How are your Genes? - Moore Public Schools
advertisement
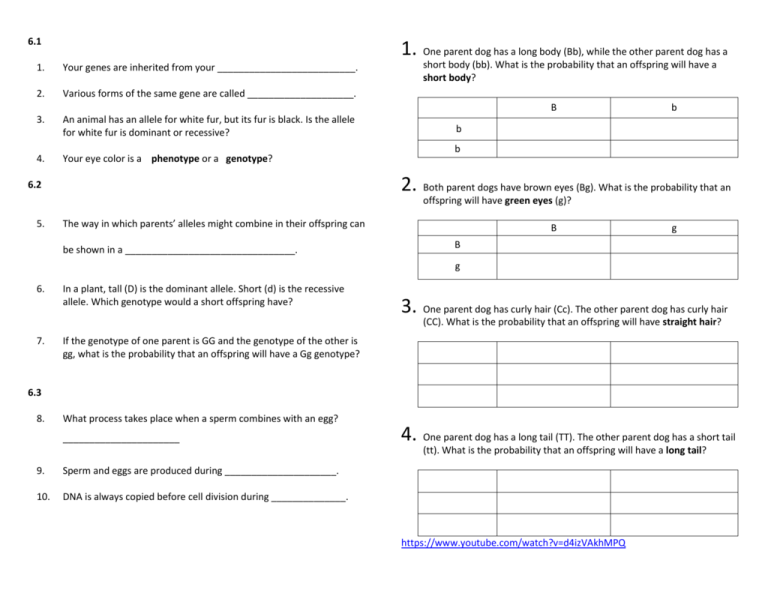
6.1 1. One parent dog has a long body (Bb), while the other parent dog has a 1. Your genes are inherited from your __________________________. 2. Various forms of the same gene are called ____________________. 3. An animal has an allele for white fur, but its fur is black. Is the allele for white fur is dominant or recessive? 4. Your eye color is a phenotype or a genotype? short body (bb). What is the probability that an offspring will have a short body? B b b b 2. Both parent dogs have brown eyes (Bg). What is the probability that an 6.2 offspring will have green eyes (g)? 5. The way in which parents’ alleles might combine in their offspring can be shown in a ________________________________. B g B g 6. In a plant, tall (D) is the dominant allele. Short (d) is the recessive allele. Which genotype would a short offspring have? 3. One parent dog has curly hair (Cc). The other parent dog has curly hair (CC). What is the probability that an offspring will have straight hair? 7. If the genotype of one parent is GG and the genotype of the other is gg, what is the probability that an offspring will have a Gg genotype? 6.3 8. What process takes place when a sperm combines with an egg? ______________________ 4. One parent dog has a long tail (TT). The other parent dog has a short tail (tt). What is the probability that an offspring will have a long tail? 9. Sperm and eggs are produced during _____________________. 10. DNA is always copied before cell division during ______________. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d4izVAkhMPQ How are your Genes? Circle You, Mom, Dad, Siblings who have the dominant and/or recessive genes for each. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Tongue rolling (D) Detached earlobe (D) Attached earlobes (r) Hitchhiker’s thumb (D) (bent backwards) Dimples (D) Widow’s peak (D) Bent little finger (D) Webbing between fingers (D) Freckles (D) Crown whorl-clockwise (D) Second toe longest (D) Handedness-Right (D), Left (r) Hand clasping – left over right (D) PTC - tasting bitterness (D) Mid digital hair on fingers (D) Pigmented irises (G,B,B) (D), blue/gray (r) Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D D Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ Sib ________ More Punnett Squares! 17. Your mom has the dominant gene for brown eyes, and her genotype is BB. Your father has the recessive gene for blue eyes. His genotype is bb. a. What are the genotypes possible for eye color for their children? ______________________________ b. What percent or fraction of their children will have brown eyes? ______________________________ 18. Your mom has the recessive gene for no freckles. Her genotype is ____. Your dad has the dominant gene for freckles, and his genotype is Ff. a. What are the genotypes possible for freckles for their children? ______________________________ b. What percent or fraction of their children will have freckles? ______________________________ 19. Your mom and dad have the recessive gene for no dimples. Their genotype is dd. a. What are the genotypes possible for dimples for their children? ______________________________ b. What percent or fraction of their children will have dimples? ______________________________ 20. Your mom and dad have the dominate gene for right handedness. Her genotype is RR and his is Rr. c. What are the genotypes possible for right handedness for their children? ______________________________ d. What percent or fraction of their children will be right handed? ______________________________ Monohybrid Mice! Directions: Work each problem showing your work. For each cross, give the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring and the probability of getting each. Answer the questions that accompany each problem. What you need to know about the mice: In laboratory mice, gray (G) is dominant over albino (g). I. Cross a female Gg with a male gg. III. Cross a gray female, whose father was albino, with a heterozygous male. 14. What is the probability of getting gray offspring? ________ 15. What is the probability of getting albino offspring? ________ 16. How many possible genotypes are there among the offspring? ________ 17. How many possible phenotypes are there among the offspring? ________ 18. What is the probability of getting heterozygous offspring? ________ 1. What is the probability of getting gray offspring? ______ Albino? _______ 2. How many possible genotypes are there among the offspring? ________ 3. How many possible phenotypes are there among the offspring? ________ 4. What is the probability of getting heterozygous offspring? ________ 5. What is the probability of getting homozygous offspring? ________ 19. What is the probability of getting homozygous offspring? ________ 20. What is the genotype of the female? ________How do you know? ____________________________________________________________ 21. What is the genotype of the male? ________How do you know? ____________________________________________________________ 6. What color is the female? ________ What color is the male? ________ II. Cross a homozygous gray female with a heterozygous male. 7. What is the probability of getting gray offspring? ______ Albino? _______ 8. How many possible genotypes are there among the offspring? ________ 9. How many possible phenotypes are there among the offspring? ________ 10. What is the probability of getting heterozygous offspring? ________ 11. What is the probability of getting homozygous offspring? ________ 12. What is the genotype and color of the female? ______________________ 13. What is the genotype and color of the male? ______________________ IV. Cross an albino female, whose father was gray, with a gray male, whose mother was albino. 22. What is the probability of getting gray offspring? ______ Albino? _______ 23. How many possible genotypes are there among the offspring? ________ 24. How many possible phenotypes are there among the offspring? ________ 25. What is the probability of getting heterozygous offspring? ________ 26. What is the probability of getting homozygous offspring? ________ 27. What was the genotype of the father of the albino female? _________ allele gamete dominant genotype gene heredity 1. Punnett square phenotype probability replication RNA mutation ratio recessive The likelihood of a specific outcome in relation to the total number of possible outcomes. Vocabulary Word pedigree selective breeding genetic engineering genome cloning Description 12. Selective breeding 2. Compares or shows the relationship between two quantities. 3. A unit of heredity that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and codes for a particular product. 4. The genes an organism has or its genetic constitution. 5. The allele that is expressed in the phenotype when two copies of it are present on the homologs 6. The actual characteristics an organism has 7. The various forms of the same gene 8. Illustrates how the parents’ alleles might combine in offspring. 9. The passing of genes from parents to offspring 10. the allele that is expressed in the phenotype even if it is the only copy present in the genotype 11. Cells that contain half the usual number of chromosomes – one chromosome from each pair. 13. By making copies, this has been used in bacteria to produce proteins and drugs that help fight disease such as diabetes. 14. genome 15. This chart can show the pattern of inheritance of the sickle-cell allele through three generations of a family. 16. This produces two identical molecules of DNA before the cell divides. 17. The organism resulting from this process is referred to as having been genetically modified. Its DNA was taken, changed, and returned to the organism. 18. mutation 19. This is what makes proteins with three different types :messenger, ribosomal, and transfer.