Name_______________________ Block_______ Eighth Grade
advertisement

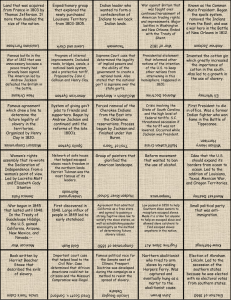
Name_______________________ Block_______ Eighth Grade American History North and South Homework Directions: The following homework assignments will be due Friday, November 16. You must complete all parts of the assignments. You cannot use a homework pass for either assignment. Part I: Key Terms (15 points) Study the key terms we have learned this unit. They can be found below and on the back of this homework sheet. You will take a quiz on Friday, November 16 and your quiz will include 15 key terms, taken from the 3 previous homework assignments. You can use your previous quizzes to study. Part II: Essay (15 points) Write a 5-paragraph essay in which you contrast (explain the differences between) the North and the South. You must have a thesis statement in the introduction paragraph and you must choose 3 areas in which the North and the South differed. These 3 areas will be the topic for each body paragraph, so they should be listed in your thesis statement. On Tuesday, November 13 we will cover this topic in class and you will be able to take home the proper resources to write the essay, but if you would like to begin earlier, I can give you the materials ahead of time. This essay is due Friday, November 16th. Follow this guide to write your essay: Paragraph 1: Introduction and thesis statement (your overall point and the 3 main ways the North and South differ) Paragraph 2: 1st way the North and South differ Paragraph 3: 2nd way the North and South differ Paragraph 4: 3rd way the North and South differ Paragraph 5: Conclusion with restatement of thesis statement Key Terms: 1. Industrial Revolution: period of extremely rapid growth in the use of machines in manufacturing and production 2. Samuel Slater: British mechanic who escaped to the U.S and created successful textile mills throughout New England 3. Mass production: the making of large numbers of identical goods 4. Interchangeable parts: Eli Whitney’s system in which each particular part of a product would be made exactly the same 5. Rhode Island System: System in which families were hired as textile workers 6. Lowell system: the employment of young, unmarried women in water power textile mills 7. Trade unions: workers organizations that try to improve pay and working conditions, usually formed for specific trades 8. Robert Fulton: successfully sent the firs steamboat, the Clermont, up the Hudson River which started a demand for steamboat ferry service Name_______________________ Block_______ 9. Gibbons vs. Ogden: First Supreme Court ruling on commerce between states, reinforced the power of the federal government over states. Gibbons was allowed to travel via steamboat between New Jersey and New York because he had a federal license, though he did not have a state license from New York 10. John Deere: Blacksmith who designed a steel plow that would not get stuck in the dirt and tough grass like iron plows tended to do 11. Cyrus McCormick: designed the mechanical reaper to cut wheat more quickly, which soon increased U.S production of wheat 12. Telegraph: a device that sends and receives pulses of electrical current through a wire. Different combinations of short and long pulses, called Morse code, allowed operators to send and receive many words per minute 13. Isaac Singer: improved the sewing machine with a clever design and a simple way to run it, soon the singer sewing machine became a staple in American homes 14. Transportation Revolution: a period of rapid improvement in the speed, ease and cost of transportation 15. Cotton Gin: device invented by Eli Whitney in 1793 to separate cotton plants’ fibers from the seeds; revolutionized the cotton industry 16. Scientific Agriculture: use of scientific techniques to improve crop production 17. Nat Turner: led a group of slaves in Virginia in an unsuccessful attempt to overthrow slavery 18. Plantation: large farms that usually specified in the growing of one type of crop 19. Folk tales: oral stories that often provide a moral lesson, slaves told them to teach lessons about how to survive under slavery 20. Spirituals: emotional Christian songs sung by slaves that blended African and European tradition to express their religious beliefs. 21. Planter: large-scale farmers who held more than twenty slaves, often had political and economic power 22. Yeoman: owners of small farms, sometimes held slaves but worked alongside them in the field 23. Cotton belt: area from South Carolina to East Texas where many farmers and their slaves settled to find land suitable for growing cotton 24. Abolition: complete end to slavery 25. Emancipation: immediate freedom from slavery for all African-Americans 26. American Colonization Society: society that founded the African colony of Liberia which 12,000 African Americans settled in 27. William Lloyd Garrison: outspoken abolitionist who published the newspaper, The Liberator 28. Frederick Douglass: escaped slave who gave many lectures and published the abolitionist newspaper, North Star 29. Underground Railroad: network of people who arranged transportation and hiding places for escaped slaves 30. Harriet Tubman: Famous conductor on the Underground Railroad who was an escaped slave and led over 300 slaves to freedom 31. Sectionalism: occurs when people favor the interests of one region over the interests of the country as a whole 32. Popular Sovereignty: voters in a territory could decide whether they wanted to ban or allow slavery based on the will of the majority 33. Compromise of 1850: plan proposed by Henry Clay in which California entered the union as a free state, and the rest of the Mexican Cession was divided into two territories which would decide to allow or ban slavery based on popular sovereignty. Slavery was also banned in the capital. 34. Daniel Webster: Massachusetts Senator who opposed the expansion of slavery but also opposed abolitionists because he wanted to preserve the union 35. Fugitive Slave Act: part of the Compromise of 1850 which made it a crime to help runaway slaves 36. Uncle Tom’s Cabin: Influential antislavery novel written in 1852 by Harriet Beecher Stowe after the passage of the Fugitive Slave Act