Calibration Process (Load Tester)
advertisement
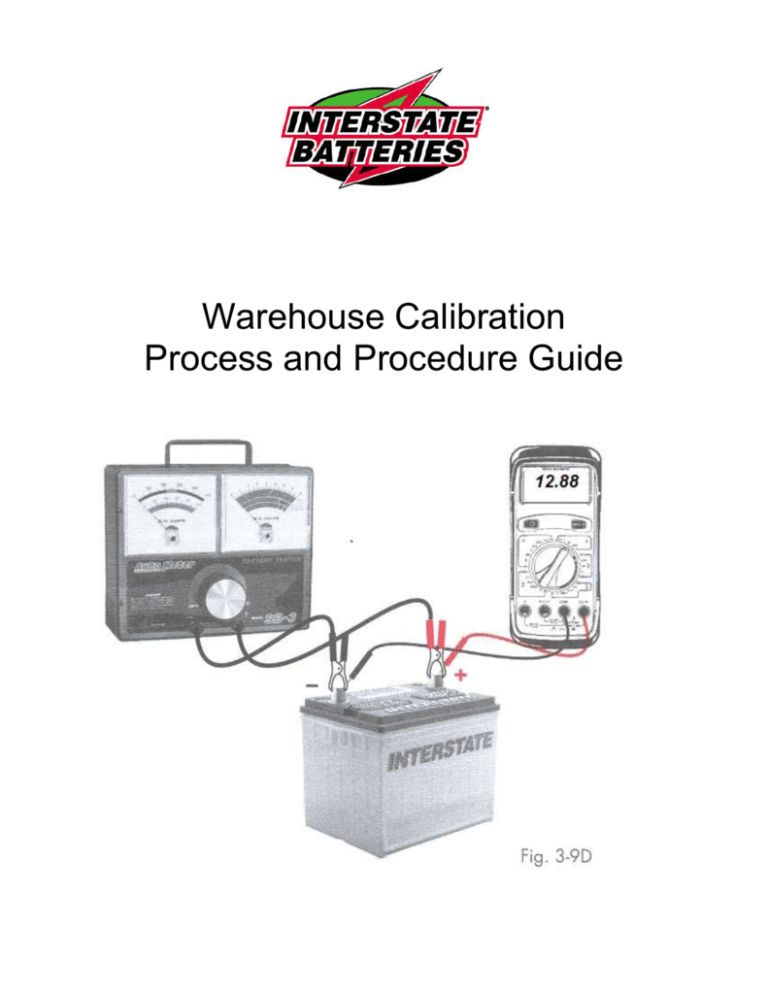
Warehouse Calibration Process and Procedure Guide Warehouse Calibration Procedure Handbook Table of Contents Page 3: List of devices requiring calibration Page 4: Testing ‘Daily Use’ Hydrometers Page 5-6: Testing Carbon Pile Load Tester’s Amps (with adjustable ammeter) using Independent Clamp-on Inductive Ammeter Page 7-8: Testing Carbon Pile Load Tester’s Amps (with adjustable ammeter) using ED-182 Accessory Clamp-on Inductive Ammeter Page 9: Testing Carbon-Pile Load Tester’s Voltmeter Accuracy Page 10-11: Testing ‘Daily Use’ Voltmeter Accuracy Page 12: Testing Series Charger’s Amps Page 13: Testing Parallel Charger’s Amps Page 14: Battery weight scales Page 15: Appendix 2 Warehouse Devices Requiring Calibration Daily Use Hydrometer Daily Use Digital Voltmeter Carbon-Pile Load Tester (Amps) Carbon-Pile Load Tester (Volts) Charger (Series) Charger (Parallel) Battery Scales Authorized Calibration Devices Test Verification for: Daily Use Digital Voltmeter: TPI -190 DMM or equivalent Daily Use Hydrometer: Upright Freas Hydrometer Load Tester Amps: Digital Clamp-on Inductive ammeter Load Tester Volts: TPI -190 DMM or equivalent Charger Amps: Digital Clamp-on Inductive ammeter These calibration devices should be stored in a temperature of (70˚For 21˚C) to (80˚F or 27˚C). 3 ‘Daily Use’ Hydrometer ≥ 50 battery test per day – Test Monthly ≤ 50 battery test per day – Test Bi-Monthly (Maximum recommended life of ‘daily use’ hydrometers is 6-months) Figure 1. Freas Hydrometer Approximate Testing time – 2 minutes 1. Select fully charged battery. 2. Test one battery cell with ‘Daily Use’ Hydrometer 3. Record Results 4. Test same battery cell with Freas Upright hydrometer. (See figure 1) 5. Record results 6. Compare Results: If ‘Daily Use’ hydrometer varies more than 10 points, on reading, from the Upright Freas (or equal) hydrometer; replace ‘Daily Use’ hydrometer with new unit. Notes: Flush Calibrated Freas Hydrometer thoroughly with water several times immediately after testing and prior to storage. 4 Testing Carbon Pile Load Tester DC Amps (with adjustable ammeter) using Independent Clamp-on Inductive Ammeter Figure 3. DC Amp Scale w/Adjustable Ammeter Figure 2. Variable Carbon Pile Calibration Adjustment load Tester Figure 4. Independent Clamp-on inductive ammeter ≥ 50 battery tests (per load tester) daily - Monthly ≤ 50 battery tests (per load tester) daily – Bi-Monthly Testing time: 2 -3 minutes per load tester 5 1. Select ‘Good’ fully-charged battery (550 CCA or above) 2. Connect Load Tester to Negative and Positive battery terminals 3. Power up Clamp-on Ammeter. 4. Adjust Clamp-on Ammeter to select ‘DC Amps’. 5. Zero test clamp-on ammeter (if applicable) 6. Clamp ammeter loop around load tester’s positive or negative cable. 7. Adjust the load tester’s amp load as close to 200 amps as possible. 8. If load tester has not been previously used that day, conduct two repetitive load tests (15 second discharges) @ 200 amps within one minute prior to calibration testing. If load tester has been used, proceed directly to step 9 9. Apply and maintain 200 amps (3rd test) to battery. Once 200 amp load level has been achieved, proceed to step 10 10. Compare and note clamp-on ammeter reading to the load amps being produced by load tester. See Note Note: If the digital clamp-on ammeter and load tester are both displaying approximately 200 amps or (190 amps- 210 amps), the load tester is within calibration. However; if the load tester is illustrating 200 amps and the digital ammeter is displaying either low or high by more than + or – 10 amps (190amps to 210amps), adjust the small plastic adjustment screw located on amps scale clockwise or counterclockwise to within calibration while load test is in progress. 