Waves Study Guide AK
advertisement
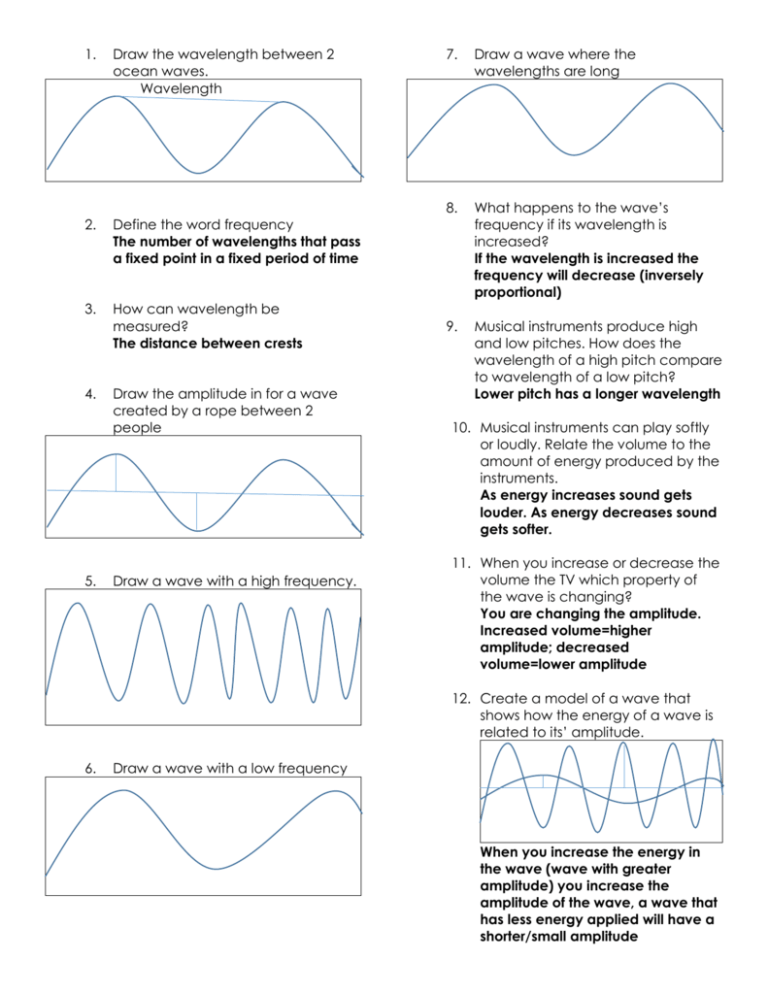
1. Draw the wavelength between 2 ocean waves. Wavelength 2. Define the word frequency The number of wavelengths that pass a fixed point in a fixed period of time 3. How can wavelength be measured? The distance between crests 4. 5. Draw the amplitude in for a wave created by a rope between 2 people Draw a wave with a high frequency. 7. Draw a wave where the wavelengths are long 8. What happens to the wave’s frequency if its wavelength is increased? If the wavelength is increased the frequency will decrease (inversely proportional) 9. Musical instruments produce high and low pitches. How does the wavelength of a high pitch compare to wavelength of a low pitch? Lower pitch has a longer wavelength 10. Musical instruments can play softly or loudly. Relate the volume to the amount of energy produced by the instruments. As energy increases sound gets louder. As energy decreases sound gets softer. 11. When you increase or decrease the volume the TV which property of the wave is changing? You are changing the amplitude. Increased volume=higher amplitude; decreased volume=lower amplitude 12. Create a model of a wave that shows how the energy of a wave is related to its’ amplitude. 6. Draw a wave with a low frequency When you increase the energy in the wave (wave with greater amplitude) you increase the amplitude of the wave, a wave that has less energy applied will have a shorter/small amplitude 13. You observed a prism in one of the wave rotation stations. Describe how a prism works on light. Light is bent and redirected as it moves through the prism 14. What can cause light to keep from moving in a straight line? Coming into contact with another object. 15. Provide a real life example of absorption. Answers may vary but anything where light energy becomes thermal energy. Flashlight shining on a lab table. 16. Create a model of a system showing how a wave is absorbed, reflected, and transmitted. You must include a title, labels identifying parts of the drawing, use scientific words, and include an explanation of the drawing. Answers may vary but model needs to include absorption, reflection, and transmission 17. What do waves transfer from place to place? Waves transfer energy not matter! 18. Compare light waves to sound waves Light waves are transverse waves and do not require a medium to move through (electromagnetic). Sound waves are longitudinal waves and do require a medium (mechanical waves). They both can absorb, reflect, or transmit. They both have similar properties: frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. 19. Define a wave. A repeating disturbance or vibration that transfers or moves energy from place to place without transporting mass 20. Photography primarily involves which type of wave behavior? Reflection 21. Give an example from the waves rotation lab that shows how waves transfer energy when they interact with matter. Shining a flashlight on a lens, making white rice dance, hitting a coat hanger on a table, creating a wave with a slinky 22. Define and draw a model of a digital signal. In digital signals transmission of information is in binary format and large amounts of data are stored as strings of 1;s and 0’s. 23. Define and draw a model of an analog signal. In analog signals information is translated into electric pulses of varying amplitude. 24. Compare digital signals to analog signals. Both are used to transmit information. In both the information is transformed into electric signals. In analog small fluctuations can occur in the signal. Can cause errors in communication with analog. Digital errors are corrected and do not cause disturbance in communication. 25. Provide evidence to prove that digital signals are more reliable than analog signals. Digital signals can transmit more information without as many errors.








