Notes Topic 6 Global Warming student
advertisement

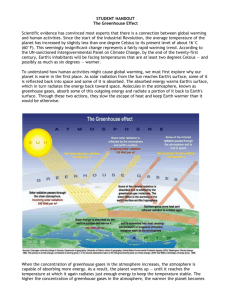
Topic 6 Global Warming Notes Ch. 6 Read and know the following parts of the text. Use textbook and internet research to answer the following questions. Use Answer sheet. 6.1 – The Greenhouse Effect : IB Qs: 2,5,7a Occurs in Troposphere Greenhouse gases: CO2 , Methane (CH4) , N2O, CFCs, O3 , H2O 1 1. Role of Greenhouse Gases in Maintaining Mean Global Temperature pp. 261 – 263 NEED TO KNOW : p. 261 all p. 262 : top paragraph only ; be able to interpret the graphs p. 263 : be able to interpret graph and the following text: DEFORESTATION – INCREASES CO2 REFORESTATION – FORESTS – ABSORB CO2 2 2. Human Activity and the Greenhouse Effect pp. 264 – 265 NEED TO KNOW : p. 264 : all p. 265 : be able to interpret graphs 3 3. The Effects of Global Warming pp. 266 – 269 4 NEED TO KNOW : IB Qs : 7 b,c, 10 a p. 266 : only the following p. 267 - 268 : know all 5 4. IB Questions 1. This question refers to the data below. Percent increase from 1750 to 1992 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Carbon dioxide Methane Nitrous oxide (Source: IPCC. Summary for policymakers of the contribution of working group I to the IPCC second assessment report, 1995. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In WWF Data Bulletin on Climate Change.) These gases cause the Greenhouse Effect because they are A. more effective at absorbing long-wave radiation than other gases in the atmosphere. B. more effective at absorbing short-wave radiation than other gases in the atmosphere. C. produced by human activities. D. not broken down in the atmosphere. 2. The major greenhouse gases are A. nitrous oxide and acid rain. B. water vapour, carbon dioxide, ozone and methane. C. carbon dioxide, nitrogen and ozone. D. ozone, water vapour and chlorine. 6 3. Methane is produced by I. bacterial activity. II. decomposition in landfill sites. III. digestive systems of cattle. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 4. What might be a consequence of a significant decrease in the amount of the CO2 in the atmosphere? A. The Earth becoming warmer B. A decrease in CFC levels in the atmosphere C. A rise in sea levels D. The Earth becoming cooler 5. Which list contains only greenhouse gases? A. Carbon dioxide, water and methane B. Methane, CFCs and sulfur dioxide C. Carbon dioxide, lead and methane D. Nitrogen, water and CFCs 7 6. The graph shows the variation in the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide since 1970 at the Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii. CO 2 concentration / ppm 375 370 365 360 355 350 345 340 335 330 2000 1995 1990 1985 1980 1975 1970 325 320 Year [Source: C D Keeling and T P Whorf (2004), Atmosphere CO2 concentrations (ppm) derived from in situ air samples, collected at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii] What has caused the annual rise and fall of CO2 levels shown in the graph? A. Seasonal functions of ozone in the troposphere B. Seasonal depletion of ozone in the stratosphere C. Seasonal variations in photosynthesis D. Seasonal variations in the numbers and intensity of forest fires 7. (a) List three greenhouse gases. (b) Outline one way in which human activities are changing the proportion of one of these greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. (c) State two possible effects of the changes in the total proportion of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. 8 5. Feedback and Global Warming pp. 270 – 272 IB Q: 9 NEED TO KNOW : all EXCEPT the case studies 9 6. Pollution Management Strategies pp. 272-274 KNOW: Kyoto Protocol , carbon taxing and trading pp. 273-274 : IB Q : 11 10 NEED TO KNOW : all EXCEPT the case studies : IB Qs : 7 b, 10 b 11 7. IB Questions 8. As a result of global warming, there could be increased I. snowfall at the poles. II. melting of polar ice caps. III. photosynthesis. Which could produce positive feedback in the Earth’s climate system? A. I, II and III B. I and III only C. II only D. III only 9. Of what is the diagram below an example? ice-caps melt global warming less energy refected increased global temperature A. Negative feedback B. Positive feedback C. Steady-state equilibrium 12 D. 10. a) Static equilibrium 8806-64 As well as their direct impact on the atmosphere, the effects of fossil fuel use are widespread. Discuss the range of effects of fossil fuel use on the environment. Specifically discuss : carbon dioxide /sulfur oxides/ nitrogen oxides/unburned hydrocarbons (b) Explain three management strategies that could be taken to reduce these effects? (c) The average cost of petrol (gasoline) for automobiles is four times higher in Europe than in the USA. Discuss the environmental implications of this difference. 13 11. The graphs below show the top ten countries in terms of total carbon emissions and emissions per capita. Graph A: Total carbon emissions from fossil fuel burning for the top ten emitting countries, in million tonnes (Mt). 1400 1200 1000 800 Carbon emissions (Mt) 600 400 200 Italy Canada Ukraine UK India Germany Japan Russia China US 0 Graph B: Total carbon emissions (tonnes) per capita for the top ten emitting countries. 6 5 4 Carbon emissions per capita (tonnes) 3 2 1 [Source: Brown, L. R. et al, State of the World, 1996, Earthscan.] 14 Italy Canada Ukraine UK India Germany Japan Russia China US 0 (a) Comment on the significance of these data. (b) Describe the Kyoto Protocol that aims to reduce the amount of carbon emissions. (c) Describe the Carbon taxing and carbon trading that aims to reduce the amount of carbon emissions 15 8. Arguments about Global Warming pp. 275-276 NEED TO KNOW : 16 17 18