11. Turn load tester off 12. Remove Clamp-on Ammeter 13. Turn off ammeter and store for future testing If the load tester cannot be properly adjusted to within above noted calibration, contact the load tester’s manufacturer or Interstate’s Technical Services Dept. @ Home Office. 6 Testing Carbon Pile Load Tester (with adjustable ammeter) using ED-18 V2 Accessory Clamp-on Inductive Ammeter Clamp-on Inductive Ammeter Figure 5: ED-182 w/Inductive ammeter ≥ 50 battery tests per load tester daily - Monthly ≤ 50 battery tests per load tester daily – Bi-Monthly Approximate Testing Time: 3 minutes per load tester 1. Use ‘Good’ fully charged battery for testing (550 CCA or above) 2. Connect Load Tester to Negative and Positive battery terminals 3. Connect ED-182’s primary leads to battery terminals. ED-182 should power up. 4. Plug in Accessory Clamp-on Ammeter into ED-182’s accessory port. 5. On ED-182 main menu (8 Icons), select DMM and Press Enter 6. Select DC Amp/Volt Icon then Press Enter 7. Choose 700 amp level, Press Enter 8. Zero test clamp-on ammeter as prompted, press Enter 9. Clamp ED-182’s ammeter loop around load tester’s positive or negative cable. 10. Adjust load tester’s current draw as close to 200 amps as possible. 11. If load tester has not been used previously that day, Conduct two repetitive load tests (15 second discharges @ 200 amps) within one minute prior to calibration test verification. If load tester has been used within last 4 hours, proceed directly to step 12 7 12. Apply a 200 amp load to battery 13. Compare and note the inductive clamp-on ammeter’s reading to load amps displayed on load tester’s amp scale. See Note Note: If the digital clamp-on ammeter and load tester are both displaying approximately 200 amps (190 amps- 210 amps), the load tester is within calibration. However; if the load tester is on 200 amps and the digital ammeter is displaying either low or high by more than + or – 10 amps (190amps to 210amps), adjust the small plastic adjustment screw located on amps scale clockwise or counterclockwise to within calibration while load test is in progress. If the load tester cannot be properly adjusted to within above noted calibration, contact the load tester’s manufacturer or Interstate’s Technical Services dept. @ Home Office. 8 Testing Carbon-Pile Load Tester’s Voltmeter Accuracy Monthly Note: This test can be completed in conjunction with Load Tester Ammeter Verification Test Calibration Adjustment Figure 6. Carbon Pile Load Figure 7. TPI-190 (calibrated voltmeter) Tester Voltmeter scale Approximate Testing Time: 2 minutes 1. Choose ‘Good’ fully charged battery of 550 CCA rating or higher. 2. Power Up DC ‘Calibrated’ Voltmeter (TPI 190) 3. Select DC Volts (20 volt scale) and connect to battery terminals 4. Connect Carbon Pile Load tester to same battery. 5. Observe and compare ‘Calibrated’ Voltmeter’s voltage to Load Tester’s voltage 6. Note but Do Not adjust at this time. 7. Apply 200 amps to the battery for 15 seconds. 8. Compare load tester’s voltage to the ‘Calibrated’ voltmeter under 200-amp load. 9. Adjust load tester’s voltage reading, if necessary, to compare with calibrated voltmeter while load is applied. Note: If the load tester’s voltmeter will not adjust to reflect the ‘Calibrated’ voltmeter’s voltage to + or - .1 volt, (1) send load tester to manufacturer for repairs or (2) use a recalibrated ‘Daily Use’ digital voltmeter in conjunction with load tester anytime load testing batteries. See front cover illustration. If the load tester cannot be properly adjusted to within above noted calibration, contact the load tester’s manufacturer or Tech Services @ Interstate’s Home Office. 9 Testing ‘Daily Use’ Voltmeter Accuracy Monthly Approximate Testing Time: 2 minutes Figure 8. Example of ‘Daily Use’ Voltmeter with Calibration Adjustment Figure 9. Example of ‘Daily Use’ Voltmeter without Calibration Adjustment 1. Select ‘Good’ fully charged battery (12.70 volts or above) 2. Power Up DC ‘Calibrated’ Voltmeter (TPI 190) See Figure 7. 