus taking away time from my other patients. That being said, I do feel all patients should have access to and receive quality health care. It is apparent to me that we fail some of these patients when I see they are readmitted to the hospital for complications or worsening of their disease because they did not understand to take their medication or have a means to get it or understand their aftercare/discharge instructions. For example, I had a family continue to give water to their family member with severe dysphagia which resulted in many admissions for aspiration pneumonia. Not only was it VULNERABLE POPULATIONS 3 not well understood why the patient could not have anything by mouth but I believe culture played a part also. Fortunately with the advent of language lines and more interpreters available than when I first entered the nursing field; communication with this population has improved. We also now have many patient education materials available in Spanish which is also has also improved communication. However there still is room to further enhance communication thus providing better health care to this population. In a study of nearly 18,000 Hispanics by DuBard, C. and Gizlice, Z. (2008) the following demographic characteristics where found. Of the Spanish speaking population include lack of education, 59% of Spanish-speaking Hispanics have less than a high school education compared to 18% of English- speaking Hispanics. Low socioeconomic status having an income less than $15,000 was reported in 36% of the Spanish-speaking as compared to 15% of English-speaking Hispanics even though more than 60% of both groups had jobs. Lack of health insurance was higher in the Spanish-speaking population; 55% as compared to 23% of English-speaking making access to care more difficult for the Spanish-speaking. According to the United States census (2011) 69% of all Hispanics have health insurance and 30% are uninsured. In the State of Michigan there are 89,953 Hispanic people (State of Michigan, 2012). In Montcalm County 3.1% of the population is Hispanic compared to 4.4% in Michigan (Mid-Michigan District Health Department, 2013). Living in an area where more Spanish-speaking people live seems to increase access to care (Gresenz, C., Rogowski, J. & Escarce, J., 2009). This was felt to be possibly due to having a stronger social networks and being able to aid one another in accessing care. Both studies found that few have a primary care physician (PCP), 58% Spanish-speaking compared to 29% Englishspeaking do not have a PCP (DuBard & Gizlice, 2008). There tends to more Spanish-speaking VULNERABLE POPULATIONS 4 physicians in areas that have a larger population of Spanish-speaking individuals (Gresenz et al. 2009). Although research supports that there is a huge disparity in health care for Spanishspeaking Hispanics, it is not for the same reason that I am biased. It is my lack of comfort in being able to give good care with the language barrier. Therefore I would say the research did not change my bias, but did open my eyes to how large this population is in the United States; many of which do not have access to health care. In looking at the number of individuals who speak Spanish I do feel as a professional that I should do something to lessen the barrier. Perhaps after school I will take some Spanish classes for health care workers. Maybe having classes in Spanish should become part of all health career education; not that everyone would be proficient but would at least have some ability to speak or understand the language. If we can communicate better with the Spanish-speaking population, we have the opportunity to understand their needs, improve education for them regarding their health care needs and the need for preventative health care. Based on the size of this population we have tremendous job ahead of us to lessen the disparities in healthcare for this group of people. VULNERABLE POPULATIONS 5 References DuBard, C., & Gizlice, Z. (2008). Language spoken and differences in health status, access to care, and receipt of preventive services among U.S. Hispanics. American Journal of Public Health, 98(11), 2021-2028. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2007.119008 Gresenz, C.,Rogowski, J. & Escarce (2009) Community demographics and access to health care among U.S. Hispanics. Health Services Research, 44(5) pp.1542-1562. doi:10.1111/j1475-6773.2009.00997.x Harkness, G. A., & DeMarco, R. F. (2012). Community and public health nursing: Evidence for practice. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Healthy People 2020 (2013) disparities. Retrieved from: http://healthypeople.gov/2020/about/DisparitiesAbout.aspx Mid-Michigan District Health Department (2013) Montcalm county community health assessment. Retrieved from: http://www.mmdhd.org/cha/montcalm/CHA_Montcalm_Co_Profile.pdf State of Michigan (2012) Census and demographics data. Retrieved from: http://michigan.gov/cgi/0,4548,7-158-54534-305736--,00.html United States Census (2011) Hispanic population in the United States: 2011. Retrieved from: http://www.census.gov/population/hispanic/data/2011.html VULNERABLE POPULATIONS 6 VULNERABLE POPULATION SCHOLARLY APA PAPER (Individual) Scholarly paper 2-3 pages in correct APA format. The focus of the paper will be on health disparities; an analysis of the etiology of the health disparity; (how the determinant(s) and culture can affect disparity; and an analysis of how personal bias can affect health care delivery. In this paper it is acceptable to speak in first person due to the personal reflection component. NUR 340 Vulnerable Populations and Self-Awareness Paper Rubric Vulnerable Population and Self-Awareness Paper Total possible points=150 Content: 100 points possible Points Points earned possible Vulnerable population clearly identified. Include factors that can cause vulnerability. Describe your personal awareness of this population (attitudes, biases, stereotypes) before studying the demographics. Describe demographics of the population based on research of professional literature and Web sites including local, state, or national levels. State the effect of research on personal attitudes after gathering knowledge. 60 60 60 60 Pts earned Pts possible 30 30 Use a self- reflection to evaluate your perception before and after learning about the population Include how knowledge of bias might affect delivery of health care. Include how this knowledge of bias can improve public policy regarding care of vulnerable populations. Paper Organization and Mechanics :30 points possible The content is scholarly, comprehensive, and accurate, and the paper is directed toward a nursing audience with a professional tone appropriate to the content and assignment. The introduction provides sufficient background on the topic and previews major points. The conclusion is logical, flows from the body of the paper, and summarizes the major points. The paper structure is clear, logical, and easy to follow, and transitions VULNERABLE POPULATIONS 7 between sections aid in maintaining the flow of thought. The paper structure (including the title page, citations, and reference page) follows APA format. Cite a minimum of four references with at least three references from a peer reviewed journal Total Points Earned: 150 150