3. Select DC Volts 20 volt scale 4. Connect ‘Calibrated’ voltmeter to pos. and neg. battery terminals 5. Power up ‘ Daily Use’ voltmeter and select 20-volt scale (where applicable) 6. Connect ‘Daily Use’ voltmeter to same battery terminals as ‘Calibrated’ voltmeter. 7. Record any voltage difference in ‘Daily Use’ voltmeter to ‘Calibrated’ voltmeter. 10 8. Adjust ‘Daily Use’ voltage calibration setting (if applicable) or apply removable sticker to ‘Daily Use’ voltmeter with voltage difference. See example below. 9. Number your warehouse ‘Daily Use’ voltmeters and maintain records of voltage variation or calibration required. Note: If the ‘working’ voltmeter has calibration accessibility, always follow voltmeter manufacturer’s recommended calibration procedures. If the ‘daily use’ voltmeter does not have accessibility to calibrate, apply removable sticker to voltmeter with date and voltage variation. Example: Calibrated Voltmeter displays 12.76 volts and ‘Daily Use’ voltmeter displays 12.74 volts. Adjust (when applicable) or attach sticker to working voltmeter with + .02 volts. Add .02 to every voltmeter test reading when using that ‘Daily Use’ voltmeter. 10-06 + .02 volts #4 Example of sticker with date tested and variance 11 Testing Series charger to verify amp reading (analog ammeter gauges only) Figure 10. Example of Series Charger Annually 1. Connect ‘Series’ charger to good batteries. 2. Turn on charger 3. Adjust charger to 5 amps or highest amp level available. 4. Connect clamp-on inductive ammeter (see figure 4 or 5) around one of the series charger leads. 5. Power up amp clamp 6. Compare amp adjustment of charger to clamp-on digital ammeter reading. 7. Place removable sticker on charger noting amp difference. Example: If charger is displaying 5-amps and digital ammeter displays 4-amps, place sticker on charger faceplate indicating charger is -1amp. If the charger is displaying 4 amps and digital displays 5 amps, place a + 1 amp sticker on charger. See Example below 10-06 - 1 amp Example of sticker with date and variance. If charger’s amp reading varies more than ±1-amp, contact charger manufacturer or Interstate Batteries Technical Services Dept. at Home Office. 12 Testing Parallel charger to verify Amp reading (analog ammeter) Figure 11: Example of Multiple battery ‘Parallel’ charger Time: Annually Note: Some parallel chargers will not allow any adjustment process. 1. Connect Parallel charger to good/discharged batteries (12.00 volts – 12.45 volts) 2. Turn on charger 3. Adjust charger to 5 amp or 10 amp range. 4. Connect clamp-on inductive ammeter around charger lead. 5. Turn on inductive ammeter 6. Compare amp adjustment of charger to clamp-on digital ammeter reading. 7. Place Sticker on charger noting amp difference. Example: If charger is displaying 4-amps and digital ammeter displays 5-amps, place sticker on charger faceplate indicating charger is + 1 amp. If the charger is displaying 6 amps and digital displays 5 amps, place a – 1 amp sticker on charger. 10-06 - 1 amp Example of sticker with date and variance. If charger’s amp reading varies more than ±1 amp, contact charger manufacturer or Interstate Batteries Technical Services Dept. at Home Office. 13 Battery Scales Annually “Weigh-Tronix WI125 Indicator w/5000 lb Prodec Floor Scale”. 1. Contact Weigh-Tronix WI 125 (see Interstate memo dated Jan. 2006) 2. Maintain a record in your files that the calibration was done. If you have any questions about the program, please call Gale Kimbrough @ 469.221.4657. or ext. 4657 14 Appendix Item IBS Part # TPI -190 DMM 384909 Upright Freas Hydrometer 381100 TPI -296 Digital Clamp-on Inductive ammeter 384912 ED-18 Clamp-on inductive meter 426170 Note: For pricing information, contact Supply Chain Management at Interstate Batteries 15